637 lines
29 KiB
Markdown
637 lines
29 KiB
Markdown
|
|
# The PySimpleGUI Cookbook
|
|
|
|
## Simple Data Entry - Return Values As List
|
|
Same GUI screen except the return values are in a list instead of a dictionary and doesn't have initial values.
|
|
|
|
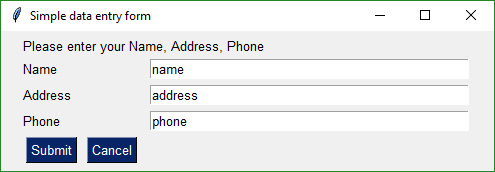
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Very basic form. Return values as a list
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Simple data entry form') # begin with a blank form
|
|
|
|
layout = [
|
|
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
|
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
|
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
|
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
print(button, values[0], values[1], values[2])
|
|
|
|
## Simple data entry - Return Values As Dictionary
|
|
A simple form with default values. Results returned in a dictionary. Does not use a context manager
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Very basic form. Return values as a dictionary
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Simple data entry form') # begin with a blank form
|
|
|
|
layout = [
|
|
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
|
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('name', key='name')],
|
|
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('address', key='address')],
|
|
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('phone', key='phone')],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
print(button, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
|
|
|
---------------------
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-----------
|
|
## Simple File Browse
|
|
Browse for a filename that is populated into the input field.
|
|
|
|
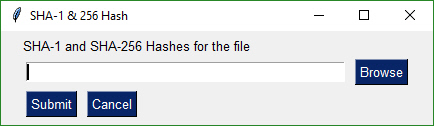
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('SHA-1 & 256 Hash') as form:
|
|
form_rows = [[sg.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
|
[sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
|
(button, (source_filename,)) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
|
|
|
print(button, source_filename)
|
|
|
|
--------------------------
|
|
## Compare 2 Files
|
|
|
|
Browse to get 2 file names that can be then compared. Uses a context manager
|
|
|
|
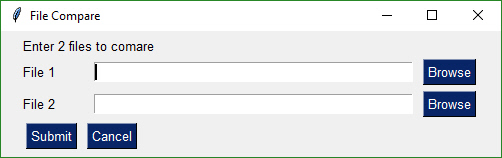
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('File Compare') as form:
|
|
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Enter 2 files to comare')],
|
|
[sg.Text('File 1', size=(8, 1)), sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.Text('File 2', size=(8, 1)), sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
|
|
|
print(button, values)
|
|
|
|
---------------
|
|
## Nearly All Widgets with Green Color Theme with Context Manager
|
|
Example of nearly all of the widgets in a single form. Uses a customized color scheme. This recipe uses a context manager, the preferred method.
|
|
|
|
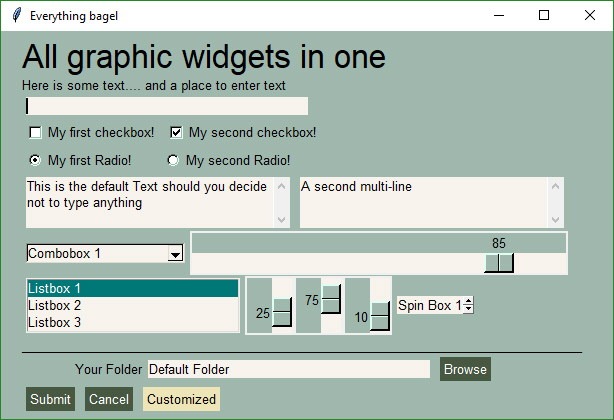
|
|
|
|
# Green & tan color scheme
|
|
sg.SetOptions(background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
text_element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
input_elements_background_color='#F7F3EC',
|
|
button_color=('white', '#475841'),
|
|
border_width=0,
|
|
slider_border_width=0,
|
|
progress_meter_border_depth=0,
|
|
scrollbar_color='#F7F3EC')
|
|
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1)) as form:
|
|
layout = [
|
|
[sg.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
|
[sg.InputText()],
|
|
[sg.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), sg.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
|
[sg.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), sg.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
|
[sg.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', size=(35, 3)),
|
|
sg.Multiline(default_text='A second multi-line', size=(35, 3))],
|
|
[sg.InputCombo(('Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'), size=(20, 3)),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(34, 20), default_value=85)],
|
|
[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3', 'Listbox 4'), size=(30, 3)),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
|
sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 1')],
|
|
[sg.Text('_' * 80)],
|
|
[sg.Text('Your Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'),
|
|
sg.InputText('Default Folder'), sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel(), sg.SimpleButton('Customized', button_color=('black', '#EDE5B7'))]]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
-------------
|
|
### All Widgets No Context Manager
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Green & tan color scheme
|
|
sg.SetOptions(background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
text_element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
input_elements_background_color='#F7F3EC',
|
|
button_color=('white', '#475841'),
|
|
border_width=0,
|
|
slider_border_width=0,
|
|
progress_meter_border_depth=0,
|
|
scrollbar_color='#F7F3EC')
|
|
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1))
|
|
layout = [
|
|
[sg.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
|
[sg.InputText('This is my text')],
|
|
[sg.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), sg.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
|
[sg.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), sg.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
|
[sg.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', size=(35, 3)),
|
|
sg.Multiline(default_text='A second multi-line', size=(35, 3))],
|
|
[sg.InputCombo(('Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'), size=(20, 3)),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(34, 20), default_value=85)],
|
|
[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'), size=(30, 3)),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
|
sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 1')],
|
|
[sg.Text('_' * 80)],
|
|
[sg.Text('Choose A Folder', size=(35, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Your Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'),
|
|
sg.InputText('Default Folder'), sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel(), sg.SimpleButton('Customized', button_color=('white', '#7E6C92'))]
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
----
|
|
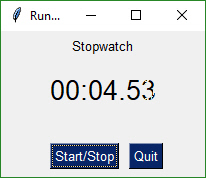
## Non-Blocking Form With Periodic Update
|
|
An async form that has a button read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. There is no context manager for this recipe because the loop that reads the form is likely to be some distance away from where the form was initialized.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
import time
|
|
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Running Timer')
|
|
# create a text element that will be updated periodically
|
|
text_element = sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center')
|
|
|
|
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Stopwatch', size=(20,2), justification='center')],
|
|
[text_element],
|
|
[sg.T(' ' * 5), sg.ReadFormButton('Start/Stop', focus=True), sg.Quit()]]
|
|
|
|
form.LayoutAndRead(form_rows, non_blocking=True)
|
|
|
|
timer_running = True
|
|
i = 0
|
|
# loop to process user clicks
|
|
while True:
|
|
i += 1 * (timer_running is True)
|
|
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
|
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
|
break
|
|
elif button == 'Start/Stop':
|
|
timer_running = not timer_running
|
|
text_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
|
|
|
time.sleep(.01)
|
|
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
|
del (form)
|
|
----
|
|
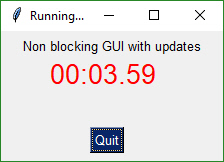
## Async Form (Non-Blocking) with Context Manager
|
|
Like the previous recipe, this form is an async form. The difference is that this form uses a context manager.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
import time
|
|
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('Running Timer') as form:
|
|
text_element = sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red', justification='center')
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates', justification='center')],
|
|
[text_element],
|
|
[sg.T(' ' * 15), sg.Quit()]]
|
|
form.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
|
|
|
for i in range(1, 500):
|
|
text_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
|
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
|
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X
|
|
break
|
|
time.sleep(.01)
|
|
else:
|
|
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
|
----
|
|
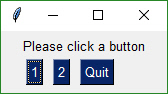
## Callback Function Simulation
|
|
The architecture of some programs works better with button callbacks instead of handling in-line. While button callbacks are part of the PySimpleGUI implementation, they are not directly exposed to the caller. The way to get the same result as callbacks is to simulate them with a recipe like this one.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# This design pattern simulates button callbacks
|
|
# Note that callbacks are NOT a part of the package's interface to the
|
|
# caller intentionally. The underlying implementation actually does use
|
|
# tkinter callbacks. They are simply hidden from the user.
|
|
|
|
# The callback functions
|
|
def button1():
|
|
print('Button 1 callback')
|
|
|
|
def button2():
|
|
print('Button 2 callback')
|
|
|
|
# Create a standard form
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Button callback example')
|
|
# Layout the design of the GUI
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('Please click a button')],
|
|
[sg.ReadFormButton('1'), sg.ReadFormButton('2'), sg.Quit()]]
|
|
# Show the form to the user
|
|
form.Layout(layout)
|
|
|
|
# Event loop. Read buttons, make callbacks
|
|
while True:
|
|
# Read the form
|
|
button, value = form.Read()
|
|
# Take appropriate action based on button
|
|
if button == '1':
|
|
button1()
|
|
elif button == '2':
|
|
button2()
|
|
elif button =='Quit' or button is None:
|
|
break
|
|
|
|
# All done!
|
|
sg.MsgBoxOK('Done')
|
|
|
|
-----
|
|
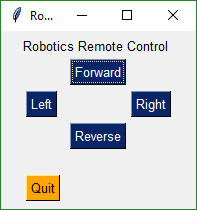
## Realtime Buttons (Good For Raspberry Pi)
|
|
This recipe implements a remote control interface for a robot. There are 4 directions, forward, reverse, left, right. When a button is clicked, PySimpleGUI immediately returns button events for as long as the buttons is held down. When released, the button events stop. This is an async/non-blocking form.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Make a form, but don't use context manager
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Robotics Remote Control', auto_size_text=True)
|
|
|
|
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Robotics Remote Control')],
|
|
[sg.T(' ' * 10), sg.RealtimeButton('Forward')],
|
|
[sg.RealtimeButton('Left'), sg.T(' ' * 15), sg.RealtimeButton('Right')],
|
|
[sg.T(' ' * 10), sg.RealtimeButton('Reverse')],
|
|
[sg.T('')],
|
|
[sg.Quit(button_color=('black', 'orange'))]
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
form.LayoutAndRead(form_rows, non_blocking=True)
|
|
|
|
#
|
|
# Some place later in your code...
|
|
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your form every now and then or
|
|
# else it won't refresh.
|
|
#
|
|
# your program's main loop
|
|
while (True):
|
|
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
|
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
|
if button is not None:
|
|
print(button)
|
|
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
|
break
|
|
|
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
|
|
|
---------
|
|
|
|
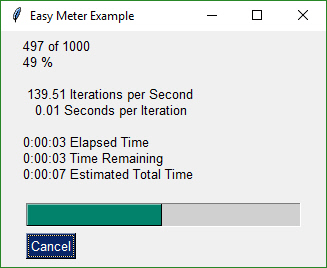
## Easy Progress Meter
|
|
This recipe shows just how easy it is to add a progress meter to your code.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
for i in range(1000):
|
|
sg.EasyProgressMeter('Easy Meter Example', i+1, 1000)
|
|
|
|
|
|
-----
|
|
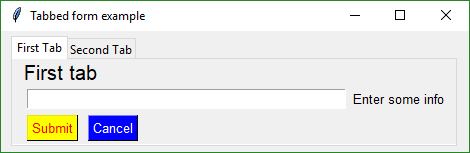
## Tabbed Form
|
|
Tabbed forms are **easy** to make and use in PySimpleGUI. You simple may your layouts for each tab and then instead of `LayoutAndRead` you call `ShowTabbedForm`. Results are returned as a list of form results. Each tab acts like a single form.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
|
with sg.FlexForm('', auto_size_text=True) as form2:
|
|
|
|
layout_tab_1 = [[sg.Text('First tab', size=(20, 1), font=('helvetica', 15))],
|
|
[sg.InputText(), sg.Text('Enter some info')],
|
|
[sg.Submit(button_color=('red', 'yellow')), sg.Cancel(button_color=('white', 'blue'))]]
|
|
|
|
layout_tab_2 = [[sg.Text('Second Tab', size=(20, 1), font=('helvetica', 15))],
|
|
[sg.InputText(), sg.Text('Enter some info')],
|
|
[sg.Submit(button_color=('red', 'yellow')), sg.Cancel(button_color=('white', 'blue'))]]
|
|
|
|
results = sg.ShowTabbedForm('Tabbed form example', (form, layout_tab_1, 'First Tab'),
|
|
(form2, layout_tab_2,'Second Tab'))
|
|
|
|
sg.MsgBox(results)
|
|
-----
|
|
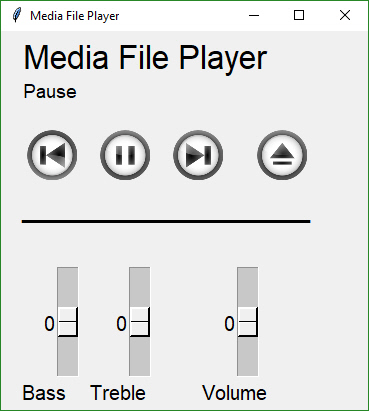
## Button Graphics (Media Player)
|
|
Buttons can have PNG of GIF images on them. This Media Player recipe requires 4 images in order to function correctly. The background is set to the same color as the button background so that they blend together.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
background = '#F0F0F0'
|
|
# Set the backgrounds the same as the background on the buttons
|
|
sg.SetOptions(background_color=background, element_background_color=background)
|
|
# Images are located in a subfolder in the Demo Media Player.py folder
|
|
image_pause = './ButtonGraphics/Pause.png'
|
|
image_restart = './ButtonGraphics/Restart.png'
|
|
image_next = './ButtonGraphics/Next.png'
|
|
image_exit = './ButtonGraphics/Exit.png'
|
|
|
|
# A text element that will be changed to display messages in the GUI
|
|
TextElem = sg.Text('', size=(15, 2), font=("Helvetica", 14))
|
|
|
|
# Open a form, note that context manager can't be used generally speaking for async forms
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Media File Player', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(20, 1),
|
|
font=("Helvetica", 25))
|
|
# define layout of the rows
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('Media File Player', size=(17, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
|
[TextElem],
|
|
[sg.ReadFormButton('Restart Song', button_color=(background, background),
|
|
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
|
sg.ReadFormButton('Pause', button_color=(background, background),
|
|
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
|
sg.ReadFormButton('Next', button_color=(background, background),
|
|
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.SimpleButton('Exit', button_color=(background, background),
|
|
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2,
|
|
border_width=0)],
|
|
[sg.Text('_' * 30)],
|
|
[sg.Text(' ' * 30)],
|
|
[
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
|
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
|
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
|
sg.Text(' ' * 8),
|
|
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
|
font=("Helvetica", 15))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Bass', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(6, 1)),
|
|
sg.Text('Treble', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(10, 1)),
|
|
sg.Text('Volume', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(7, 1))]
|
|
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
# Call the same LayoutAndRead but indicate the form is non-blocking
|
|
form.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
|
# Our event loop
|
|
while (True):
|
|
# Read the form (this call will not block)
|
|
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
|
if button == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
|
break
|
|
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
|
if button:
|
|
TextElem.Update(button)
|
|
----
|
|
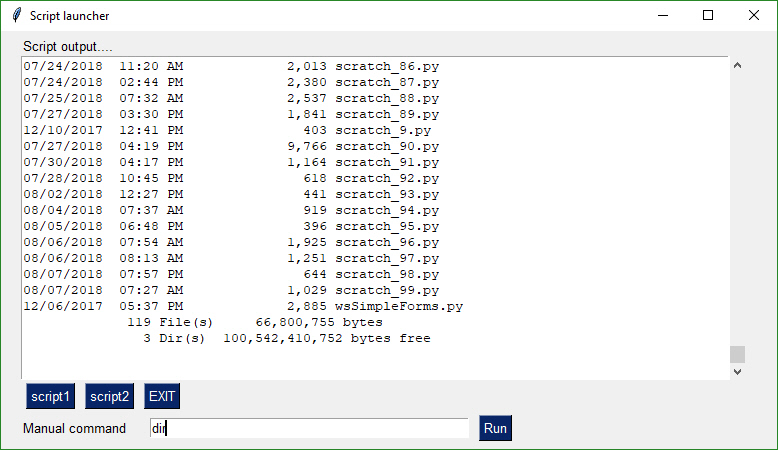
## Script Launcher - Persistent Form
|
|
This form doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are specified as `sg.ReadFormButton` instead of `sg.SimpleButton`. The exception to this is the EXIT button. Clicking it will close the form. This program will run commands and display the output in the scrollable window.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
import subprocess
|
|
|
|
def Launcher():
|
|
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Script launcher')
|
|
|
|
layout = [
|
|
[sg.Text('Script output....', size=(40, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Output(size=(88, 20))],
|
|
[sg.ReadFormButton('script1'), sg.ReadFormButton('script2'), sg.SimpleButton('EXIT')],
|
|
[sg.Text('Manual command', size=(15,1)), sg.InputText(focus=True), sg.ReadFormButton('Run', bind_return_key=True)]
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
form.Layout(layout)
|
|
|
|
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI --- #
|
|
while True:
|
|
(button, value) = form.Read()
|
|
if button == 'EXIT' or button is None:
|
|
break # exit button clicked
|
|
if button == 'script1':
|
|
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('pip','list')
|
|
elif button == 'script2':
|
|
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('python', '--version')
|
|
elif button == 'Run':
|
|
ExecuteCommandSubprocess(value[0])
|
|
|
|
|
|
def ExecuteCommandSubprocess(command, *args):
|
|
try:
|
|
sp = subprocess.Popen([command,*args], shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
|
out, err = sp.communicate()
|
|
if out:
|
|
print(out.decode("utf-8"))
|
|
if err:
|
|
print(err.decode("utf-8"))
|
|
except: pass
|
|
|
|
|
|
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
|
Launcher()
|
|
----
|
|
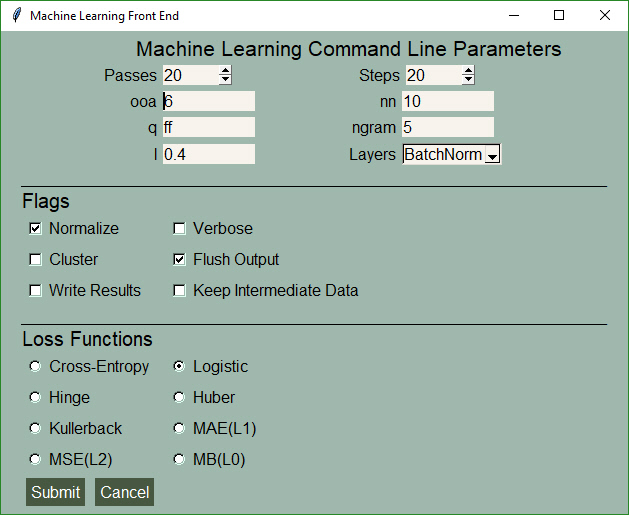
## Machine Learning GUI
|
|
A standard non-blocking GUI with lots of inputs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Green & tan color scheme
|
|
sg.SetOptions(background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
text_element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
element_background_color='#9FB8AD',
|
|
input_elements_background_color='#F7F3EC',
|
|
button_color=('white', '#475841'),
|
|
border_width=0,
|
|
slider_border_width=0,
|
|
progress_meter_border_depth=0,
|
|
scrollbar_color='#F7F3EC')
|
|
|
|
sg.SetOptions(text_justification='right')
|
|
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Machine Learning Front End', font=("Helvetica", 12)) # begin with a blank form
|
|
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('Machine Learning Command Line Parameters', font=('Helvetica', 16))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Passes', size=(15, 1)), sg.Spin(values=[i for i in range(1, 1000)], initial_value=20, size=(6, 1)),
|
|
sg.Text('Steps', size=(18, 1)), sg.Spin(values=[i for i in range(1, 1000)], initial_value=20, size=(6, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('ooa', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='6', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('nn', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='10', size=(10, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('q', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='ff', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('ngram', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='5', size=(10, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('l', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='0.4', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('Layers', size=(15, 1)), sg.Drop(values=('BatchNorm', 'other'),auto_size_text=True)],
|
|
[sg.Text('_' * 100, size=(65, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Flags', font=('Helvetica', 15), justification='left')],
|
|
[sg.Checkbox('Normalize', size=(12, 1), default=True), sg.Checkbox('Verbose', size=(20, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Checkbox('Cluster', size=(12, 1)), sg.Checkbox('Flush Output', size=(20, 1), default=True)],
|
|
[sg.Checkbox('Write Results', size=(12, 1)), sg.Checkbox('Keep Intermediate Data', size=(20, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('_' * 100, size=(65, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Text('Loss Functions', font=('Helvetica', 15), justification='left')],
|
|
[sg.Radio('Cross-Entropy', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('Logistic', 'loss', default=True, size=(12, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Radio('Hinge', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('Huber', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Radio('Kullerback', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('MAE(L1)', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Radio('MSE(L2)', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('MB(L0)', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
|
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
|
|
|
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
-------
|
|
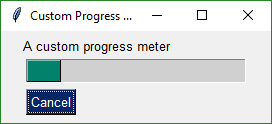
## Custom Progress Meter / Progress Bar
|
|
Perhaps you don't want all the statistics that the EasyProgressMeter provides and want to create your own progress bar. Use this recipe to do just that.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
def CustomMeter():
|
|
# create the progress bar element
|
|
progress_bar = sg.ProgressBar(10000, orientation='h', size=(20,20))
|
|
# layout the form
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
|
[progress_bar],
|
|
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
|
|
|
# create the form
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Custom Progress Meter')
|
|
# display the form as a non-blocking form
|
|
form.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
|
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
|
for i in range(10000):
|
|
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
|
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
|
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
|
break
|
|
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
|
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
|
# done with loop... need to destroy the window as it's still open
|
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
|
|
|
----
|
|
|
|
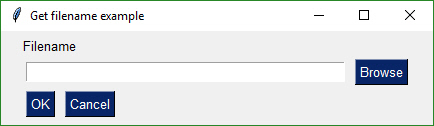
## The One-Line GUI
|
|
|
|
For those of you into super-compact code, a complete customized GUI can be specified, shown, and received the results using a single line of Python code. The way this is done is to combine the call to `FlexForm` and the call to `LayoutAndRead`. `FlexForm` returns a `FlexForm` object which has the `LayoutAndRead` method.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instead of
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
layout = [[sg.Text('Filename')],
|
|
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
|
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]
|
|
|
|
button, (number,) = sg.FlexForm('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
you can write this line of code for the exact same result (OK, two lines with the import):
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
button, (filename,) = sg.FlexForm('Get filename example'). LayoutAndRead([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ])
|
|
--------------------
|
|
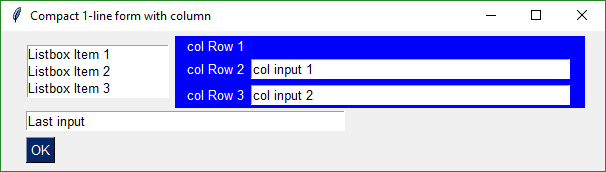
## Multiple Columns
|
|
Starting in version 2.9 (not yet released but you can get from current GitHub) you can use the Column Element. A Column is required when you have a tall element to the left of smaller elements.
|
|
|
|
This example uses a Column. There is a Listbox on the left that is 3 rows high. To the right of it are 3 single rows of text and input. These 3 rows are in a Column Element.
|
|
|
|
To make it easier to see the Column in the window, the Column background has been shaded blue. The code is wordier than normal due to the blue shading. Each element in the column needs to have the color set to match blue background.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
# Demo of how columns work
|
|
# Form has on row 1 a vertical slider followed by a COLUMN with 7 rows
|
|
# Prior to the Column element, this layout was not possible
|
|
# Columns layouts look identical to form layouts, they are a list of lists of elements.
|
|
|
|
# sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('BlueMono')
|
|
|
|
# Column layout
|
|
col = [[sg.Text('col Row 1', text_color='white', background_color='blue')],
|
|
[sg.Text('col Row 2', text_color='white', background_color='blue'), sg.Input('col input 1')],
|
|
[sg.Text('col Row 3', text_color='white', background_color='blue'), sg.Input('col input 2')]]
|
|
|
|
layout = [[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox Item 1', 'Listbox Item 2', 'Listbox Item 3'), select_mode=sg.LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE, size=(20,3)), sg.Column(col, background_color='blue')],
|
|
[sg.Input('Last input')],
|
|
[sg.OK()]]
|
|
|
|
# Display the form and get values
|
|
# If you're willing to not use the "context manager" design pattern, then it's possible
|
|
# to collapse the form display and read down to a single line of code.
|
|
button, values = sg.FlexForm('Compact 1-line form with column').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
|
|
|
sg.MsgBox(button, values, line_width=200)
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Persistent Form With Text Element Updates
|
|
|
|
This simple program keep a form open, taking input values until the user terminates the program using the "X" button.
|
|
|
|
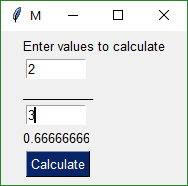
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
|
|
|
form = sg.FlexForm('Math')
|
|
|
|
output = sg.Txt('', size=(8,1))
|
|
|
|
layout = [ [sg.Txt('Enter values to calculate')],
|
|
[sg.In(size=(8,1), key='numerator')],
|
|
[sg.Txt('_' * 10)],
|
|
[sg.In(size=(8,1), key='denominator')],
|
|
[output],
|
|
[sg.ReadFormButton('Calculate', bind_return_key=True)]]
|
|
|
|
form.Layout(layout)
|
|
|
|
while True:
|
|
button, values = form.Read()
|
|
|
|
if button is not None:
|
|
try:
|
|
numerator = float(values['numerator'])
|
|
denominator = float(values['denominator'])
|
|
calc = numerator / denominator
|
|
except:
|
|
calc = 'Invalid'
|
|
|
|
output.Update(calc)
|
|
else:
|
|
break
|
|
|
|
|