Release 3.12.0 & 1.12.0
This commit is contained in:
parent
42c5499687
commit
f60137c4b2
83 changed files with 2030 additions and 1118 deletions
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ layout = [
|
|||
[sg.InputOptionMenu(('Menu Option 1', 'Menu Option 2', 'Menu Option 3'))],
|
||||
[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'), size=(30, 3)),
|
||||
sg.Frame('Labelled Group',[[
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25, tick_interval=25),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
||||
sg.Column(column1, background_color='lightblue')]])],
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
50
Demo_Buttons_Mac.py
Normal file
50
Demo_Buttons_Mac.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import time
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
def show_win():
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(border_width=0, margins=(0,0), element_padding=(5,3))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
frame_layout = [ [sg.Button('', image_data=mac_red, button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), key='_exit_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=mac_orange, button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT)),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=mac_green, button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), key='_minimize_'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' '*40)],]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Frame('',frame_layout)],
|
||||
[sg.T('')],
|
||||
[ sg.Text(' My Mac-alike window', size=(25,2)) ],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window',
|
||||
no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True,
|
||||
alpha_channel=0,
|
||||
).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(100):
|
||||
window.SetAlpha(i/100)
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == '_exit_':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == '_minimize_':
|
||||
# window.Minimize() # cannot minimize a window with no titlebar
|
||||
pass
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mac_red = 'iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABgAAAAZCAYAAAArK+5dAAAACXBIWXMAAA7EAAAOxAGVKw4bAAAAGHRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQBwYWludC5uZXQgNC4xLjFjKpxLAAAGfklEQVR42o1W6VNTVxR/Kv4Htp1xZA0JhCWsAQmQAC4Yd0GtKBqXUUAREBdE8pYAWVhUotVWVOpGpzpVqI51pnas+sFtOnXUmXY6o10sErYASUAgybun5yUEoWOnfvjNOe/dc35nufe9cymO4ygBLMt6JMey01mansmaTJS5sVFRrdlsrpq/0LVNEk62RkTB5vBIvjBKRiqyFz0zlpQydUeOUFU6HcVoaT8fzwQXYgo5yzDTWGGhtpYyFO+u2afK7EBSt0Yk5ncEBUGJvz+UInYEBZMtoRKyPSaOr1i67EEDTS+r1usphqan+4jfBXhHPp3FTKppes6hJUvvbhWHQ1FgEDQEBpAboiB4mhQPr5Sp8EqVCk8T4+F6oD8cDphDivwDoCRBDrrtO3RCYsjjN6UC1tcWJGcrKz8pT1X+tkMkhkZRiPNhYABvkUoBtmkIGGsBmj/3os5ARlfnkI7AYHgSEuxuCPQfLcKEKtZvqNLp3wURIJDPoIWIWu3H5WnKX4pDxXAlVDTWKZGABdswuGwZcTc1grPtKrifPPLA9e01cNYboTNeTrok4dApCSPtIcFju0NEsD9v/QEdtktot6cCbVXVTKPROKsmd83z3WIJ3BaLXD3SCOjAjXwtkcLQVg3wF88B/9MTICMjHgg6f74F+ubPh9fiMNIRKYPeiEhyJzTEWYYclRpNuQ7bhXviR9EGPVVfVsaUR8mgTSIe60PjjugY8kYWAx1hUrCvWwv8hRZwP3oIZKAfeAFCJWeboSctHTqkkfAG7f+OjgFrVDRpw9YeTEyCOi2diZ2ZTh0xmRIPZas7T4QE813RMt4Sm0A6ZbFgiY2HTnTqmZsCTqYKyDeXgdy/C/y9H4FcvQKOokLoxKQsMXFeW1ksQV+wREW7zKIQol3z6S0WW0XpC4qauNg4eC4Nhz48DZa4BOiKT/TAIkh07sUg9o35MHLoIIxUHYTB9XnQHY92k2y78Bl9iTVBzt8Xi3itUvXaVFc3m+Jy1wx8KQ3jrXHx0C1PJt1YXo882YtxvRsDd2Om3UjUgxD0CZtJEHz7kubCXzKZ67AsGuh9+6TUfiS+FxUBtpRU6MZMe1MUU9CH7/sUiNQ06EXZ69Px/b9thXb2pKSS/uRk/hxW0cTpzJQ+Jpq8iI2BAUUaLiq8ZON4F0QxQewL5LHxrU+yFzhsqN+QhEKLlgXqs8hw+D0pEWyqDOhPV0K/UuWFoOO7wQULYDA7GwbVarAtXjwB4Xlw4UIYmDcPrJP8+hBDGZnkVkQYmItLXNTRSKn7ZbIcHJmZSKiCgYwMGEDpIczJAVturgf298C3ZluxAgYxkOBnRf9h5PouXAJnOQ6oRkUKPEtKIMP40fRnZZEBXLTlrALH5s1g27QJ7AjHuJwCjcYjbRs3gh1t7fn5nor6szLJcNY8cgMPTuuRo72UYX3+D3cSYmF4vFzb8uVgLyoCe2GhBw5B/x/YBNtduzxBbQsWglWV7vpakQwGjlNStfsrdp5PTXFZM1XEplYTzIo4DhwAe3k5OPbu/SAItnaUtj17yFBODv9nstx9Mjvbom9omEXp6utmNK7Lu/04IY68VatdtoICcHAcsdM0OBjmw+C1JTaUb1evdt7FU2koKGDp6mr82XEsZaKZeedxc96kK9wjBYXEXl8PQwYDDBmNHwSHwUDsJiOM1NTwHco0d8uiRf26mtqPWIaeSQnjkaupoYy7issvyxPcg4vVo6NGI3GcOEGGjh4lw2YzDB879p8YamoijqYmGGludg9szHdez1CCWVddSnvnjN/EqGQwyKmS0kc38Mh2r1ox5jx5gn/b2gqOlhYyfPo0vAdk6MwZMnzxIjhbW139xTvh+0wVmLX0floYXiwzg500MqcJ/26TyTT78K5i/Vcpc+FFlgo3rtzlPHPWPXbtGhlpayOjbe3gwbU2MtbeDs7LV9x2g8H568rlcCkr4w8TTS/iqms843f8AjE+9McfGIbBPeGo45WHmLOrVva1yxPhUUY6vNyQ5+7aWei2Vh4gVm0l6dm7x/1yi8b1eIkarmMyp/LWPahmOZHgyzHMjMkXiYnhzHrlNKFvQol6nS7gWFlZ48k1a38+hx/fJSS6kJwE5xGCfhG/m9Mb8p9+wenqaGHYe5OcQj4lADc+pH2Ggq7FY8YZDFQ9w8h1FQfjb5qPPb9pPv6cQ/1wba2cw7tTlUCGSSGm+Tox+dryD68sSIU4MRj4AAAAAElFTkSuQmCC'
|
||||
|
||||
mac_green = 'iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABkAAAAZCAYAAADE6YVjAAAACXBIWXMAAA7EAAAOxAGVKw4bAAAAGHRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQBwYWludC5uZXQgNC4xLjFjKpxLAAAHAElEQVR42o1WaVBUVxZ+CvmbmuhEoUyMJMaJWCQGUNawLwINFEtkp4GGprsBW2Vp6O639M4iLVAzjomaURKNCCONsimKogwko6IwgnEJOEaBTCpJZRaTorvvmXtfwIAmVf746p5733fOd8/prnsOxXEctQCWZfmVYWhHjtVQ5toGSq1XyhMLBD3uca72V31ftq3zc4a1vqttb0W42LdlhfSUM7t3mGv3UizNUTTxWxRnAb9sWG5egHHQafQUyzErU4oSO92iNjzGQZGT90totd+L4ByMEfgiOPn8Dr3iswq5hr/xY3xeVKfGyPrpdQbeH8dZtljoaQFHvdZAFVVIpO6xrg+cvV+CteEr4G2RM8Sa3EF6JBZ2tiSB/FgCpDb5god8Dbwev5IIgnvcRpCWi6XEX62ml2bypEQs42jQGSlhcYZkfcgaWBe6Crx2rLNG/PE1pOhNRGe/bEafP+yCGzP9cG26DwYfnERcfyaKOeCCgrg3rOtjV1ldApwhT55Vuaduz+/VtPpJRgsCDlpcIpFcKHEJcoKN8Wus2+o22NJb3CDz+GZ0/LoZrjzogy++vgpffX8PJr8dh5szQ9A5cQiyPvVA6S1vQ9JHrsij8JU5l5DVUKQS9xrxhXFllvOZkAw0nJZS6RRit5j14Jb66lzSQVd7TpsHpB99B0naAqD3djOMzw7DN/99BHZkh8dz/4H7303A36ZOQYklHNKOuiHhCQ+U3fouCqRdfno91GkutyRLRkqH/0QOFE3TDgaDfkV0XvDsxgRn2/uH3Gyi9i0gbPEkjpDTtgUs4x/AxOxnMPPv+/CT9TH88OO3vMiFeycg/68+IDzhDjknPHmIOjyRf7mLzSPxLWD0aj+WYZdRRl01JVfLmE2CtRBrdp0rPO0Nea1bUf5JLyg46Q3C1nfB0J8LQ//sgjv/GoEH39+GKVyusZlBMF8uxgKbeR7hi9q2ImLntHpaN2evQcni2FMkPlVfY14uyA275lPyml122s8mtfgjqcUPZB3+TyCx+IDyTCL85aoWOnBWLaP1oO/PBkm7D0gX8YiftN0PlXS/Z4+q2WAPTPO8X1tT60Tpa7nS4GzPx0n73GBHdyCSWfyh6NR7z6DQ4g0F7Vt5W4JtcbvXr/KIWPHpAMg9vsXqlfMmlCl2v0ml5Sdy/uI/gAzfYldXEMg7A2EnXpciGH/D6A7h97u6f7GfBu/fGYR29gTZfYvX2bU17F4qs3B7Q7hiEyo9GwJlvWGorDcUys+EPQHZl86fVZwNh6q+SKjsi4CKM+FQ3hsGpT0hsNiH2GU9oaA4Hw4R9AbQmKuAKtidfSbe8A6oLm7jAxAoz2H73M82czEGqoeTof5KKjRcS4em65k8iE3OTEPJPIf3PTfvezYS6EvRSGByBbm6YI5KFSUp4vWbkXogClTnopDqPF4xmAsx0HA1HfaP5sIHY3nPYOH8wzERbzdcycA+AlCe5+MAe1kAAv0m0NbjTPKKMw1xKg8gIuxALL6VALiBONh/IwcO3RTDARzkwD/yfxtj+TyHcP+MfTSX4oG+IEDaoTgUzbnaG/fVfkM1NppLkxVB/9t1OhiZhpOQ5lIc+tOIED6ZkMHhm4VwZFwCRyak8+u8/fQe24T7MfbZd10IussJWCjGmkB7A6dhfKk6Y/2ygsrUGzkHvaB+JMVG6v/xRBF8+sUOOHarhF+fBwvc5nEZMl9Ls8stQbbtZWGPak17VlLk3dJVs/KEKi8rezHW2jiSgY7fkqO2O7uh9fYuIOvzYJ6LWm7JoWk0Yy5t7xYoqhBVajkdRbrZC8SQKrP60vGHxtEMKyF23C1H7XfLoONe+XOh/W4pstzB/KlyW0V3hC1TGTmr0+pWkB6FOyC7HL/5Dhod5yxUCr4u+MjfdvhO4VzvpAq6vqxEGNA9WYWh/A1UQSfh3auE8w9Zm/nzlDlhdSjoa1gxx3AkvsNCb1/O4oO6BpM4j40G8eEAOHq7yHrxoQb1T3Gob5JGfVM0/Ar4bwNfadHAtMZqHkwDkTkCOKNSQmYEFvcp0nWJ0rwQg7sYRxmrdYHZFdEjWWZfqO5PsZ6aLLcOTuvtwzMmNDRtRMPTJsDAqxE+mzWhS9M627GxEmvp0UjIVEWOaHVsIPmdcTy+YZH4S6YUkhpDs5RGy60s04u70lQBkNPkB4rWaGgaFNoOXS20fTJaDM3XZfYP/55vM/a8by8+GAapWvyoMpldHB4+SEX4DBbFfWYc4rAQyYi0Y41B5S9ns7tzlNGPUmk/SGF9IFntBdsZH0jFEDIRINdlDxnr2RINq+MHEnLRp8eiJVMFSY3lJxcWl45x5MVYA2UwGBxprcKd1ii2Nnc0gXm/bl8VXeZeU2dw02tMFMke+zrypf9ZaEnc/wNvUH/BVaIfLQAAAABJRU5ErkJggg=='
|
||||
|
||||
mac_orange = 'iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABgAAAAZCAYAAAArK+5dAAAACXBIWXMAAA7EAAAOxAGVKw4bAAAAGHRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQBwYWludC5uZXQgNC4xLjFjKpxLAAAGzklEQVR42o2W+1dTVxbHr6+/wIJj0LRCYUZ88JRQFJTBB2q1yzrooCjIq8griIAxyc3NDXmQF/JQQNuq1Qqo1IK2S9GO1XbGcYpWxzVWZK2xRYUEE5JAEALJPXvOvQnodKar/eGz9j53f/c+9+ys3H0IuVxOsFAUxVk5RU2nSHIWpdURNXp9nCJtR614RZw7MyAAZQTwIYM3H3L4fCRfk+TW5eXWNjU2xkmVKkKGc3D+dMpXb5L/Kk7JZNM4gVJJqPPzKstjY55nzud7Mng8JmeeHxQHzubIxX7G3LlMzluBSLQq4SdaWLSJVqkJKSnFdahpUy/LbfCq+HSKVhAKUjpPkpx0I2vu72Av3w/0cXNQx5950CVaBt3qROjWJMKdgzFwMTUADMv9Ud682ZAdwAPDnrQbRqNxvlgiYetNmzwJQU22BRenxKI5+wXhj3MD/EAXHzDxj0I+Y6oMgqHm3Wj021oY7TrlBfuOlnTUj2NdxW8yxpW88VzebKjLyXhsqDb6k1LpDFyTOwlbfAbJnoKU+pcJwn8oWOAP57a/OW5ShcCAMgiZj72HHN80wciDL2Cs9y4H6ztuHgHToQQ0oHwbmTW/h/ad/DFhoB+QO7ZXU7hdbEe4E0glklmaqqo3VFvWPygOmgPXcoPcVn0o9KkXoWeKYLC25sHI3bPgenYPmAkXh+v5fXDeaYGBpo3wnH4baxejQX0o+jovcKIk2B+ku1JLaRX3w88kpGoNod9XICsLnQ9tOwPHbTVLoU8Xhkz6cOjXLATLJ6l4g1Zw9XYBM+rgcPXeAWdXMww0JkN/VSiY9GHQp10K9rpwdCVrgVscFQxaUpyIOzOdqNZVRZOrl/cbEniMyRjGmKujUL8xAszVkWAyRoL5UBTYOspwWy7C2JNbHCP/vAj2Swdxi6LBVD2pjUD92FrrI90nNgUg6XsbLlMaDUHo9mbUiKKD4UZRCNiOxHBJ5ppoGKhdxmGuieKwNqeB47IcHFfkYG1J5zTs8ykdxlQTjSyHBUw39QdGnRzxVKPV8QjNlnX2qsQFTK8hAiwN76CBegEMHI59jXe81OFi9TFeWB/HXnCx17Q411wfC7YmgbttRxAcKBIuJCpwv05uCwHrUSxuXIFZDi+aVvwPlqPx2Mb71vFg+T8aFnPDcmT/OIH5riyYOSSuqCVEghDUnr0QHMcTYODYSnhxLAEsH670wvq4MGdxzPrRKrAeTwQLtt5nvtik/kNvvg1rejRh0CorAuKgIBg6ixbD8KerwXJyNQx+4uNkEgyeWgO2s5vA/tlWsH+eAo6ObWBr3w72C9vw+k9gb9sCtuYNr3Kw3oqt/dO16GmdAE6UprkJSVyIp7NoCTibcfC1DeznNoPj4nZwfLEDhl7n0ivfG0sFB97MdmY92Hy5jjPr4GldDJxXCoFQrw2HjrwlyHluPfs2yHYmGSdshaFrGeDo3A1Dnbswu3+ZKzh+NZ2z9tZ38UbJyNm2GT3WRzHnDJSF0Kdv/up02kIYbE7Ggo24He/D8I0sTCYMf50JTuz/GpzuZhbeJA1sLRvB2bbJfVcRC4qDogTCcKA4vyFlqfunxkQ0fOF9NNS5E43c+gCcf82Gkb/l/CYmtc5vs5Hj8xTG0ZLsaSteaZKr9G8QtFY/49Ced6/9ZX8YGrmU4h6+ngEv7+Sjka692GK6fgPfcRY5b38AL6+mTTzUxYIuP5UiK1UEIZErCC0pSjqdHgHPPl7jGbuZhV7eL4TRewUwep+l8Ne5V4BeYr3rfiHzomWDp7UgwUZTtB9FyWbhzyoejwoloSvJLL2QHeqxd2x1jT8UotFHJWjsByFydZeAq3vfLzL2CGsfCmHiSQUavr5z4lp5LNTRohISzxc5JZs5NSplChVxvHzX7SuFS8DSnjLO/Luccf1YAWM9pcjVUwqunv0/o9Qbe1IOqE/M2K/vGr8uioN62f4Kkq7EY1g2g5qcyeyIY7/dVVotr0aYprqQuxgeNSTByO0cN9N7wMOYJMjTL8ZIwIsYMWYJQv0Sz9i/itw9J9bBlyUCOEyVidnichk503eB8A1930JGygj2aA2UUHY6N956Gf8B7+rj4cfzWz2Wr3Z77LeykOPv2Wjwmz2eZ+0pnns1q+Dqvgg4lZ/UpyXL11OKSrbleJJRUxeJqenvG9LT2L6RtJJQVcr5Ryr2GD7K/eP3rZkR0Ja5CM5nefksexGczY6G43lrvz8m3Wuo0qj5Uormxq/3lvKza8vkcSgOOUFjIetLaBVBqbSEnhYto0X7IjuPKh6w0AdKIo1KcplcrSPE8kpCJiPZ6wp3J/K++atry38AI6a42QLVvMIAAAAASUVORK5CYII='
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
show_win()
|
||||
75
Demo_Buttons_Nice_Graphics.py
Normal file
75
Demo_Buttons_Nice_Graphics.py
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('Test of reading input field') ],
|
|||
key='_in5'), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.T('This input clears after submit'),sg.In(change_submits=True,
|
||||
key='_in6_'), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demonstration of InputText with change_submits',
|
||||
auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ to collect user input that is sent to the chatbot. The reply is displayed in th
|
|||
# Create the 'Trainer GUI'
|
||||
# The Trainer GUI consists of a lot of progress bars stacked on top of each other
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
sg.DebugWin()
|
||||
# sg.DebugWin()
|
||||
MAX_PROG_BARS = 20 # number of training sessions
|
||||
bars = []
|
||||
texts = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,8 +39,8 @@ def print_progress_bar(description, iteration_counter, total_items, progress_bar
|
|||
global texts
|
||||
global training_window
|
||||
# update the window and the bars
|
||||
button, values = training_window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is None and values is None: # if user closed the window on us, exit
|
||||
button, values = training_window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if button is None: # if user closed the window on us, exit
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
if bars[current_bar].UpdateBar(iteration_counter, max=total_items) is False:
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ chatbot.train("chatterbot.corpus.english")
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Output(size=(80, 20))],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('SEND', bind_return_key=True), sg.ReadButton('EXIT')]]
|
||||
sg.Button('SEND', bind_return_key=True), sg.Button('EXIT')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Chat Window', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30, 2)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1649,8 +1649,8 @@ def show_all_colors_on_buttons():
|
|||
row_len = 20
|
||||
for i, c in enumerate(colors):
|
||||
hex = get_hex_from_name(c)
|
||||
button1 = sg.Button(button_text=c, button_color=(get_complementary_hex(hex), hex), size=(8, 1))
|
||||
button2 = sg.Button(button_text=c, button_color=(hex, get_complementary_hex(hex)), size=(8, 1))
|
||||
button1 = sg.CButton(button_text=c, button_color=(get_complementary_hex(hex), hex), size=(8, 1))
|
||||
button2 = sg.CButton(button_text=c, button_color=(hex, get_complementary_hex(hex)), size=(8, 1))
|
||||
row.append(button1)
|
||||
row.append(button2)
|
||||
if (i+1) % row_len == 0:
|
||||
|
|
@ -1717,8 +1717,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
complementary_color = get_name_from_hex(complementary_hex)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('That color and it\'s compliment are shown on these buttons. This form auto-closes')],
|
||||
[sg.Button(button_text=color_name, button_color=(color_hex, complementary_hex))],
|
||||
[sg.Button(button_text=complementary_hex + ' ' + complementary_color, button_color=(complementary_hex , color_hex), size=(30, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.CloseButton(button_text=color_name, button_color=(color_hex, complementary_hex))],
|
||||
[sg.CloseButton(button_text=complementary_hex + ' ' + complementary_color, button_color=(complementary_hex , color_hex), size=(30, 1))],
|
||||
]
|
||||
sg.Window('Color demo', default_element_size=(100, 1), auto_size_text=True, auto_close=True, auto_close_duration=5, icon=MY_WINDOW_ICON).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -686,7 +686,7 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Hover mouse to see RGB value, click for white & black text',
|
|||
# -- Create primary color viewer window by building rows and appending to layout --
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
for i, color in enumerate(color_map):
|
||||
row.append(sg.RButton(color, button_color=('black', color), key=color, tooltip=color_map[color]))
|
||||
row.append(sg.Button(color, button_color=('black', color), key=color, tooltip=color_map[color]))
|
||||
if (i+1) % 15 == 0: # every 15 buttons make a new row
|
||||
layout.append(row)
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -700,4 +700,4 @@ while True:
|
|||
break
|
||||
# -- Create a secondary window that shows white and black text on chosen color
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('white', event), tooltip=color_map[event]), sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('black', event), tooltip=color_map[event])] ]
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Click on a color square to see both white and black text on
|
|||
row = []
|
||||
# -- Create primary color viewer window --
|
||||
for i, color in enumerate(COLORS):
|
||||
row.append(sg.RButton(color, button_color=('black', color), key=color))
|
||||
row.append(sg.Button(color, button_color=('black', color), key=color))
|
||||
if (i+1) % 12 == 0:
|
||||
layout.append(row)
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,4 +110,4 @@ while True:
|
|||
break
|
||||
# -- Create a secondary window that shows white and black text on chosen color
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('white', event)), sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('black', event))]]
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
793
Demo_Cookbook_Browser.py
Normal file
793
Demo_Cookbook_Browser.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,793 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
# import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
|
||||
def SimpleDataEntry():
|
||||
"""Simple Data Entry - Return Values As List
|
||||
Same GUI screen except the return values are in a list instead of a dictionary and doesn't have initial values.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
# Very basic window. Return values as a list
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry form') # begin with a blank form
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values[0], values[1], values[2])
|
||||
|
||||
def SimpleReturnAsDict():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simple data entry - Return Values As Dictionary
|
||||
A simple form with default values. Results returned in a dictionary. Does not use a context manager
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Very basic window. Return values as a dictionary
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry form') # begin with a blank form
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('name', key='name')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('address', key='address')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('phone', key='phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
|
||||
def FileBrowse():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simple File Browse
|
||||
Browse for a filename that is populated into the input field.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.Window('SHA-1 & 256 Hash') as form:
|
||||
form_rows = [[sg.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
(button, (source_filename,)) = window.LayoutAndRead(form_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, source_filename)
|
||||
|
||||
def GUIAddOn():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Add GUI to Front-End of Script
|
||||
Quickly add a GUI allowing the user to browse for a filename if a filename is not supplied on the command line using this 1-line GUI. It's the best of both worlds.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
button, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').Layout([[sg.T('Document to open')],
|
||||
[sg.In(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Open(), sg.Cancel()]]).Read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fname = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if not fname:
|
||||
sg.Popup("Cancel", "No filename supplied")
|
||||
# raise SystemExit("Cancelling: no filename supplied")
|
||||
|
||||
def Compare2Files():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Compare 2 Files
|
||||
Browse to get 2 file names that can be then compared. Uses a context manager
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.Window('File Compare') as form:
|
||||
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Enter 2 files to comare')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('File 1', size=(8, 1)), sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('File 2', size=(8, 1)), sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(form_rows).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
|
||||
def AllWidgetsWithContext():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Nearly All Widgets with Green Color Theme with Context Manager
|
||||
Example of nearly all of the widgets in a single window. Uses a customized color scheme. This recipe uses a context manager, the preferred method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
# Green & tan color scheme
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False) as form:
|
||||
|
||||
column1 = [[sg.Text('Column 1', background_color='#F7F3EC', justification='center', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 3')]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[sg.InputText('This is my text')],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Checkbox'), sg.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), sg.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', size=(35, 3)),
|
||||
sg.Multiline(default_text='A second multi-line', size=(35, 3))],
|
||||
[sg.InputCombo(('Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(34, 20), default_value=85)],
|
||||
[sg.InputOptionMenu(('Menu Option 1', 'Menu Option 2', 'Menu Option 3'))],
|
||||
[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'), size=(30, 3)),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
||||
sg.Column(column1, background_color='#F7F3EC')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 80)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Choose A Folder', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Your Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'),
|
||||
sg.InputText('Default Folder'), sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
def AllWidgetsNoContext():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
All Widgets No Context Manager
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
|
||||
column1 = [[sg.Text('Column 1', background_color='#F7F3EC', justification='center', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 3')]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[sg.InputText('This is my text')],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Checkbox'), sg.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), sg.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', size=(35, 3)),
|
||||
sg.Multiline(default_text='A second multi-line', size=(35, 3))],
|
||||
[sg.InputCombo(('Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(34, 20), default_value=85)],
|
||||
[sg.InputOptionMenu(('Menu Option 1', 'Menu Option 2', 'Menu Option 3'))],
|
||||
[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'), size=(30, 3)),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
||||
sg.Column(column1, background_color='#F7F3EC')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 80)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Choose A Folder', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Your Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'),
|
||||
sg.InputText('Default Folder'), sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
def NonBlockingWithUpdates():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Non-Blocking Form With Periodic Update
|
||||
An async form that has a button read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. There is no context manager for this recipe because the loop that reads the form is likely to be some distance away from where the form was initialized.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer')
|
||||
# create a text element that will be updated periodically
|
||||
|
||||
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Stopwatch', size=(20,2), justification='center')],
|
||||
[ sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 5), sg.ReadButton('Start/Stop', focus=True), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window.LayoutAndRead(form_rows, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
timer_running = True
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
# loop to process user clicks
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
i += 1 * (timer_running is True)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button == 'Start/Stop':
|
||||
timer_running = not timer_running
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
def NonBlockingWithContext():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Async Form (Non-Blocking) with Context Manager
|
||||
Like the previous recipe, this form is an async window. The difference is that this form uses a context manager.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.Window('Running Timer') as form:
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates', justification='center')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red', justification='center', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 15), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
window.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, 500):
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
def CallbackSimulation():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Callback Function Simulation
|
||||
The architecture of some programs works better with button callbacks instead of handling in-line. While button callbacks are part of the PySimpleGUI implementation, they are not directly exposed to the caller. The way to get the same result as callbacks is to simulate them with a recipe like this one.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# This design pattern simulates button callbacks
|
||||
# Note that callbacks are NOT a part of the package's interface to the
|
||||
# caller intentionally. The underlying implementation actually does use
|
||||
# tkinter callbacks. They are simply hidden from the user.
|
||||
|
||||
# The callback functions
|
||||
def button1():
|
||||
print('Button 1 callback')
|
||||
|
||||
def button2():
|
||||
print('Button 2 callback')
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a standard form
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Button callback example')
|
||||
# Layout the design of the GUI
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Please click a button')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('1'), sg.ReadButton('2'), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
# Show the form to the user
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# Event loop. Read buttons, make callbacks
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# Read the form
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
# Take appropriate action based on button
|
||||
if button == '1':
|
||||
button1()
|
||||
elif button == '2':
|
||||
button2()
|
||||
elif button =='Quit' or button is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# All done!
|
||||
sg.PopupOK('Done')
|
||||
|
||||
def RealtimeButtons():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Realtime Buttons (Good For Raspberry Pi)
|
||||
This recipe implements a remote control interface for a robot. There are 4 directions, forward, reverse, left, right. When a button is clicked, PySimpleGUI immediately returns button events for as long as the buttons is held down. When released, the button events stop. This is an async/non-blocking window.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Make a form, but don't use context manager
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Robotics Remote Control')
|
||||
|
||||
form_rows = [[sg.Text('Robotics Remote Control')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 10), sg.RealtimeButton('Forward')],
|
||||
[sg.RealtimeButton('Left'), sg.T(' ' * 15), sg.RealtimeButton('Right')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 10), sg.RealtimeButton('Reverse')],
|
||||
[sg.T('')],
|
||||
[sg.Quit(button_color=('black', 'orange'))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window.LayoutAndRead(form_rows, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your form every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button is 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
def EasyProgressMeter():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Easy Progress Meter
|
||||
This recipe shows just how easy it is to add a progress meter to your code.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1000):
|
||||
sg.EasyProgressMeter('Easy Meter Example', i+1, 1000)
|
||||
|
||||
def TabbedForm():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Tabbed Form
|
||||
Tabbed forms are easy to make and use in PySimpleGUI. You simple may your layouts for each tab and then instead of LayoutAndRead you call ShowTabbedwindow. Results are returned as a list of form results. Each tab acts like a single window.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.Window('') as form:
|
||||
with sg.Window('') as form2:
|
||||
|
||||
layout_tab_1 = [[sg.Text('First tab', size=(20, 1), font=('helvetica', 15))],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(), sg.Text('Enter some info')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(button_color=('red', 'yellow')), sg.Cancel(button_color=('white', 'blue'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout_tab_2 = [[sg.Text('Second Tab', size=(20, 1), font=('helvetica', 15))],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(), sg.Text('Enter some info')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(button_color=('red', 'yellow')), sg.Cancel(button_color=('white', 'blue'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
results = sg.ShowTabbedForm('Tabbed form example', (form, layout_tab_1, 'First Tab'),
|
||||
(form2, layout_tab_2,'Second Tab'))
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(results)
|
||||
|
||||
def MediaPlayer():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Button Graphics (Media Player)
|
||||
Buttons can have PNG of GIF images on them. This Media Player recipe requires 4 images in order to function correctly. The background is set to the same color as the button background so that they blend together.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
background = '#F0F0F0'
|
||||
# Set the backgrounds the same as the background on the buttons
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(background_color=background, element_background_color=background)
|
||||
# Images are located in a subfolder in the Demo Media Player.py folder
|
||||
image_pause = './ButtonGraphics/Pause.png'
|
||||
image_restart = './ButtonGraphics/Restart.png'
|
||||
image_next = './ButtonGraphics/Next.png'
|
||||
image_exit = './ButtonGraphics/Exit.png'
|
||||
|
||||
# Open a form, note that context manager can't be used generally speaking for async forms
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Media File Player', default_element_size=(20, 1),
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 25))
|
||||
# define layout of the rows
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Media File Player', size=(17, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 2), font=("Helvetica", 14), key='out')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Restart Song', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Pause', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Next', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.Button('Exit', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2,
|
||||
border_width=0)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 20)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(' ' * 30)],
|
||||
[sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 8),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Bass', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(6, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Treble', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(10, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Volume', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(7, 1))] ]
|
||||
|
||||
# Call the same LayoutAndRead but indicate the form is non-blocking
|
||||
window.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# Read the form (this call will not block)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if button:
|
||||
window.FindElement('out').Update(button)
|
||||
|
||||
def ScriptLauncher():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Script Launcher - Persistent Form
|
||||
This form doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are specified as sg.ReadButton instead of sg.Button. The exception to this is the EXIT button. Clicking it will close the window. This program will run commands and display the output in the scrollable window.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
|
||||
def Launcher():
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Script launcher')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Script output....', size=(40, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(88, 20))],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('script1'), sg.ReadButton('script2'), sg.Button('EXIT')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Manual command', size=(15,1)), sg.InputText(focus=True), sg.ReadButton('Run', bind_return_key=True)]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'EXIT' or button is None:
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
if button == 'script1':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('pip','list')
|
||||
elif button == 'script2':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('python', '--version')
|
||||
elif button == 'Run':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess(value[0])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def ExecuteCommandSubprocess(command, *args):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
expanded_args = []
|
||||
for a in args:
|
||||
expanded_args += a
|
||||
sp = subprocess.Popen([command,expanded_args], shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
out, err = sp.communicate()
|
||||
if out:
|
||||
print(out.decode("utf-8"))
|
||||
if err:
|
||||
print(err.decode("utf-8"))
|
||||
except: pass
|
||||
|
||||
Launcher()
|
||||
|
||||
def MachineLearning():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Machine Learning GUI
|
||||
A standard non-blocking GUI with lots of inputs.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('LightGreen')
|
||||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(text_justification='right')
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Machine Learning Front End', font=("Helvetica", 12)) # begin with a blank form
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Machine Learning Command Line Parameters', font=('Helvetica', 16))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Passes', size=(15, 1)), sg.Spin(values=[i for i in range(1, 1000)], initial_value=20, size=(6, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Steps', size=(18, 1)), sg.Spin(values=[i for i in range(1, 1000)], initial_value=20, size=(6, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('ooa', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='6', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('nn', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='10', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('q', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='ff', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('ngram', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='5', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('l', size=(15, 1)), sg.In(default_text='0.4', size=(10, 1)), sg.Text('Layers', size=(15, 1)), sg.Drop(values=('BatchNorm', 'other'),auto_size_text=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 100, size=(65, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Flags', font=('Helvetica', 15), justification='left')],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Normalize', size=(12, 1), default=True), sg.Checkbox('Verbose', size=(20, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Cluster', size=(12, 1)), sg.Checkbox('Flush Output', size=(20, 1), default=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Write Results', size=(12, 1)), sg.Checkbox('Keep Intermediate Data', size=(20, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 100, size=(65, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Loss Functions', font=('Helvetica', 15), justification='left')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('Cross-Entropy', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('Logistic', 'loss', default=True, size=(12, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('Hinge', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('Huber', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('Kullerback', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('MAE(L1)', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('MSE(L2)', 'loss', size=(12, 1)), sg.Radio('MB(L0)', 'loss', size=(12, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
def CustromProgressMeter():
|
||||
""""
|
||||
Custom Progress Meter / Progress Bar
|
||||
Perhaps you don't want all the statistics that the EasyProgressMeter provides and want to create your own progress bar. Use this recipe to do just that.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
def CustomMeter():
|
||||
# create the progress bar element
|
||||
progress_bar = sg.ProgressBar(10000, orientation='h', size=(20,20))
|
||||
# layout the form
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
||||
[progress_bar],
|
||||
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Custom Progress Meter')
|
||||
# display the form as a non-blocking form
|
||||
window.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
||||
# done with loop... need to destroy the window as it's still open
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
CustomMeter()
|
||||
|
||||
def OneLineGUI():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The One-Line GUI
|
||||
For those of you into super-compact code, a complete customized GUI can be specified, shown, and received the results using a single line of Python code. The way this is done is to combine the call to Window and the call to LayoutAndRead. Window returns a Window object which has the LayoutAndRead method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Filename')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
you can write this line of code for the exact same result (OK, two lines with the import):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example'). LayoutAndRead([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ])
|
||||
|
||||
def MultipleColumns():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Multiple Columns
|
||||
Starting in version 2.9 (not yet released but you can get from current GitHub) you can use the Column Element. A Column is required when you have a tall element to the left of smaller elements.
|
||||
|
||||
This example uses a Column. There is a Listbox on the left that is 3 rows high. To the right of it are 3 single rows of text and input. These 3 rows are in a Column Element.
|
||||
|
||||
To make it easier to see the Column in the window, the Column background has been shaded blue. The code is wordier than normal due to the blue shading. Each element in the column needs to have the color set to match blue background.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Demo of how columns work
|
||||
# Form has on row 1 a vertical slider followed by a COLUMN with 7 rows
|
||||
# Prior to the Column element, this layout was not possible
|
||||
# Columns layouts look identical to form layouts, they are a list of lists of elements.
|
||||
|
||||
# sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('BlueMono')
|
||||
|
||||
# Column layout
|
||||
col = [[sg.Text('col Row 1', text_color='white', background_color='blue')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('col Row 2', text_color='white', background_color='blue'), sg.Input('col input 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('col Row 3', text_color='white', background_color='blue'), sg.Input('col input 2')]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox Item 1', 'Listbox Item 2', 'Listbox Item 3'), select_mode=sg.LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE, size=(20,3)), sg.Column(col, background_color='blue')],
|
||||
[sg.Input('Last input')],
|
||||
[sg.OK()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Display the form and get values
|
||||
# If you're willing to not use the "context manager" design pattern, then it's possible
|
||||
# to collapse the form display and read down to a single line of code.
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line form with column').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
def PersistentForm():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Persistent Form With Text Element Updates
|
||||
This simple program keep a form open, taking input values until the user terminates the program using the "X" button.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Math')
|
||||
|
||||
output = sg.Txt('', size=(8,1))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [ [sg.Txt('Enter values to calculate')],
|
||||
[sg.In(size=(8,1), key='numerator')],
|
||||
[sg.Txt('_' * 10)],
|
||||
[sg.In(size=(8,1), key='denominator')],
|
||||
[output],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Calculate', bind_return_key=True)]]
|
||||
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
numerator = float(values['numerator'])
|
||||
denominator = float(values['denominator'])
|
||||
calc = numerator / denominator
|
||||
except:
|
||||
calc = 'Invalid'
|
||||
|
||||
output.Update(calc)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
def CanvasWidget():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
tkinter Canvas Widget
|
||||
The Canvas Element is one of the few tkinter objects that are directly accessible. The tkinter Canvas widget itself can be retrieved from a Canvas Element like this:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as gui
|
||||
|
||||
canvas = gui.Canvas(size=(100,100), background_color='red')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[canvas],
|
||||
[gui.T('Change circle color to:'), gui.ReadButton('Red'), gui.ReadButton('Blue')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = gui.Window('Canvas test', grab_anywhere=True)
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
cir = canvas.TKCanvas.create_oval(50, 50, 100, 100)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Blue':
|
||||
canvas.TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill = "Blue")
|
||||
elif button is 'Red':
|
||||
canvas.TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill = "Red")
|
||||
|
||||
def InputElementUpdate():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Input Element Update
|
||||
This Recipe implements a Raspberry Pi touchscreen based keypad entry. As the digits are entered using the buttons, the Input Element above it is updated with the input digits. There are a number of features used in this Recipe including: Default Element Size auto_size_buttons ReadButton Dictionary Return values Update of Elements in form (Input, Text) do_not_clear of Input Elements
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as g
|
||||
|
||||
# Demonstrates a number of PySimpleGUI features including:
|
||||
# Default element size
|
||||
# auto_size_buttons
|
||||
# ReadButton
|
||||
# Dictionary return values
|
||||
# Update of elements in form (Text, Input)
|
||||
# do_not_clear of Input elements
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[g.Text('Enter Your Passcode')],
|
||||
[g.Input(size=(10, 1), do_not_clear=True, key='input')],
|
||||
[g.ReadButton('1'), g.ReadButton('2'), g.ReadButton('3')],
|
||||
[g.ReadButton('4'), g.ReadButton('5'), g.ReadButton('6')],
|
||||
[g.ReadButton('7'), g.ReadButton('8'), g.ReadButton('9')],
|
||||
[g.ReadButton('Submit'), g.ReadButton('0'), g.ReadButton('Clear')],
|
||||
[ g.Text('', size=(15, 1), font=('Helvetica', 18), text_color='red', key='output')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = g.Window('Keypad', default_element_size=(5, 2), auto_size_buttons=False)
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# Loop forever reading the form's values, updating the Input field
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read() # read the form
|
||||
if button is None: # if the X button clicked, just exit
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Clear': # clear keys if clear button
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
elif button in '1234567890':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input'] # get what's been entered so far
|
||||
keys_entered += button # add the new digit
|
||||
elif button is 'Submit':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input']
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(keys_entered) # output the final string
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('input').Update(keys_entered) # change the form to reflect current key string
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def TableSimulation():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display data in a table format
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark1')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Table Test')]]
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(20):
|
||||
layout.append([sg.T('{} {}'.format(i,j), size=(4, 1), background_color='black', pad=(1, 1)) for j in range(10)])
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Window('Table').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def TightLayout():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Turn off padding in order to get a really tight looking layout.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('User:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('User 1', 'User 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
sg.T('0', size=(8, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.T('Customer:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('Customer 1', 'Customer 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
sg.T('1', size=(8, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.T('Notes:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.In(size=(44, 1), background_color='white', text_color='black')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Start', button_color=('white', 'black')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Stop', button_color=('white', 'black')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Reset', button_color=('white', '#9B0023')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Submit', button_color=('white', 'springgreen4')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Exit', button_color=('white', '#00406B')),
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Time Tracker", default_element_size=(12, 1), text_justification='r', auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False, no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
default_button_element_size=(12, 1))
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# -------------------------------- GUI Starts Here -------------------------------#
|
||||
# fig = your figure you want to display. Assumption is that 'fig' holds the #
|
||||
# information to display. #
|
||||
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
fig_dict = {'Simple Data Entry':SimpleDataEntry, 'Simple Entry Return Data as Dict':SimpleReturnAsDict, 'File Browse' : FileBrowse,
|
||||
'GUI Add On':GUIAddOn, 'Compare 2 Files':Compare2Files, 'All Widgets With Context Manager':AllWidgetsWithContext, 'All Widgets No Context Manager':AllWidgetsNoContext,
|
||||
'Non-Blocking With Updates':NonBlockingWithUpdates, 'Non-Bocking With Context Manager':NonBlockingWithContext, 'Callback Simulation':CallbackSimulation,
|
||||
'Realtime Buttons':RealtimeButtons, 'Easy Progress Meter':EasyProgressMeter, 'Tabbed Form':TabbedForm, 'Media Player':MediaPlayer, 'Script Launcher':ScriptLauncher,
|
||||
'Machine Learning':MachineLearning, 'Custom Progress Meter':CustromProgressMeter, 'One Line GUI':OneLineGUI, 'Multiple Columns':MultipleColumns,
|
||||
'Persistent Form':PersistentForm, 'Canvas Widget':CanvasWidget, 'Input Element Update':InputElementUpdate,
|
||||
'Table Simulation':TableSimulation, 'Tight Layout':TightLayout}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# define the form layout
|
||||
listbox_values = [key for key in fig_dict.keys()]
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark')
|
||||
# sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_listbox = [[sg.Listbox(values=listbox_values, size=(max(len(x) for x in listbox_values),min(len(listbox_values), 20)), change_submits=False, key='func')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Run', pad=(0,0)), sg.ReadButton('Show Code', button_color=('white', 'gray25'), pad=(0,0)), sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), pad=(0,0))]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('PySimpleGUI Coookbook', font=('current 18'))],
|
||||
[sg.Column(col_listbox), sg.Multiline(size=(50,min(len(listbox_values), 20)), do_not_clear=True, key='multi')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form and show it without the plot
|
||||
# window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI', default_button_element_size=(9,1),auto_size_buttons=False, grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
choice = values['func'][0]
|
||||
func = fig_dict[choice]
|
||||
except:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'Show Code' and values['multi']:
|
||||
window.FindElement('multi').Update(inspect.getsource(func))
|
||||
elif button is 'Run' and values['func']:
|
||||
# sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('SystemDefault')
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
func()
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('ILLEGAL values')
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,6 +52,8 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ]]
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
# if you have operations on elements that must take place before the event loop, do them here
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,6 +29,9 @@ def Launcher():
|
|||
|
||||
namesonly = [f for f in os.listdir(ROOT_PATH) if f.endswith('.py') ]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(namesonly) == 0:
|
||||
namesonly = ['test 1', 'test 2', 'test 3']
|
||||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0), button_element_size=(12,1), auto_size_buttons=False)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Combo(values=namesonly, size=(35,30), key='demofile'),
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,7 +42,7 @@ def Launcher():
|
|||
sg.Button('EXIT', button_color=('white','firebrick3'))],
|
||||
[sg.T('', text_color='white', size=(50,1), key='output')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Floating Toolbar', no_titlebar=True, keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Floating Toolbar', no_titlebar=True, grab_anywhere=True, keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and executing appropriate program --- #
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ GRAPH_WIDTH = 120 # each individual graph size in pixels
|
|||
GRAPH_HEIGHT = 40
|
||||
TRANSPARENCY = .8 # how transparent the window looks. 0 = invisible, 1 = normal window
|
||||
NUM_COLS = 4
|
||||
POLL_FREQUENCY = 400 # how often to update graphs in milliseconds
|
||||
POLL_FREQUENCY = 500 # how often to update graphs in milliseconds
|
||||
|
||||
colors = ('#23a0a0', '#56d856', '#be45be', '#5681d8', '#d34545', '#BE7C29')
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0), margins=(1,1), border_width=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- Create Layout ----------------
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.RButton('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('black', 'black'), key='Exit', tooltip='Closes window'),
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Button('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('black', 'black'), key='Exit', tooltip='Closes window'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' CPU Core Usage')] ]
|
||||
|
||||
# add on the graphs
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
for i in range(num_cores):
|
||||
graphs[i].graph_percentage_abs(stats[i])
|
||||
graphs[i].text_display('{} CPU {:2.0f}'.format(i, stats[i]))
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
# the clever Red X graphic
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,8 +54,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
prev_x, prev_y = 0, 0
|
||||
while True: # the Event Loop
|
||||
time.sleep(.5)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None: # always give ths user a way out
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None: # always give ths user a way out
|
||||
break
|
||||
# do CPU measurement and graph it
|
||||
current_cpu = int(g_cpu_percent*10)
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,5 +73,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
i += STEP_SIZE if i < SAMPLES else 0
|
||||
last_cpu = current_cpu
|
||||
|
||||
g_exit = True
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,6 +54,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
window = sg.Window('CPU Utilization',
|
||||
no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
keep_on_top=True,
|
||||
alpha_channel=.8,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# start cpu measurement thread
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,9 +30,9 @@ def gui():
|
|||
sg.SetOptions(border_width=0, margins=(0, 0), element_padding=(4, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Email New Mail Notification' + 48 * ' '),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=refresh, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'), key='_refresh_',
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=refresh, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'), key='_refresh_',
|
||||
tooltip='Refreshes Email'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'), key='_quit_',
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'), key='_quit_',
|
||||
tooltip='Closes window')],
|
||||
[sg.T('', key='_status_', size=(25, 1))], ]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,8 +26,8 @@ sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='text')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Pause', key='button', button_color=('white', '#001480')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Reset', button_color=('white', '#007339'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
[sg.Button('Pause', key='button', button_color=('white', '#001480')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Reset', button_color=('white', '#007339'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), key='Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', no_titlebar=True, auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True, grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ import psutil
|
|||
|
||||
GRAPH_WIDTH = 120 # each individual graph size in pixels
|
||||
GRAPH_HEIGHT = 40
|
||||
ALPHA = .7
|
||||
|
||||
class DashGraph(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, graph_elem, starting_count, color):
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +48,7 @@ class DashGraph(object):
|
|||
self.graph_current_item += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def human_size(bytes, units=(' bytes','KB','MB','GB','TB', 'PB', 'EB')):
|
||||
def human_size(bytes, units=[' bytes','KB','MB','GB','TB', 'PB', 'EB']):
|
||||
""" Returns a human readable string reprentation of bytes"""
|
||||
return str(bytes) + units[0] if bytes < 1024 else human_size(bytes>>10, units[1:])
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,17 +64,19 @@ def main():
|
|||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0), margins=(1,1), border_width=0)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('System Status Dashboard'+' '*18), sg.RButton('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('black', 'black'), key='Exit', tooltip='Closes window')],
|
||||
[sg.Column([[Txt('Net Out ', key='_NET_OUT_'), ],
|
||||
[sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_OUT_')]], pad=(2, 2)),
|
||||
sg.Column([[Txt('Net In', key='_NET_IN_'),],
|
||||
[sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_IN_')]], pad=(0, 2))],
|
||||
[sg.Column([[Txt('Disk Read', key='_DISK_READ_')],
|
||||
[sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_DISK_READ_')]], pad=(2,2)),
|
||||
sg.Column([[Txt('Disk Write', key='_DISK_WRITE_')],
|
||||
[sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_DISK_WRITE_')]], pad=(0, 2))],
|
||||
[sg.Column([[Txt('CPU Usage', key='_CPU_USAGE_')], [sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_CPU_USAGE_')]], pad=(2,2)),
|
||||
sg.Column([[Txt('Memory Usage', key='_MEM_USAGE_')], [sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black', key='_GRAPH_MEM_USAGE_')]], pad=(2, 2))]]
|
||||
def GraphColumn(name, key):
|
||||
col = sg.Column([[Txt(name, key=key+'TXT_'), ],
|
||||
[sg.Graph((GRAPH_WIDTH, GRAPH_HEIGHT), (0, 0), (GRAPH_WIDTH, 100), background_color='black',
|
||||
key=key+'GRAPH_')]], pad=(2, 2))
|
||||
return col
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('System Status Dashboard'+' '*18), sg.Button('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('black', 'black'), key='Exit', tooltip='Closes window')],
|
||||
[GraphColumn('Net Out', '_NET_OUT_'),
|
||||
GraphColumn('Net In', '_NET_IN_')],
|
||||
[GraphColumn('Disk Read', '_DISK_READ_'),
|
||||
GraphColumn('Disk Write', '_DISK_WRITE_')],
|
||||
[GraphColumn('CPU Usage', '_CPU_'),
|
||||
GraphColumn('Memory Usage', '_MEM_')],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('PSG System Dashboard',
|
||||
keep_on_top=True,
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,22 +85,24 @@ def main():
|
|||
no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
default_button_element_size=(12, 1),
|
||||
return_keyboard_events=True,
|
||||
alpha_channel=.9,
|
||||
alpha_channel=ALPHA,
|
||||
use_default_focus=False,
|
||||
).Layout(layout)
|
||||
).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
# setup graphs & initial values
|
||||
netio = psutil.net_io_counters()
|
||||
net_graph_in = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_IN_'), netio.bytes_recv, '#23a0a0')
|
||||
net_graph_out = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_OUT_'), netio.bytes_sent, '#56d856')
|
||||
net_graph_in = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_NET_IN_GRAPH_'), netio.bytes_recv, '#23a0a0')
|
||||
net_graph_out = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_NET_OUT_GRAPH_'), netio.bytes_sent, '#56d856')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
diskio = psutil.disk_io_counters()
|
||||
disk_graph_write = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_DISK_WRITE_'), diskio.write_bytes, '#be45be')
|
||||
disk_graph_read = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_DISK_READ_'), diskio.read_bytes, '#5681d8')
|
||||
disk_graph_write = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_DISK_WRITE_GRAPH_'), diskio.write_bytes, '#be45be')
|
||||
disk_graph_read = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_DISK_READ_GRAPH_'), diskio.read_bytes, '#5681d8')
|
||||
|
||||
cpu_usage_graph = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_CPU_USAGE_'), 0, '#d34545')
|
||||
mem_usage_graph = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_GRAPH_MEM_USAGE_'), 0, '#BE7C29')
|
||||
cpu_usage_graph = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_CPU_GRAPH_'), 0, '#d34545')
|
||||
mem_usage_graph = DashGraph(window.FindElement('_MEM_GRAPH_'), 0, '#BE7C29')
|
||||
|
||||
print(psutil.cpu_percent(percpu=True))
|
||||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window once a second--------
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,22 +113,22 @@ def main():
|
|||
netio = psutil.net_io_counters()
|
||||
write_bytes = net_graph_out.graph_value(netio.bytes_sent)
|
||||
read_bytes = net_graph_in.graph_value(netio.bytes_recv)
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_NET_OUT_', 'Net out {}'.format(human_size(write_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_NET_IN_', 'Net In {}'.format(human_size(read_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_NET_OUT_TXT_', 'Net out {}'.format(human_size(write_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_NET_IN_TXT_', 'Net In {}'.format(human_size(read_bytes)))
|
||||
# ----- Disk Graphs -----
|
||||
diskio = psutil.disk_io_counters()
|
||||
write_bytes = disk_graph_write.graph_value(diskio.write_bytes)
|
||||
read_bytes = disk_graph_read.graph_value(diskio.read_bytes)
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_DISK_WRITE_', 'Disk Write {}'.format(human_size(write_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_DISK_READ_', 'Disk Read {}'.format(human_size(read_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_DISK_WRITE_TXT_', 'Disk Write {}'.format(human_size(write_bytes)))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_DISK_READ_TXT_', 'Disk Read {}'.format(human_size(read_bytes)))
|
||||
# ----- CPU Graph -----
|
||||
cpu = psutil.cpu_percent(0)
|
||||
cpu_usage_graph.graph_percentage_abs(cpu)
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_CPU_USAGE_', '{0:2.0f}% CPU Used'.format(cpu))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_CPU_TXT_', '{0:2.0f}% CPU Used'.format(cpu))
|
||||
# ----- Memory Graph -----
|
||||
mem_used = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
|
||||
mem_usage_graph.graph_percentage_abs(mem_used)
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_MEM_USAGE_', '{}% Memory Used'.format(mem_used))
|
||||
Txt_Update(window, '_MEM_TXT_', '{}% Memory Used'.format(mem_used))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
# the clever Red X graphic
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ for key in key_list: window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=True) # don't do
|
|||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
if event in (None, 'exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Disable':
|
||||
for key in key_list: window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,8 +54,8 @@ def FindDuplicatesFilesInFolder(path):
|
|||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
|
||||
source_folder = None
|
||||
rc, source_folder = sg.PopupGetFolder('Duplicate Finder - Count number of duplicate files', 'Enter path to folder you wish to find duplicates in')
|
||||
if rc is True and source_folder is not None:
|
||||
source_folder = sg.PopupGetFolder('Duplicate Finder - Count number of duplicate files', 'Enter path to folder you wish to find duplicates in')
|
||||
if source_folder is not None:
|
||||
FindDuplicatesFilesInFolder(source_folder)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sg.PopupCancel('Cancelling', '*** Cancelling ***')
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -52,10 +52,10 @@ def ShowMeTheButtons():
|
|||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(auto_size_buttons=True, margins=(0,0), button_color=sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT)
|
||||
|
||||
toolbar_buttons = [[sg.RButton('', image_data=get_image_bytes(close64),button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0,0), key='_close_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=get_image_bytes(timer64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0, 0), key='_timer_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=get_image_bytes(house64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0, 0), key='_house_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=get_image_bytes(cpu64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0,0), key='_cpu_'),]]
|
||||
toolbar_buttons = [[sg.Button('', image_data=get_image_bytes(close64),button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0,0), key='_close_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=get_image_bytes(timer64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0, 0), key='_timer_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=get_image_bytes(house64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0, 0), key='_house_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=get_image_bytes(cpu64), button_color=('white', 'black'), pad=(0,0), key='_cpu_'),]]
|
||||
|
||||
# layout = toolbar_buttons
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Frame('Launcher', toolbar_buttons,title_color='white', background_color='black')]]
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ fonts = list(font.families())
|
|||
fonts.sort()
|
||||
root.destroy()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark')
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My Text Element',
|
||||
size=(20,1),
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My Text Element',
|
|||
click_submits=True,
|
||||
relief=sg.RELIEF_GROOVE,
|
||||
font = 'Courier` 25',
|
||||
text_color='red',
|
||||
text_color='#FF0000',
|
||||
background_color='white',
|
||||
justification='center',
|
||||
pad=(5,3),
|
||||
|
|
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My Text Element',
|
|||
) ],
|
||||
[sg.Listbox(fonts, size=(30,20), change_submits=True, key='_list_')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='_in_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read', bind_return_key=True), sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read', bind_return_key=True), sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window',
|
||||
# grab_anywhere=True,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('This is my sample text',size=(20,1), key='_text_') ],
|
|||
[sg.Slider((6,50), default_value=12, size=(14,20), orientation='h', key='_slider_', change_submits=True),
|
||||
sg.Text('Font size')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Font string = '), sg.Text('', size=(25,1), key='_fontstring_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Exit')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Font string builder').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Filename', )],
|
||||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
event, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(
|
||||
[[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ import os
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('What would you like me to say?')],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline(size=(60,10), enter_submits=True)],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Speak', bind_return_key=True), sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Speak', bind_return_key=True), sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Google Text to Speech').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -43,10 +43,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
i=0
|
||||
prev_x, prev_y = 0, 0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=200)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if g_response_time is None or prev_response_time == g_response_time:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [ [sg.Quit( button_color=('white','black'))],
|
||||
layout = [ [sg.Button('Quit', button_color=('white','black'))],
|
||||
[sg.Graph(CANVAS_SIZE, (0,0), (SAMPLES,SAMPLE_MAX),background_color='black', key='graph')],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Canvas test', grab_anywhere=True, background_color='black', no_titlebar=False, use_default_focus=False).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,9 +45,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
graph_value = 250
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
graph_offset = random.randint(-10, 10)
|
||||
graph_value = graph_value + graph_offset
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,15 +11,15 @@ layout = [[sg.Text("Hold down a key")],
|
|||
window = sg.Window("Realtime Keyboard Test", return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_focus=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
|
||||
if event == "OK":
|
||||
print(event, values, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
if event is not sg.TIMEOUT_KEY:
|
||||
if len(event) == 1:
|
||||
print('%s - %s' % (event, ord(event)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
elif values is None:
|
||||
elif event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ else:
|
|||
# Demonstrates a number of PySimpleGUI features including:
|
||||
# Default element size
|
||||
# auto_size_buttons
|
||||
# ReadButton
|
||||
# Button
|
||||
# Dictionary return values
|
||||
# Update of elements in form (Text, Input)
|
||||
# do_not_clear of Input elements
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,10 +17,10 @@ else:
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Enter Your Passcode')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(size=(10, 1), do_not_clear=True, key='input')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('1'), sg.ReadButton('2'), sg.ReadButton('3')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('4'), sg.ReadButton('5'), sg.ReadButton('6')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('7'), sg.ReadButton('8'), sg.ReadButton('9')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Submit'), sg.ReadButton('0'), sg.ReadButton('Clear')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('1'), sg.Button('2'), sg.Button('3')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('4'), sg.Button('5'), sg.Button('6')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('7'), sg.Button('8'), sg.Button('9')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Submit'), sg.Button('0'), sg.Button('Clear')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 1), font=('Helvetica', 18), text_color='red', key='out')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ class GUI():
|
|||
layout = [[sg.Column(clock, background_color='black')],
|
||||
[sg.Column(weather_cols[x], background_color='black') for x in range(NUM_COLS)],
|
||||
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Exit', button_color=('black', 'black'),
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit', button_color=('black', 'black'),
|
||||
image_data=orangeround[22:], tooltip='close window', pad=((450,0),(10,0)))]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the window
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('My LED Status Indicators', size=(20,1))],
|
|||
[sg.Text('RAM'), LEDIndicator('_ram_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Temperature'), LEDIndicator('_temp_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Server 1'), LEDIndicator('_server1_')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Exit')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window', default_element_size=(12, 1), auto_size_text=False).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -66,14 +66,14 @@ class PlayerGUI():
|
|||
[sg.T('MIDI File Player', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[self.TextElem],
|
||||
[self.SliderElem],
|
||||
[sg.ReadFormButton('PAUSE', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('NEXT', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Restart Song', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, )]
|
||||
[sg.Button('', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='PAUSE'), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='NEXT'), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Restart Song'), sg.T(' '),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=sg.TRANSPARENT_BUTTON,
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50,50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0,key='EXIT')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('MIDI File Player', default_element_size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25)).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,8 +90,8 @@ class PlayerGUI():
|
|||
if 'window' not in locals() or window is None: # if the widnow has been destoyed don't mess with it
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_EXIT
|
||||
self.TextElem.Update(DisplayString)
|
||||
event, (values) = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None:
|
||||
event, (values) = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_EXIT
|
||||
if event == 'PAUSE':
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_PAUSE
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -43,17 +43,17 @@ def MachineLearningGUI():
|
|||
def CustomMeter():
|
||||
# layout the form
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(10000, orientation='h', size=(20,20), key='progress')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(1000, orientation='h', size=(20,20), key='progress')],
|
||||
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form`
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Custom Progress Meter').Layout(layout)
|
||||
progress_bar = window.FindElement('progress')
|
||||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
for i in range(1000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or event == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,8 +36,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
|
||||
dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10)
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
slider_elem.Update(i)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,8 +26,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
canvas = canvas_elem.TKCanvas
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10)
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
def PyplotScatterWithLegend():
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -646,7 +646,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
global g_my_globals
|
||||
|
||||
# define the form layout
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Canvas(size=SIZE, background_color='white',key='canvas') , sg.ReadButton('Exit', pad=(0, (210, 0)))]]
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Canvas(size=SIZE, background_color='white',key='canvas') , sg.Button('Exit', pad=(0, (210, 0)))]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Ping Graph', background_color='white', grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
|
@ -662,8 +662,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
|
||||
run_a_ping_and_graph()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
# define the form layout
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Animated Ping', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(640, 480), key='canvas')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((280, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((280, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,8 +96,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
run_a_ping_and_graph()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,17 +27,16 @@ def MediaPlayerGUI():
|
|||
# define layout of the rows
|
||||
layout= [[sg.Text('Media File Player',size=(17,1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 2), font=("Helvetica", 14), key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Restart Song', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
[sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Restart Song'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Pause', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Pause'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Next', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background), image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Next'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.Button('Exit', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0)],
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Exit')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_'*20)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(' '*30)],
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,15 +52,14 @@ def MediaPlayerGUI():
|
|||
|
||||
# Open a form, note that context manager can't be used generally speaking for async forms
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Media File Player', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(20, 1),
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 25), no_titlebar=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 25)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while(True):
|
||||
# Read the form (this call will not block)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=100) # Poll every 100 ms
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if event:
|
||||
if event != sg.TIMEOUT_KEY:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
MediaPlayerGUI()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,18 +15,18 @@ def ShowMeTheButtons():
|
|||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(auto_size_buttons=True, margins=(0,0), button_color=sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT)
|
||||
|
||||
toolbar_buttons = [[sg.RButton('', image_data=close64[22:],button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0,0), key='_close_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=timer64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_timer_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=house64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_house_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=cpu64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_cpu_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=camera64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_camera_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=checkmark64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_checkmark_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=cookbook64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_cookbook_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=download64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_download_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=github64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_github_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=psg64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_psg_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=run64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_run_'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('', image_data=storage64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_storage_'),
|
||||
toolbar_buttons = [[sg.Button('', image_data=close64[22:],button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0,0), key='_close_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=timer64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_timer_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=house64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_house_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=cpu64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_cpu_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=camera64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_camera_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=checkmark64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_checkmark_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=cookbook64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_cookbook_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=download64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_download_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=github64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_github_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=psg64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_psg_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=run64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_run_'),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=storage64[22:], button_color=('white', sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT), pad=(0, 0), key='_storage_'),
|
||||
]]
|
||||
|
||||
# layout = toolbar_buttons
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,13 +33,16 @@ def TestMenus():
|
|||
|
||||
# ------ GUI Defintion ------ #
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Menu(menu_def, tearoff=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Menu(menu_def, tearoff=False, pad=(20,1))],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(60,20))],
|
||||
[sg.In('Test', key='input', do_not_clear=True)]
|
||||
[sg.Text('Status Bar', relief=sg.RELIEF_SUNKEN, size=(55,1), pad=(0,3),key='_status_')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Windows-like program", default_element_size=(12, 1), auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False, default_button_element_size=(12, 1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Windows-like program",
|
||||
default_element_size=(12, 1),
|
||||
auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False,
|
||||
default_button_element_size=(12, 1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# ------ Loop & Process button menu choices ------ #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,9 +52,9 @@ def TestMenus():
|
|||
print('Event = ', event)
|
||||
# ------ Process menu choices ------ #
|
||||
if event == 'About...':
|
||||
# window.Hide()
|
||||
window.Disappear()
|
||||
sg.Popup('About this program','Version 1.0', 'PySimpleGUI rocks...', grab_anywhere=True)
|
||||
# window.UnHide()
|
||||
window.Reappear()
|
||||
elif event == 'Open':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('file to open', no_window=True)
|
||||
print(filename)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,27 +7,27 @@ else:
|
|||
|
||||
layout1 = [[ sg.Text('Window 1') ],
|
||||
[sg.Input(do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window1 = sg.Window('My new window', location=(800,500)).Layout(layout1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
layout2 = [[ sg.Text('Window 2') ],
|
||||
[sg.Input(do_not_clear=False)],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[sg.Input(do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window2 = sg.Window('My new window', location=(800, 625)).Layout(layout2)
|
||||
window2 = sg.Window('My new window', location=(800, 625), return_keyboard_events=True).Layout(layout2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
layout3 = [[ sg.Text('Window 3') ],
|
||||
[sg.Input(do_not_clear=False)],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window3 = sg.Window('My new window', location=(800,750), return_keyboard_events=True).Layout(layout3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window1.Read(timeout=100)
|
||||
event, values = window1.Read(timeout=50)
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event != '__timeout__':
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,22 +13,22 @@ def StatusOutputExample():
|
|||
# Create the rows
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Non-blocking GUI with updates')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('LED On'), sg.ReadButton('LED Off'), sg.ReadButton('Quit')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('LED On'), sg.Button('LED Off'), sg.Button('Quit')]]
|
||||
# Layout the rows of the Window and perform a read. Indicate the Window is non-blocking!
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# You need to perform a Read on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10)
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == 'LED On':
|
||||
print('Turning on the LED')
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,10 +37,9 @@ def StatusOutputExample():
|
|||
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
# Your code begins here
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
# Broke out of main loop. Close the window.
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def RemoteControlExample():
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,14 +62,13 @@ def RemoteControlExample():
|
|||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if event is not 'timeout':
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ bcolor=('black', '#282923')
|
|||
sg.SetOptions(border_width=0, margins=(0,0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Notification'+' '*14),
|
||||
sg.Button('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'))],
|
||||
sg.CloseButton('', image_data=red_x, button_color=('#282923', '#282923'))],
|
||||
[sg.T('')],
|
||||
[sg.T('You have 6 new emails')],]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
layout = [[sg.Text('OpenCV Demo', size=(15, 1),pad=((510,0),3), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename='', key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.Slider(range=(0, num_frames), size=(115, 10), orientation='h', key='slider')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((600, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((600, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - OpenCV Integration', no_titlebar=False, location=(0,0)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,8 +40,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
# ---===--- LOOP through video file by frame --- #
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
while vidFile.isOpened():
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
ret, frame = vidFile.read()
|
||||
if not ret: # if out of data stop looping
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from sys import exit as exit
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,57 +21,68 @@ blur: simple Gaussian blur, slider sets the sigma, i.e. the amount of blur
|
|||
hue: moves the image hue values by the amount selected on the slider
|
||||
enhance: applies local contrast enhancement on the luma channel to make the image fancier - slider controls fanciness.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('LightGreen')
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('LightGreen')
|
||||
# define the window layout
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('OpenCV Demo', size=(40, 1), justification='center')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename='', key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('None', 'Radio', True, size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('threshold', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='thresh'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(40, 15), key='thresh_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('canny', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='canny'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='canny_slider_a'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='canny_slider_b')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('contour', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='contour'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='contour_slider'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 255), 80, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='base_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('blur', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='blur'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((1, 11), 1, 1, orientation='h', size=(40, 15), key='blur_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('hue', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='hue'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((0, 225), 0, 1, orientation='h', size=(40, 15), key='hue_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('enhance', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='enhance'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((1, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(40, 15), key='enhance_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit', size=(10, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
# define the window layout
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('OpenCV Demo', size=(40, 1), justification='center')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename='', key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('None', 'Radio', True, size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('threshold', 'Radio', size=(10, 1),key='thresh'),sg.Slider((0,255),128,1,orientation='h', size=(40, 15),key='thresh_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('canny', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='canny'),sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='canny_slider_a'),sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='canny_slider_b')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('contour', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='contour'),sg.Slider((0, 255), 128, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='contour_slider'),sg.Slider((0, 255), 80, 1, orientation='h', size=(20, 15), key='base_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('blur', 'Radio', size=(10, 1),key='blur'),sg.Slider((1,11),1,1,orientation='h', size=(40, 15),key='blur_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('hue', 'Radio', size=(10, 1), key='hue'),sg.Slider((0, 225), 0, 1, orientation='h', size=(40, 15), key='hue_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('enhance', 'Radio', size=(10, 1),key='enhance'),sg.Slider((1,255),128,1,orientation='h', size=(40, 15),key='enhance_slider')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 1))]]
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - OpenCV Integration',
|
||||
location=(800, 400))
|
||||
window.Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - OpenCV Integration',
|
||||
location=(800,400))
|
||||
window.Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
ret, frame = cap.read()
|
||||
if values['thresh']:
|
||||
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)[:, :, 0]
|
||||
_, frame = cv2.threshold(frame, values['thresh_slider'], 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
|
||||
if values['canny']:
|
||||
frame = cv2.Canny(frame, values['canny_slider_a'], values['canny_slider_b'])
|
||||
if values['blur']:
|
||||
frame = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (21, 21), values['blur_slider'])
|
||||
if values['hue']:
|
||||
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
|
||||
frame[:, :, 0] += values['hue_slider']
|
||||
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
|
||||
if values['enhance']:
|
||||
enh_val = values['enhance_slider'] / 40
|
||||
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=enh_val, tileGridSize=(8, 8))
|
||||
lab = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
|
||||
lab[:, :, 0] = clahe.apply(lab[:, :, 0])
|
||||
frame = cv2.cvtColor(lab, cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)
|
||||
if values['contour']:
|
||||
hue = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
|
||||
hue = cv2.GaussianBlur(hue, (21, 21), 1)
|
||||
hue = cv2.inRange(hue, np.array([values['contour_slider'], values['base_slider'], 40]),
|
||||
np.array([values['contour_slider'] + 30, 255, 220]))
|
||||
_, cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(hue, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
cv2.drawContours(frame, cnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
|
||||
imgbytes = cv2.imencode('.png', frame)[1].tobytes() # ditto
|
||||
window.FindElement('image').Update(data=imgbytes)
|
||||
|
||||
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
ret, frame = cap.read()
|
||||
if values['thresh']:
|
||||
frame=cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)[:,:,0]
|
||||
_,frame=cv2.threshold(frame,values['thresh_slider'],255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
|
||||
if values['canny']:
|
||||
frame=cv2.Canny(frame,values['canny_slider_a'],values['canny_slider_b'])
|
||||
if values['blur']:
|
||||
frame=cv2.GaussianBlur(frame,(21,21),values['blur_slider'])
|
||||
if values['hue']:
|
||||
frame=cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
|
||||
frame[:,:,0]+=values['hue_slider']
|
||||
frame=cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
|
||||
if values['enhance']:
|
||||
enh_val=values['enhance_slider']/40
|
||||
clahe=cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=enh_val, tileGridSize=(8,8))
|
||||
lab=cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
|
||||
lab[:,:,0]=clahe.apply(lab[:,:,0])
|
||||
frame=cv2.cvtColor(lab,cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)
|
||||
if values['contour']:
|
||||
hue=cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
|
||||
hue=cv2.GaussianBlur(hue,(21,21),1)
|
||||
hue=cv2.inRange(hue,np.array([values['contour_slider'],values['base_slider'],40]),np.array([values['contour_slider']+30,255,220]))
|
||||
_,cnts,_=cv2.findContours(hue,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
cv2.drawContours(frame,cnts,-1,(0,0,255),2)
|
||||
imgbytes=cv2.imencode('.png', frame)[1].tobytes() #ditto
|
||||
window.FindElement('image').Update(data=imgbytes)
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,10 +18,10 @@ def main():
|
|||
# define the window layout
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('OpenCV Demo', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename='', key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Record', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('Stop', size=(10, 1), font='Any 14'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('About', size=(10,1), font='Any 14')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Record', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Stop', size=(10, 1), font='Any 14'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Exit', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.Button('About', size=(10,1), font='Any 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - OpenCV Integration',
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,9 +32,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
elif event == 'Record':
|
||||
recording = True
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,3 +55,4 @@ def main():
|
|||
window.FindElement('image').Update(data=imgbytes)
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
exit()
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,8 +44,8 @@ from binascii import hexlify
|
|||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
rc, fname = sg.PopupGetFile('PDF Browser', 'PDF file to open', file_types=(("PDF Files", "*.pdf"),))
|
||||
if rc is False:
|
||||
fname = sg.PopupGetFile('PDF Browser', 'PDF file to open', file_types=(("PDF Files", "*.pdf"),))
|
||||
if fname is None:
|
||||
sg.PopupCancel('Cancelling')
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,17 +99,17 @@ goto = sg.InputText(str(cur_page + 1), size=(5, 1), do_not_clear=True)
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Next'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Prev'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Prev'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Next'),
|
||||
sg.Text('Page:'),
|
||||
goto,
|
||||
],
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.Text("Zoom:"),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Top-L'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Top-R'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Bot-L'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Bot-R'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Top-L'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Top-R'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Bot-L'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Bot-R'),
|
||||
],
|
||||
[image_elem],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,13 +124,11 @@ old_zoom = 0 # used for zoom on/off
|
|||
# the zoom buttons work in on/off mode.
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=100)
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = False
|
||||
if event is None and values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if event in ("Escape:27",): # this spares me a 'Quit' button!
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ buttons = []
|
|||
for display_index in range(ROWS):
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
for j in range(COLUMNS):
|
||||
row.append(sg.RButton('',border_width=0,button_color=sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT, key=(display_index, j)))
|
||||
row.append(sg.Button('',border_width=0,button_color=sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT, key=(display_index, j)))
|
||||
buttons.append(row)
|
||||
|
||||
col_buttons = [[]]
|
||||
|
|
@ -117,12 +117,6 @@ while True:
|
|||
for j in range(ROWS):
|
||||
for i in range(COLUMNS):
|
||||
set_image_to_blank((i,j))
|
||||
# img = Image.new('RGB', (1,1), (255,255,255))
|
||||
# img.thumbnail((1,1), Image.ANTIALIAS)
|
||||
# bio = io.BytesIO()
|
||||
# img.save(bio, format='PNG')
|
||||
# imgbytes = bio.getvalue()
|
||||
# [window.FindElement((i,j)).Update(image_data=imgbytes) for j in range(ROWS) for i in range(COLUMNS)]
|
||||
elif event == 'About':
|
||||
sg.Popup('Demo PNG Viewer Program', 'Please give PySimpleGUI a try!')
|
||||
elif type(event) is tuple:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ menu = [['File', ['Open Folder', 'Exit']], ['Help', ['About',]]]
|
|||
# define layout, show and read the window
|
||||
col = [[sg.Text(png_files[0], size=(80, 3), key='filename')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename=png_files[0], key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Next', size=(8,2)), sg.ReadButton('Prev', size=(8,2)),
|
||||
[sg.Button('Next', size=(8,2)), sg.Button('Prev', size=(8,2)),
|
||||
sg.Text('File 1 of {}'.format(len(png_files)), size=(15,1), key='filenum')]]
|
||||
|
||||
col_files = [[sg.Listbox(values=filenames_only, size=(60,30), key='listbox')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Menu(menu)], [sg.Column(col_files), sg.Column(col)]]
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Image Browser', return_keyboard_events=True, location=(0,0), use_default_focus=False ).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -376,9 +376,77 @@ Window( title
|
|||
text_justification=None
|
||||
no_titlebar=False
|
||||
grab_anywhere=False
|
||||
keep_on_top=False)
|
||||
keep_on_top=False
|
||||
resizable=False)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
desc_window_methods = """
|
||||
Layout(rows)
|
||||
Call to set the window layout. Must be called prior to Read. Most likely "chained" in line with the Window creation.
|
||||
|
||||
Finalize()
|
||||
Call to force a window to go through the final stages of initialization. This will cause the tkinter resources to be allocated so that they can then be modified.
|
||||
|
||||
Read()
|
||||
Read the Window's input values and button clicks in a blocking-fashion
|
||||
Returns event, values
|
||||
|
||||
ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
Read the Window's input values and button clicks but without blocking. It will immediately return.
|
||||
|
||||
Refresh()
|
||||
Cause changes to the window to be displayed on the screen. Normally not needed unless the changes are immediately required or if it's going to be a while before another call to Read.
|
||||
|
||||
SetIcon(icon)
|
||||
Sets the window's icon that will be shown on the titlebar.
|
||||
|
||||
Fill(values_dict)
|
||||
Populates the windows fields with the values shown in the dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
FindElement(key)
|
||||
Rerturns the Element that has a matching key. If the key is not found, an Error Element is returned so that the program will not crash should the user try to perform an "update". A Popup message will be shown
|
||||
|
||||
SaveToDisk(filename)
|
||||
Saves the window's values to disk
|
||||
|
||||
LoadFromDisk(filename)
|
||||
Fills in a window's fields based on previously saved file
|
||||
|
||||
GetScreenDimensions()
|
||||
Returns the size (w,h) of the screen in pixels
|
||||
|
||||
Move(x, y)
|
||||
Move window to (x,y) position on the screen
|
||||
|
||||
Minimize()
|
||||
Sends the window to the taskbar
|
||||
|
||||
CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
Closes a non-blocking window
|
||||
|
||||
Disable()
|
||||
Stops a window from responding until Enable is called
|
||||
|
||||
Enable()
|
||||
Re-enables a previously disabled window
|
||||
|
||||
Hide()
|
||||
Completely hides a window, including removing from the taskbar
|
||||
|
||||
UnHide()
|
||||
Restores a window hidden using Hide
|
||||
|
||||
Disappear()
|
||||
Makes a window disappear while leaving the icon on the taskbar
|
||||
|
||||
Reappear()
|
||||
Makes a window reappear that was previously made to disappear using Disappear()
|
||||
|
||||
SetAlpha(alpha)
|
||||
Sets the window's transparency. 0 is completely transparent. 1 is fully visible, normal
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
desc_menu= """
|
||||
Menu(menu_definition
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -390,8 +458,8 @@ desc_menu= """
|
|||
|
||||
desc_button_types = """
|
||||
There are multiple button types / names to choose from
|
||||
SimpleButton = Button
|
||||
ReadFormButton = ReadButton = RButton
|
||||
CloseButton = CButton = SimpleButton
|
||||
Button = ReadFormButton = ReadButton = RButton
|
||||
RealtimeButton
|
||||
DummyButton
|
||||
FolderBrowse
|
||||
|
|
@ -501,7 +569,7 @@ tab_multiline = [[sg.Column([[sg.Multiline(size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_multiline
|
|||
tab_output= [[sg.Column([[sg.Text(desc_output, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_progressbar = [[sg.Column([[sg.Text(desc_progressbar, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_optionmenu = [[sg.Column([[sg.OptionMenu([1,2,3,4,5], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_inputoptionmenu, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_combo = [[sg.Column([[sg.Combo([1,2,3,4,5], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_inputoptionmenu, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_combo = [[sg.Column([[sg.Combo([1,2,3,4,5], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_inputcombo, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_frame = [[sg.Column([[sg.Frame('Frame',[[sg.T(' ')]], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_frame, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_column = [[sg.Text(desc_column, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_graph = [[sg.Text(desc_graph, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
|
|
@ -511,11 +579,14 @@ tab_image = [[sg.Text(desc_image, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
|||
tab_table = [[sg.Text(desc_table, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_tree = [[sg.Text(desc_tree, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_menu = [[sg.Text(desc_menu, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_button = [[sg.Text(desc_button, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_button_types = [[sg.Text(desc_button_types, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_popup = [[sg.Text(desc_popup, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_popups = [[sg.Text(desc_popups, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_one_line_prog_meter = [[sg.Text(desc_one_line_progress_meter, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_window = [[sg.Text(desc_window, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
tab_window = [[ sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Parms',[[sg.Text(desc_window, font=('Consolas 12'))]]),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Methods', [[sg.Column([[sg.Text(desc_window_methods)]], size=(500,500), scrollable=True, )]])]])]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Window',tab_window),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Text',tab_text),
|
||||
|
|
@ -539,6 +610,7 @@ layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Window',tab_window),
|
|||
sg.Tab('Tab', tab_tab),
|
||||
sg.Tab('TabGroup', tab_tabgroup),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Menu', tab_menu),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Button', tab_button),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Button Types', tab_button_types),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Popup', tab_popup),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Popups', tab_popups),
|
||||
|
|
@ -551,17 +623,20 @@ layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Window',tab_window),
|
|||
# sg.Text(desc_text, size=(55, 25), font=('Consolas 13'), text_color='darkblue', key='_out_')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('PySimpleGUI SDK Quick Reference',
|
||||
font='Any 12',
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
font='Consolas 12',
|
||||
).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
element = values['_in_'][0]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
desc = descriptions[element]
|
||||
except:
|
||||
desc = ''
|
||||
window.FindElement('_out_').Update(desc)
|
||||
if event == 'Methods':
|
||||
sg.PopupScrolled(desc_window_methods, size=(50,20))
|
||||
# element = values['_in_'][0]
|
||||
# try:
|
||||
# desc = descriptions[element]
|
||||
# except:
|
||||
# desc = ''
|
||||
# window.FindElement('_out_').Update(desc)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(button, values)
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,8 +34,8 @@ def FlashLED():
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Raspberry Pi LEDs')],
|
||||
[sg.T('', size=(14, 1), key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Switch LED')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Flash LED')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Switch LED')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Flash LED')],
|
||||
[sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Raspberry Pi GUI', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,8 +49,9 @@ while True:
|
|||
window.FindElement('output').Update(SwitchLED())
|
||||
elif event is 'Flash LED':
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('LED is Flashing')
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Refresh()
|
||||
FlashLED()
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('')
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
sg.Popup('Done... exiting')
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,9 +24,10 @@ def RemoteControlExample():
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Robotics Remote Control')],
|
||||
[sg.T('', justification='center', size=(19,1), key='status')],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('Forward', image_filename=image_forward, pad=((50,0),0))],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('Left', image_filename=image_left), sg.RealtimeButton('Right', image_filename=image_right, pad=((50,0), 0))],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('Reverse', image_filename=image_backward, pad=((50,0),0))],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('', key='Forward', image_filename=image_forward, pad=((50,0),0))],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('', key='Left', image_filename=image_left),
|
||||
sg.RealtimeButton('', key='Right', image_filename=image_right, pad=((50,0), 0))],
|
||||
[ sg.RealtimeButton('', key='Reverse', image_filename=image_backward, pad=((50,0),0))],
|
||||
[sg.T('')],
|
||||
[sg.Quit(button_color=('black', 'orange'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,16 +41,16 @@ def RemoteControlExample():
|
|||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(event)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
elif event != 'timeout':
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update('')
|
||||
# if user clicked quit button OR closed the form using the X, then break out of loop
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def RemoteControlExample_NoGraphics():
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,25 +68,26 @@ def RemoteControlExample_NoGraphics():
|
|||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your form every now and then or
|
||||
# You need to perform a Read on your form every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
# Notice how the timeout is 100ms. You don't have to use a timeout = 0 for all of your hardware
|
||||
# applications. Leave some CPU for other threads or for your GUI. The longer you are in the GUI, the more
|
||||
# responsive the GUI itself will be Match your timeout with your hardware's capabilities
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=100, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
# print(event, values)
|
||||
if event != 'timeout':
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(event)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update('')
|
||||
# if user clicked quit button OR closed the form using the X, then break out of loop
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Quit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------------------------------- main -------------------------------------
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -638,8 +638,8 @@ prev_x, prev_y = canvas_left, canvas_bottom
|
|||
while True:
|
||||
time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if g_response_time is None or prev_response_time == g_response_time:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ class pongbat2():
|
|||
def pong():
|
||||
# ------------- Define GUI layout -------------
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Canvas(size=(700, 400), background_color='black', key='canvas')],
|
||||
[sg.T(''), sg.ReadButton('Quit')]]
|
||||
[sg.T(''), sg.Button('Quit')]]
|
||||
# ------------- Create window -------------
|
||||
window = sg.Window('The Classic Game of Pong', return_keyboard_events=True).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
# window.Finalize() # TODO Replace with call to window.Finalize once code released
|
||||
|
|
@ -155,9 +155,9 @@ def pong():
|
|||
bat2.draw()
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------- Read the form, get keypresses -------------
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
# ------------- If quit -------------
|
||||
if event is None and values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
# ------------- Keypresses -------------
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,10 +20,10 @@ else:
|
|||
|
||||
def PopupDropDown(title, text, values):
|
||||
window = sg.Window(title).Layout([[sg.Text(text)],
|
||||
[sg.DropDown(values, key='_drop')],
|
||||
[sg.DropDown(values, key='_DROP_')],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
return None if event != 'OK' else values['_drop']
|
||||
return None if event != 'OK' else values['_DROP_']
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------------------- Calling your PopupDropDown function -----------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ from PySimpleGUI import Print as print
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
print('test')
|
||||
sg.PopupGetFile('Get file', save_as=True,file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.jpg")))
|
||||
sg.PopupGetFile('Get file', save_as=True,file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.jpg"),))
|
||||
|
||||
# Here, have some windows on me....
|
||||
[sg.PopupNoWait('No-wait Popup', location=(500+100*x,500)) for x in range(10)]
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ def DemoOneLineProgressMeter():
|
|||
sg.T('Delay'), sg.In(default_text='10', key='TimeOuter', size=(5,1), do_not_clear=True), sg.T('ms')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Inner Loop Count', size=(15,1), justification='r'), sg.In(default_text='100', size=(5,1), key='CountInner', do_not_clear=True) ,
|
||||
sg.T('Delay'), sg.In(default_text='10', key='TimeInner', size=(5,1), do_not_clear=True), sg.T('ms')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Show', pad=((0,0), 3), bind_return_key=True), sg.T('me the meters!')]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Show', pad=((0,0), 3), bind_return_key=True), sg.T('me the meters!')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('One-Line Progress Meter Demo').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,22 +68,22 @@ def DemoOneLineProgressMeter():
|
|||
def CustomMeter():
|
||||
# layout the form
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(10000, orientation='h', size=(20,20), key='progress')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(1000, orientation='h', size=(20,20), key='progress')],
|
||||
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the form`
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Custom Progress Meter').Layout(layout)
|
||||
progress_bar = window.FindElement('progress')
|
||||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
for i in range(1000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or event == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
||||
# done with loop... need to destroy the window as it's still open
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
CustomMeter()
|
||||
DemoOneLineProgressMeter()
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ def Launcher2():
|
|||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Listbox(values=namesonly, size=(30, 19), select_mode=sg.SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED, key='demolist'), sg.Output(size=(88, 20), font='Courier 10')],
|
||||
[sg.Checkbox('Wait for program to complete', default=False, key='wait')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Run'), sg.ReadButton('Shortcut 1'), sg.ReadButton('Fav Program'), sg.Button('EXIT')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Run'), sg.Button('Shortcut 1'), sg.Button('Fav Program'), sg.Button('EXIT')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,9 +19,9 @@ stores the result in the variable fname, just like the command line parsing did.
|
|||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
event, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').LayoutAndRead([[sg.T('Document to open')],
|
||||
event, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').Layout([[sg.T('Document to open')],
|
||||
[sg.In(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Open(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
[sg.CloseButton('Open'), sg.CloseButton('Cancel')]]).Read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fname = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,9 +11,9 @@ else:
|
|||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0))
|
||||
# sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark')
|
||||
# --- Define our "Big-Button-Spinner" compound element. Has 2 buttons and an input field --- #
|
||||
NewSpinner = [sg.ReadButton('-', size=(2,1), font='Any 12'),
|
||||
NewSpinner = [sg.Button('-', size=(2,1), font='Any 12'),
|
||||
sg.In('0', size=(2,1), font='Any 14', justification='r', key='spin'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('+', size=(2,1), font='Any 12')]
|
||||
sg.Button('+', size=(2,1), font='Any 12')]
|
||||
# --- Define Window --- #
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Spinner simulation')],
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,10 +11,10 @@ else:
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='name')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='name'), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('2', key='address')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('3', key='phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
[sg.CloseButton('Submit'), sg.CloseButton('Cancel')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple Data Entry Window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -28,16 +28,14 @@ def table_example():
|
|||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data,
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Table(values=data,
|
||||
headings=header_list,
|
||||
max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True,
|
||||
justification='right',
|
||||
alternating_row_color='lightblue',
|
||||
num_rows=len(data))]]
|
||||
num_rows=min(len(data), 20))]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13*10*len(header_list), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 char per column * num columns
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,19 +19,28 @@ if filename is not None:
|
|||
except:
|
||||
sg.PopupError('Error reading file')
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
# sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0))
|
||||
headings = [data[0][x] for x in range(len(data[0]))]
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data[1:][:], headings=headings, max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True, display_row_numbers=True, justification='right', num_rows=len(data), alternating_row_color='lightblue')]]
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Table(values=data[1:][:], headings=headings, max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True, display_row_numbers=True, justification='right', num_rows=20, alternating_row_color='lightblue', key='_table_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read'), sg.Button('Double')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Read = read which rows are selected')],[sg.T('Double = double the amount of data in the table')]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13 * 10 * len(headings), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 per column * num columns
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False, resizable=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)],]
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == 'Double':
|
||||
for i in range(len(data)):
|
||||
data.append(data[i])
|
||||
window.FindElement('_table_').Update(values = data)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values)
|
||||
# print(event, values)
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -28,16 +28,12 @@ def table_example():
|
|||
except:
|
||||
sg.PopupError('Error reading file')
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
# sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data, headings=header_list, display_row_numbers=True,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=False, num_rows=len(data))]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13*10*len(header_list), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 per column * num columns
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)]]
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Table(values=data, headings=header_list, display_row_numbers=True,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=False, num_rows=min(25,len(data)))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
event, values = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@ def TableSimulation():
|
|||
Display data in a table format
|
||||
"""
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0))
|
||||
sg.PopupNoWait('Give it a few seconds to load please...', auto_close=True)
|
||||
|
||||
menu_def = [['File', ['Open', 'Save', 'Exit']],
|
||||
['Edit', ['Paste', ['Special', 'Normal',], 'Undo'],],
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,7 +19,7 @@ def TableSimulation():
|
|||
|
||||
columm_layout = [[]]
|
||||
|
||||
MAX_ROWS = 60
|
||||
MAX_ROWS = 20
|
||||
MAX_COL = 10
|
||||
for i in range(MAX_ROWS):
|
||||
inputs = [sg.T('{}'.format(i), size=(4,1), justification='right')] + [sg.In(size=(10, 1), pad=(1, 1), justification='right', key=(i,j), do_not_clear=True) for j in range(MAX_COL)]
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +33,7 @@ def TableSimulation():
|
|||
sg.In(key='value', size=(8,1), pad=(1,1), justification='right', do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Column(columm_layout, size=(800,600), scrollable=True)] ]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', return_keyboard_events=True, grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', return_keyboard_events=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout, background_color='darkslat
|
|||
selected_title_color='green', tab_location='left'),
|
||||
sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 4', tab4_layout,background_color='darkseagreen', key='_mykey_'),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Tab 5', tab5_layout)]], key='_group4_', tab_location='bottom', selected_title_color='purple')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ layout = [[sg.T('My Window!')], [sg.Frame('A Frame', layout=
|
|||
[[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout), sg.Tab('Tab 2', tab2_layout)]]), sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab3', tab3_layout), sg.Tab('Tab 4', tab4_layout)]])]])],
|
||||
[sg.T('This text is on a row with a column'),sg.Column(layout=[[sg.T('In a column')],
|
||||
[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 5', tab5_layout), sg.Tab('Tab 6', tab6_layout)]])],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Click me')]])],]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Click me')]])],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,13 +7,13 @@ else:
|
|||
|
||||
tab1_layout = [[sg.T('Tab 1')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Put your layout in here')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Input something'),sg.In(key='_in0_')]]
|
||||
[sg.T('Input something'),sg.In(key='_IN0_')]]
|
||||
|
||||
tab2_layout = [[sg.T('Tab2')]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout), sg.Tab('Tab 2', tab2_layout)]])],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout), sg.Tab('Tab 2', tab2_layout)]], key='_TABGROUP_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,15 +11,15 @@ else:
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Next Window')]]
|
||||
[ sg.CloseButton('Next Window')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -------------------------------------#
|
||||
# DESIGN PATTERN 2 - Persistent Window #
|
||||
# -------------------------------------#
|
||||
# --------------------------------------------------#
|
||||
# DESIGN PATTERN 2 - Persistent Window (stays open) #
|
||||
# --------------------------------------------------#
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,13 +27,13 @@ if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
|||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read The Window')]]
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My Window') ],
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read The Window')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My Window Title').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
if event is None: # if window closed with X
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,84 +1,99 @@
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class keyboard():
|
||||
def __init__(self,font=('Arial',16)):
|
||||
self.font=font
|
||||
numberRow='1234567890'
|
||||
topRow='QWERTYUIOP'
|
||||
midRow='ASDFGHJKL'
|
||||
bottomRow='ZXCVBNM'
|
||||
keyboard_layout=[[sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in numberRow]+[sg.ReadButton('⌫', key='back', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font),sg.ReadButton('Esc', key='close', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font)],
|
||||
[sg.T(' '*4)]+[sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in topRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' '*11)]+[sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in midRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' '*18)]+[sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in bottomRow]]
|
||||
def __init__(self, font=('Arial', 16)):
|
||||
self.font = font
|
||||
numberRow = '1234567890'
|
||||
topRow = 'QWERTYUIOP'
|
||||
midRow = 'ASDFGHJKL'
|
||||
bottomRow = 'ZXCVBNM'
|
||||
keyboard_layout = [[sg.Button(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in numberRow] + [
|
||||
sg.Button('⌫', key='back', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font),
|
||||
sg.Button('Esc', key='close', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font)],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 4)] + [sg.Button(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
topRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 11)] + [sg.Button(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
midRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 18)] + [sg.Button(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
bottomRow]]
|
||||
|
||||
self.window=sg.Window('keyboard', grab_anywhere=True, keep_on_top=True, no_titlebar=True).Layout(
|
||||
keyboard_layout).Finalize()
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
|
||||
def _keyboardhandler(self):
|
||||
if self.event is not None:
|
||||
if self.event=='close':
|
||||
self.window = sg.Window('keyboard',
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True,
|
||||
keep_on_top=True,
|
||||
alpha_channel=0,
|
||||
location=(850,350),
|
||||
no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
).Layout(keyboard_layout).Finalize()
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
elif len(self.event)==1:
|
||||
self.focus.Update(self.focus.Get()+self.event)
|
||||
elif self.event=='back':
|
||||
Text=self.focus.Get()
|
||||
if len(Text)>0:
|
||||
Text=Text[:-1]
|
||||
self.focus.Update(Text)
|
||||
|
||||
def hide(self):
|
||||
self.visible=False
|
||||
self.window.Disappear()
|
||||
def _keyboardhandler(self):
|
||||
if self.event is not None:
|
||||
if self.event == 'close':
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
elif len(self.event) == 1:
|
||||
self.focus.Update(self.focus.Get() + self.event)
|
||||
elif self.event == 'back':
|
||||
Text = self.focus.Get()
|
||||
if len(Text) > 0:
|
||||
Text = Text[:-1]
|
||||
self.focus.Update(Text)
|
||||
|
||||
def show(self):
|
||||
self.visible=True
|
||||
self.window.Reappear()
|
||||
def hide(self):
|
||||
self.visible = False
|
||||
self.window.Disappear()
|
||||
|
||||
def togglevis(self):
|
||||
if self.visible:
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.show()
|
||||
def show(self):
|
||||
self.visible = True
|
||||
self.window.Reappear()
|
||||
|
||||
def update(self,focus):
|
||||
self.event,_=self.window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
self.focus=focus
|
||||
self._keyboardhandler()
|
||||
def togglevis(self):
|
||||
if self.visible:
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.show()
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
self.window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
def update(self, focus):
|
||||
self.event, _ = self.window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if focus is not None:
|
||||
self.focus = focus
|
||||
self._keyboardhandler()
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
self.window.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GUI():
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Enter Text')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(size=(17, 1), key='input1',)],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(size=(17, 1), key='input2')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('on-screen keyboard',key='keyboard')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('close',key='close')]]
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Enter Text')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(size=(17, 1), key='input1', do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(size=(17, 1), key='input2', do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Button('on-screen keyboard', key='keyboard')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('close', key='close')]]
|
||||
|
||||
self.mainWindow = sg.Window('On-screen test', grab_anywhere=False,no_titlebar=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
self.keyboard=keyboard()
|
||||
self.focus=None
|
||||
self.mainWindow = sg.Window('On-screen test',
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True,
|
||||
no_titlebar=False,
|
||||
).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
self.keyboard = keyboard()
|
||||
self.focus = None
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
cur_focus = self.mainWindow.FindElementWithFocus()
|
||||
if cur_focus is not None:
|
||||
self.focus = cur_focus
|
||||
event, values = self.mainWindow.Read(timeout=200, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if self.focus is not None:
|
||||
self.keyboard.update(self.focus)
|
||||
if event == 'keyboard':
|
||||
self.keyboard.togglevis()
|
||||
elif event == 'close' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
self.keyboard.close()
|
||||
self.mainWindow.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
for row in self.mainWindow.Rows:
|
||||
for element in row:
|
||||
if element.Type=='input' and element.TKEntry is not None and element.TKEntry is element.TKEntry.focus_get():
|
||||
self.focus=element
|
||||
event, values=self.mainWindow.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
self.keyboard.update(self.focus)
|
||||
if event=='keyboard':
|
||||
self.keyboard.togglevis()
|
||||
elif event=='close':
|
||||
break
|
||||
self.keyboard.close()
|
||||
self.mainWindow.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
app=GUI()
|
||||
app.run()
|
||||
app = GUI()
|
||||
app.run()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class keyboard():
|
||||
def __init__(self, font=('Arial', 16)):
|
||||
self.font = font
|
||||
numberRow = '1234567890'
|
||||
topRow = 'QWERTYUIOP'
|
||||
midRow = 'ASDFGHJKL'
|
||||
bottomRow = 'ZXCVBNM'
|
||||
keyboard_layout = [[sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in numberRow] + [
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('⌫', key='back', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Esc', key='close', pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font)],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 4)] + [sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
topRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 11)] + [sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
midRow],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 18)] + [sg.ReadButton(c, key=c, pad=(0, 0), size=(4, 2), font=self.font) for c in
|
||||
bottomRow]]
|
||||
|
||||
self.window = sg.Window('keyboard', grab_anywhere=True, keep_on_top=True, no_titlebar=True).Layout(
|
||||
keyboard_layout).Finalize()
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
|
||||
def _keyboardhandler(self):
|
||||
if self.event is not None:
|
||||
if self.event == 'close':
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
elif len(self.event) == 1:
|
||||
self.focus.Update(self.focus.Get() + self.event)
|
||||
elif self.event == 'back':
|
||||
Text = self.focus.Get()
|
||||
if len(Text) > 0:
|
||||
Text = Text[:-1]
|
||||
self.focus.Update(Text)
|
||||
|
||||
def hide(self):
|
||||
self.visible = False
|
||||
self.window.Disappear()
|
||||
|
||||
def show(self):
|
||||
self.visible = True
|
||||
self.window.Reappear()
|
||||
|
||||
def togglevis(self):
|
||||
if self.visible:
|
||||
self.hide()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.show()
|
||||
|
||||
def update(self, focus):
|
||||
self.event, _ = self.window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if focus is not None:
|
||||
self.focus = focus
|
||||
self._keyboardhandler()
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
self.window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GUI():
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Enter Text')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(size=(17, 1), key='input1', do_not_clear=True )],
|
||||
[sg.InputText(size=(17, 1), key='input2', do_not_clear=True)],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('on-screen keyboard', key='keyboard')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('close', key='close')]]
|
||||
|
||||
self.mainWindow = sg.Window('On-screen test', grab_anywhere=False, no_titlebar=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
self.keyboard = keyboard()
|
||||
self.focus = None
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
cur_focus = self.mainWindow.FindElementWithFocus()
|
||||
if cur_focus is not None:
|
||||
self.focus = cur_focus
|
||||
event, values = self.mainWindow.Read(timeout=200, timeout_key='timeout')
|
||||
if self.focus is not None:
|
||||
self.keyboard.update(self.focus)
|
||||
if event == 'keyboard':
|
||||
self.keyboard.togglevis()
|
||||
elif event == 'close':
|
||||
break
|
||||
self.keyboard.close()
|
||||
self.mainWindow.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
app = GUI()
|
||||
app.run()
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,8 +17,8 @@ treedata.Insert("_A1_", '_A3_', 'A30', ['getting deep'])
|
|||
treedata.Insert("_C_", '_C2_', 'C2', ['nothing', 'at', 'all'])
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('Tree Test') ],
|
||||
[ sg.Tree(data=treedata, headings=['col1', 'col2', 'col3'], auto_size_columns=True, num_rows=10, col0_width=10)],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Tree(data=treedata, headings=['col1', 'col2', 'col3'], auto_size_columns=True, num_rows=10, col0_width=10, key='_tree_', show_expanded=True)],
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Tree Element Test').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,8 +19,8 @@ import turtle
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(800,800), key='_canvas_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('F'), sg.RButton('B'), sg.RButton('L'), sg.RButton('R')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Spiral'), sg.RButton('Inside Out'), sg.RButton('Circles')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('F'), sg.Button('B'), sg.Button('L'), sg.Button('R')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Spiral'), sg.Button('Inside Out'), sg.Button('Circles')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ else:
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My Window') ],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Disappear')]]
|
||||
[ sg.Button('Disappear')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,10 +31,10 @@ def DownloadSubtitlesGUI():
|
|||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in ('EXIT', None):
|
||||
if event in ('Exit', None):
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
link = values['link']
|
||||
if event is 'Get List':
|
||||
if event == 'Get List':
|
||||
print('Getting list of subtitles....')
|
||||
window.Refresh()
|
||||
command = [f'C:/Python/PycharmProjects/GooeyGUI/youtube-dl --list-subs {link}',]
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,9 +46,9 @@ def main():
|
|||
[sg.Listbox(values=[' '], size=(50, 30), select_mode=sg.SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED, font=('Courier', 12), key='_processes_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Click refresh once or twice.. once for list, second to get CPU usage')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Filter by typing name', font='ANY 14'), sg.In(size=(15,1), font='any 14', key='_filter_')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Sort by Name', ),
|
||||
sg.RButton('Sort by % CPU', button_color=('white', 'DarkOrange2')),
|
||||
sg.RButton('Kill', button_color=('white','red'), bind_return_key=True),
|
||||
[sg.Button('Sort by Name', ),
|
||||
sg.Button('Sort by % CPU', button_color=('white', 'DarkOrange2')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Kill', button_color=('white','red'), bind_return_key=True),
|
||||
sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'sea green'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Process Killer',
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,12 +63,14 @@ def main():
|
|||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if 'Mouse' in event or 'Control' in event or 'Shift' in event:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# skip mouse, control key and shift key events entirely
|
||||
if 'Mouse' in event or 'Control' in event or 'Shift' in event:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if event == 'Sort by Name':
|
||||
psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
|
||||
procs = psutil.process_iter()
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,7 +98,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
for process in sorted_by_cpu_procs:
|
||||
display_list.append('{:5d} {:5.2f} {}\n'.format(process[2], process[0]/10, process[1]))
|
||||
window.FindElement('_processes_').Update(display_list)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
else: # was a typed character
|
||||
if display_list is not None:
|
||||
new_output = []
|
||||
for line in display_list:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2457,6 +2457,7 @@ class Table(Element):
|
|||
if self.AlternatingRowColor is not None:
|
||||
self.TKTreeview.tag_configure(1, background=self.AlternatingRowColor)
|
||||
self.Values = values
|
||||
self.SelectedRows = []
|
||||
|
||||
def treeview_selected(self, event):
|
||||
selections = self.TKTreeview.selection()
|
||||
|
|
@ -5991,7 +5992,7 @@ def PopupGetFolder(message, default_path='', no_window=False, size=(None, None),
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1)), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
|
|
@ -6052,7 +6053,7 @@ def PopupGetFile(message, default_path='', default_extension='', save_as=False,
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), browse_button],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(6, 1)), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(6, 1))]]
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(6, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(6, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, font=font,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
|
|
@ -6091,7 +6092,7 @@ def PopupGetText(message, default_text='', password_char='', size=(None, None),
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color, font=font)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_text, size=size, password_char=password_char)],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1)), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, no_titlebar=no_titlebar,
|
||||
background_color=background_color, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
322
PySimpleGUI27.py
322
PySimpleGUI27.py
|
|
@ -1183,7 +1183,7 @@ class Output(Element):
|
|||
# Button Class #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
class Button(Element):
|
||||
def __init__(self, button_text='', button_type=BUTTON_TYPE_CLOSES_WIN, target=(None, None), tooltip=None,
|
||||
def __init__(self, button_text='', button_type=BUTTON_TYPE_READ_FORM, target=(None, None), tooltip=None,
|
||||
file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.*"),), initial_folder=None, disabled=False, image_filename=None,
|
||||
image_data=None, image_size=(None, None), image_subsample=None, border_width=None, size=(None, None),
|
||||
auto_size_button=None, button_color=None, font=None, bind_return_key=False,
|
||||
|
|
@ -2469,6 +2469,7 @@ class Table(Element):
|
|||
if self.AlternatingRowColor is not None:
|
||||
self.TKTreeview.tag_configure(1, background=self.AlternatingRowColor)
|
||||
self.Values = values
|
||||
self.SelectedRows = []
|
||||
|
||||
def treeview_selected(self, event):
|
||||
selections = self.TKTreeview.selection()
|
||||
|
|
@ -4706,7 +4707,7 @@ def _ProgressMeter(title, max_value, *args, **_3to2kwargs):
|
|||
bar_text = Text(single_line_message, size=(width, height + 3), auto_size_text=True)
|
||||
form.AddRow(bar_text)
|
||||
form.AddRow((bar2))
|
||||
form.AddRow((Cancel(button_color=button_color)))
|
||||
form.AddRow((CloseButton('Cancel', button_color=button_color)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
single_line_message, width, height = ConvertArgsToSingleString(*args)
|
||||
bar2.TextToDisplay = single_line_message
|
||||
|
|
@ -4714,7 +4715,7 @@ def _ProgressMeter(title, max_value, *args, **_3to2kwargs):
|
|||
bar2.CurrentValue = 0
|
||||
bar_text = Text(single_line_message, size=(width, height + 3), auto_size_text=True)
|
||||
form.AddRow(bar2, bar_text)
|
||||
form.AddRow((Cancel(button_color=button_color)))
|
||||
form.AddRow((CloseButton('Cancel', button_color=button_color)))
|
||||
|
||||
form.NonBlocking = True
|
||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
|
@ -5121,165 +5122,6 @@ def PopupScrolled(*args, **_3to2kwargs):
|
|||
ScrolledTextBox = PopupScrolled
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
# GetPathBox #
|
||||
# Pre-made dialog that looks like this roughly #
|
||||
# MESSAGE #
|
||||
# __________________________ #
|
||||
# |__________________________| (BROWSE) #
|
||||
# (SUBMIT) (CANCEL) #
|
||||
# RETURNS two values: #
|
||||
# True/False, path #
|
||||
# (True if Submit was pressed, false otherwise) #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
|
||||
def PopupGetFolder(message, default_path='', no_window=False, size=(None, None), button_color=None,
|
||||
background_color=None, text_color=None, icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False, location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display popup with text entry field and browse button. Browse for folder
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_path:
|
||||
:param no_window:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: Contents of text field. None if closed using X or cancelled
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if no_window:
|
||||
root = tk.Tk()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
root.attributes('-alpha', 0) # hide window while building it. makes for smoother 'paint'
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
folder_name = tk.filedialog.askdirectory() # show the 'get folder' dialog box
|
||||
root.destroy()
|
||||
return folder_name
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[Ok(size=(5, 1)), Cancel(size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
font=font, no_titlebar=no_titlebar, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top,
|
||||
location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = input_values[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#####################################
|
||||
# PopupGetFile #
|
||||
#####################################
|
||||
def PopupGetFile(message, default_path='', default_extension='', save_as=False, file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.*"),),
|
||||
no_window=False, size=(None, None), button_color=None, background_color=None, text_color=None,
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False, grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False,
|
||||
location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display popup with text entry field and browse button. Browse for file
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_path:
|
||||
:param default_extension:
|
||||
:param save_as:
|
||||
:param file_types:
|
||||
:param no_window:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: string representing the path chosen, None if cancelled or window closed with X
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if no_window:
|
||||
root = tk.Tk()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
root.attributes('-alpha', 0) # hide window while building it. makes for smoother 'paint'
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
if save_as:
|
||||
filename = tk.filedialog.asksaveasfilename(filetypes=file_types,
|
||||
defaultextension=default_extension) # show the 'get file' dialog box
|
||||
else:
|
||||
filename = tk.filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=file_types,
|
||||
defaultextension=default_extension) # show the 'get file' dialog box
|
||||
root.destroy()
|
||||
return filename
|
||||
|
||||
browse_button = SaveAs(file_types=file_types) if save_as else FileBrowse(file_types=file_types)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), browse_button],
|
||||
[Ok(size=(6, 1)), Cancel(size=(6, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, font=font,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
no_titlebar=no_titlebar, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top, location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = input_values[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#####################################
|
||||
# PopupGetText #
|
||||
#####################################
|
||||
def PopupGetText(message, default_text='', password_char='', size=(None, None), button_color=None,
|
||||
background_color=None, text_color=None, icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False, location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display Popup with text entry field
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_text:
|
||||
:param password_char:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: Text entered or None if window was closed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color, font=font)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_text, size=size, password_char=password_char)],
|
||||
[Ok(size=(5, 1)), Cancel(size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, no_titlebar=no_titlebar,
|
||||
background_color=background_color, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top,
|
||||
location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return input_values[0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ============================== SetGlobalIcon ======#
|
||||
# Sets the icon to be used by default #
|
||||
|
|
@ -5879,7 +5721,7 @@ def Popup(*args, **_3to2kwargs):
|
|||
if non_blocking:
|
||||
PopupButton = DummyButton # important to use or else button will close other windows too!
|
||||
else:
|
||||
PopupButton = Button
|
||||
PopupButton = CloseButton
|
||||
# show either an OK or Yes/No depending on paramater
|
||||
if button_type is POPUP_BUTTONS_YES_NO:
|
||||
window.AddRow(PopupButton('Yes', button_color=button_color, focus=True, bind_return_key=True, pad=((20, 5), 3),
|
||||
|
|
@ -6461,6 +6303,160 @@ def PopupYesNo(*args, **_3to2kwargs):
|
|||
grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top, location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##############################################################################
|
||||
# The PopupGet_____ functions - Will return user input #
|
||||
##############################################################################
|
||||
|
||||
# --------------------------- PopupGetFolder ---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def PopupGetFolder(message, default_path='', no_window=False, size=(None, None), button_color=None,
|
||||
background_color=None, text_color=None, icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False, location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display popup with text entry field and browse button. Browse for folder
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_path:
|
||||
:param no_window:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: Contents of text field. None if closed using X or cancelled
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if no_window:
|
||||
root = tk.Tk()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
root.attributes('-alpha', 0) # hide window while building it. makes for smoother 'paint'
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
folder_name = tk.filedialog.askdirectory() # show the 'get folder' dialog box
|
||||
root.destroy()
|
||||
return folder_name
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
font=font, no_titlebar=no_titlebar, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top,
|
||||
location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = input_values[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# --------------------------- PopupGetFile ---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
def PopupGetFile(message, default_path='', default_extension='', save_as=False, file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.*"),),
|
||||
no_window=False, size=(None, None), button_color=None, background_color=None, text_color=None,
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False, grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False,
|
||||
location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display popup with text entry field and browse button. Browse for file
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_path:
|
||||
:param default_extension:
|
||||
:param save_as:
|
||||
:param file_types:
|
||||
:param no_window:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: string representing the path chosen, None if cancelled or window closed with X
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if no_window:
|
||||
root = tk.Tk()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
root.attributes('-alpha', 0) # hide window while building it. makes for smoother 'paint'
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
if save_as:
|
||||
filename = tk.filedialog.asksaveasfilename(filetypes=file_types,
|
||||
defaultextension=default_extension) # show the 'get file' dialog box
|
||||
else:
|
||||
filename = tk.filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=file_types,
|
||||
defaultextension=default_extension) # show the 'get file' dialog box
|
||||
root.destroy()
|
||||
return filename
|
||||
|
||||
browse_button = SaveAs(file_types=file_types) if save_as else FileBrowse(file_types=file_types)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_path, size=size), browse_button],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(6, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(6, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, font=font,
|
||||
background_color=background_color,
|
||||
no_titlebar=no_titlebar, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top, location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = input_values[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# --------------------------- PopupGetText ---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
def PopupGetText(message, default_text='', password_char='', size=(None, None), button_color=None,
|
||||
background_color=None, text_color=None, icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, font=None, no_titlebar=False,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=False, keep_on_top=False, location=(None, None)):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display Popup with text entry field
|
||||
:param message:
|
||||
:param default_text:
|
||||
:param password_char:
|
||||
:param size:
|
||||
:param button_color:
|
||||
:param background_color:
|
||||
:param text_color:
|
||||
:param icon:
|
||||
:param font:
|
||||
:param no_titlebar:
|
||||
:param grab_anywhere:
|
||||
:param keep_on_top:
|
||||
:param location:
|
||||
:return: Text entered or None if window was closed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[Text(message, auto_size_text=True, text_color=text_color, background_color=background_color, font=font)],
|
||||
[InputText(default_text=default_text, size=size, password_char=password_char)],
|
||||
[CloseButton('Ok', size=(5, 1), bind_return_key=True), CloseButton('Cancel', size=(5, 1))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = Window(title=message, icon=icon, auto_size_text=True, button_color=button_color, no_titlebar=no_titlebar,
|
||||
background_color=background_color, grab_anywhere=grab_anywhere, keep_on_top=keep_on_top,
|
||||
location=location)
|
||||
|
||||
(button, input_values) = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button != 'Ok':
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return input_values[0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
layout = [[Text('You are running the PySimpleGUI.py file itself')],
|
||||
[Text('You should be importing it rather than running it', size=(50, 2))],
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
615
docs/cookbook.md
615
docs/cookbook.md
|
|
@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ with
|
|||
|
||||
There is a short section in the Readme with instruction on installing PySimpleGUI
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this Cookbook, then you'll LOVE the 100+ sample programs that are just like these. You'll find them in the GitHub at http://www.PySimpleGUI.com. These Recipes are simply several of those programs displayed in document format.
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple Data Entry - Return Values As List
|
||||
Same GUI screen except the return values are in a list instead of a dictionary and doesn't have initial values.
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,7 +97,7 @@ Quickly add a GUI allowing the user to browse for a filename if a filename is no
|
|||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
event, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').Layout([[sg.Text('Document to open')],
|
||||
[sg.In(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Open(), sg.Cancel()]]).Read()
|
||||
[sg.CButton('Open'), sg.CButton('Cancel')]]).Read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fname = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -191,37 +192,60 @@ Example of nearly all of the widgets in a single window. Uses a customized colo
|
|||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Window that stays open reading inputs and button clicks
|
||||
|
||||
This is the most basic form of a "Persistent Window", a window that remains open after button clicks and data entry.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Persistent window')],
|
||||
[sg.Input()],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read'), sg.Exit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Window that stays open').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-Blocking Window With Periodic Update
|
||||
An async Window that has a event read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. Note that `value` is checked for None which indicates the window was closed using X.
|
||||
An async Window that has a event read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. Note that `value` is checked for None which indicates the window was closed using X.
|
||||
Use caution when using windows with a timeout. You should rarely need to use a timeout=0, non-blocking call, so try not to abuse this design pattern.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
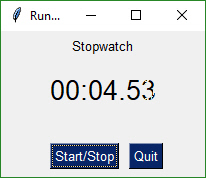
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
gui_rows = [[sg.Text('Stopwatch', size=(20, 2), justification='center')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 5), sg.ReadButton('Start/Stop', focus=True), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer').Layout(gui_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
timer_running = True
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
# Event Loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
i += 1 * (timer_running is True)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Start/Stop':
|
||||
timer_running = not timer_running
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
gui_rows = [[sg.Text('Stopwatch', size=(20, 2), justification='center')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(10, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ' * 5), sg.Button('Start/Stop', focus=True), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer').Layout(gui_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
timer_running = True
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
# Event Loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
i += 1 * (timer_running is True)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10) # Please try and use a timeout when possible
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Start/Stop':
|
||||
timer_running = not timer_running
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -247,7 +271,7 @@ The architecture of some programs works better with button callbacks instead of
|
|||
|
||||
# Layout the design of the GUI
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Please click a button', auto_size_text=True)],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('1'), sg.ReadButton('2'), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('1'), sg.Button('2'), sg.Quit()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Show the Window to the user
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Button callback example').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
|
@ -261,7 +285,8 @@ The architecture of some programs works better with button callbacks instead of
|
|||
button1()
|
||||
elif event == '2':
|
||||
button2()
|
||||
elif event =='Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
elif event =='Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# All done!
|
||||
|
|
@ -288,19 +313,19 @@ This recipe implements a remote control interface for a robot. There are 4 dire
|
|||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
# You need to perform a Read or Refresh on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it will appear your program has hung
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10)
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking() # Don't forget to close your window!
|
||||
window.Close() # Don't forget to close your window!
|
||||
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -324,63 +349,83 @@ Buttons can have PNG of GIF images on them. This Media Player recipe requires 4
|
|||
|
||||
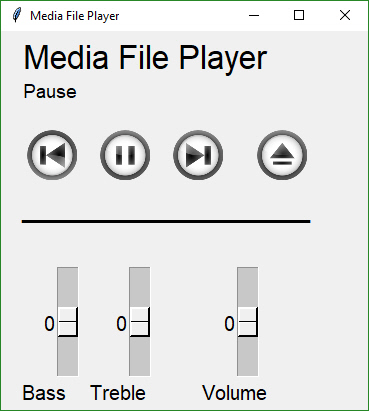
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
background = '#F0F0F0'
|
||||
# Set the backgrounds the same as the background on the buttons
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(background_color=background, element_background_color=background)
|
||||
# Images are located in a subfolder in the Demo Media Player.py folder
|
||||
image_pause = './ButtonGraphics/Pause.png'
|
||||
image_restart = './ButtonGraphics/Restart.png'
|
||||
image_next = './ButtonGraphics/Next.png'
|
||||
image_exit = './ButtonGraphics/Exit.png'
|
||||
|
||||
# define layout of the rows
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Media File Player', size=(17, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 2), font=("Helvetica", 14), key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Restart Song', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Pause', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Next', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.Button('Exit', button_color=(background, background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2,
|
||||
border_width=0)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 30)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(' ' * 30)],
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 8),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical',
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 15))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Bass', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(6, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Treble', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(10, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Volume', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(7, 1))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Media File Player', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(20, 1),
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 25)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# Read the window (this call will not block)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if event:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# An Async Demonstration of a media player
|
||||
# Uses button images for a super snazzy look
|
||||
# See how it looks here:
|
||||
# https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/13696193/43159403-45c9726e-8f50-11e8-9da0-0d272e20c579.jpg
|
||||
#
|
||||
def MediaPlayerGUI():
|
||||
background = '#F0F0F0'
|
||||
# Set the backgrounds the same as the background on the buttons
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(background_color=background, element_background_color=background)
|
||||
# Images are located in a subfolder in the Demo Media Player.py folder
|
||||
image_pause = './ButtonGraphics/Pause.png'
|
||||
image_restart = './ButtonGraphics/Restart.png'
|
||||
image_next = './ButtonGraphics/Next.png'
|
||||
image_exit = './ButtonGraphics/Exit.png'
|
||||
|
||||
# A text element that will be changed to display messages in the GUI
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# define layout of the rows
|
||||
layout= [[sg.Text('Media File Player',size=(17,1), font=("Helvetica", 25))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 2), font=("Helvetica", 14), key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_restart, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Restart Song'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_pause, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Pause'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background), image_filename=image_next, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Next'),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2), sg.Button('', button_color=(background,background),
|
||||
image_filename=image_exit, image_size=(50, 50), image_subsample=2, border_width=0, key='Exit')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_'*20)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(' '*30)],
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical', font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical', font=("Helvetica", 15)),
|
||||
sg.Text(' ' * 2),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(-10, 10), default_value=0, size=(10, 20), orientation='vertical', font=("Helvetica", 15))],
|
||||
[sg.Text(' Bass', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(9, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Treble', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(7, 1)),
|
||||
sg.Text('Volume', font=("Helvetica", 15), size=(7, 1))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Open a form, note that context manager can't be used generally speaking for async forms
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Media File Player', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(20, 1),
|
||||
font=("Helvetica", 25)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while(True):
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=100) # Poll every 100 ms
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if event != sg.TIMEOUT_KEY:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
MediaPlayerGUI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
## Script Launcher - Persistent Window
|
||||
This Window doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are specified as `sg.ReadButton` instead of `sg.Button`. The exception to this is the EXIT button. Clicking it will close the window. This program will run commands and display the output in the scrollable window.
|
||||
This Window doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are specified as `sg.Button` instead of `sg.Button`. The exception to this is the EXIT button. Clicking it will close the window. This program will run commands and display the output in the scrollable window.
|
||||
|
||||
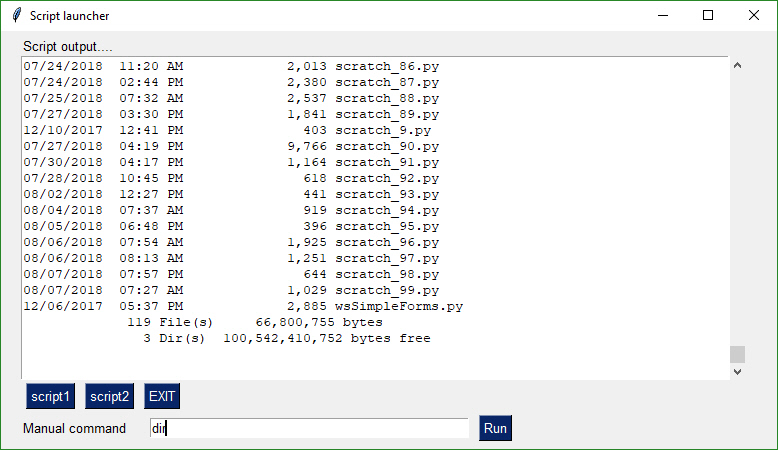
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -403,8 +448,8 @@ This Window doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are
|
|||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Script output....', size=(40, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(88, 20))],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('script1'), sg.ReadButton('script2'), sg.Button('EXIT')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Manual command', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText(focus=True), sg.ReadButton('Run', bind_return_key=True)]
|
||||
[sg.Button('script1'), sg.Button('script2'), sg.Button('EXIT')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Manual command', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText(focus=True), sg.Button('Run', bind_return_key=True)]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -469,25 +514,27 @@ Perhaps you don't want all the statistics that the EasyProgressMeter provides an
|
|||
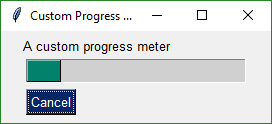
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# layout the Window
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(10000, orientation='h', size=(20, 20), key='progbar')],
|
||||
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the Window
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Custom Progress Meter').Layout(layout)
|
||||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
window.FindElement('progbar').UpdateBar(i + 1)
|
||||
# done with loop... need to destroy the window as it's still open
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# layout the Window
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('A custom progress meter')],
|
||||
[sg.ProgressBar(1000, orientation='h', size=(20, 20), key='progbar')],
|
||||
[sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the Window
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Custom Progress Meter').Layout(layout)
|
||||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(1000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
window.FindElement('progbar').UpdateBar(i + 1)
|
||||
# done with loop... need to destroy the window as it's still open
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
|
|
@ -570,7 +617,7 @@ This simple program keep a window open, taking input values until the user termi
|
|||
[sg.Txt('_' * 10)],
|
||||
[sg.In(size=(8,1), key='denominator')],
|
||||
[sg.Txt('', size=(8,1), key='output') ],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Calculate', bind_return_key=True)]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Calculate', bind_return_key=True)]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Math').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -609,7 +656,7 @@ While it's fun to scribble on a Canvas Widget, try Graph Element makes it a down
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(100, 100), background_color='red', key= 'canvas')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Change circle color to:'), sg.ReadButton('Red'), sg.ReadButton('Blue')]
|
||||
[sg.T('Change circle color to:'), sg.Button('Red'), sg.Button('Blue')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Canvas test')
|
||||
|
|
@ -639,7 +686,7 @@ Just like you can draw on a tkinter widget, you can also draw on a Graph Element
|
|||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Graph(canvas_size=(400, 400), graph_bottom_left=(0,0), graph_top_right=(400, 400), background_color='red', key='graph')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Change circle color to:'), sg.ReadButton('Red'), sg.ReadButton('Blue'), sg.ReadButton('Move')]
|
||||
[sg.T('Change circle color to:'), sg.Button('Red'), sg.Button('Blue'), sg.Button('Move')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Graph test')
|
||||
|
|
@ -674,7 +721,7 @@ This Recipe implements a Raspberry Pi touchscreen based keypad entry. As the di
|
|||
There are a number of features used in this Recipe including:
|
||||
* Default Element Size
|
||||
* auto_size_buttons
|
||||
* ReadButton
|
||||
* Button
|
||||
* Dictionary Return values
|
||||
* Update of Elements in window (Input, Text)
|
||||
* do_not_clear of Input Elements
|
||||
|
|
@ -689,17 +736,17 @@ There are a number of features used in this Recipe including:
|
|||
# Demonstrates a number of PySimpleGUI features including:
|
||||
# Default element size
|
||||
# auto_size_buttons
|
||||
# ReadButton
|
||||
# Button
|
||||
# Dictionary return values
|
||||
# Update of elements in window (Text, Input)
|
||||
# do_not_clear of Input elements
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Enter Your Passcode')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(size=(10, 1), do_not_clear=True, justification='right', key='input')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('1'), sg.ReadButton('2'), sg.ReadButton('3')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('4'), sg.ReadButton('5'), sg.ReadButton('6')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('7'), sg.ReadButton('8'), sg.ReadButton('9')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Submit'), sg.ReadButton('0'), sg.ReadButton('Clear')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('1'), sg.Button('2'), sg.Button('3')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('4'), sg.Button('5'), sg.Button('6')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('7'), sg.Button('8'), sg.Button('9')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Submit'), sg.Button('0'), sg.Button('Clear')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(15, 1), font=('Helvetica', 18), text_color='red', key='out')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -729,60 +776,61 @@ Use the Canvas Element to create an animated graph. The code is a bit tricky to
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from tkinter import *
|
||||
from random import randint
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as g
|
||||
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg, FigureCanvasAgg
|
||||
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
|
||||
import matplotlib.backends.tkagg as tkagg
|
||||
import tkinter as Tk
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
fig = Figure()
|
||||
|
||||
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
|
||||
ax.set_xlabel("X axis")
|
||||
ax.set_ylabel("Y axis")
|
||||
ax.grid()
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[g.Text('Animated Matplotlib', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[g.Canvas(size=(640, 480), key='canvas')],
|
||||
[g.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((280, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
window = g.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI').Layout(layout)
|
||||
window.Finalize() # needed to access the canvas element prior to reading the window
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_elem = window.FindElement('canvas')
|
||||
|
||||
graph = FigureCanvasTkAgg(fig, master=canvas_elem.TKCanvas)
|
||||
canvas = canvas_elem.TKCanvas
|
||||
|
||||
dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
ax.cla()
|
||||
ax.grid()
|
||||
|
||||
ax.plot(range(20), dpts[i:i + 20], color='purple')
|
||||
graph.draw()
|
||||
figure_x, figure_y, figure_w, figure_h = fig.bbox.bounds
|
||||
figure_w, figure_h = int(figure_w), int(figure_h)
|
||||
photo = Tk.PhotoImage(master=canvas, width=figure_w, height=figure_h)
|
||||
|
||||
canvas.create_image(640 / 2, 480 / 2, image=photo)
|
||||
|
||||
figure_canvas_agg = FigureCanvasAgg(fig)
|
||||
figure_canvas_agg.draw()
|
||||
|
||||
tkagg.blit(photo, figure_canvas_agg.get_renderer()._renderer, colormode=2)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from tkinter import *
|
||||
from random import randint
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg, FigureCanvasAgg
|
||||
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
|
||||
import matplotlib.backends.tkagg as tkagg
|
||||
import tkinter as Tk
|
||||
|
||||
fig = Figure()
|
||||
|
||||
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
|
||||
ax.set_xlabel("X axis")
|
||||
ax.set_ylabel("Y axis")
|
||||
ax.grid()
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Animated Matplotlib', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(640, 480), key='canvas')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((280, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI').Layout(layout)
|
||||
window.Finalize() # needed to access the canvas element prior to reading the window
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_elem = window.FindElement('canvas')
|
||||
|
||||
graph = FigureCanvasTkAgg(fig, master=canvas_elem.TKCanvas)
|
||||
canvas = canvas_elem.TKCanvas
|
||||
|
||||
dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=20)
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
ax.cla()
|
||||
ax.grid()
|
||||
|
||||
ax.plot(range(20), dpts[i:i + 20], color='purple')
|
||||
graph.draw()
|
||||
figure_x, figure_y, figure_w, figure_h = fig.bbox.bounds
|
||||
figure_w, figure_h = int(figure_w), int(figure_h)
|
||||
photo = Tk.PhotoImage(master=canvas, width=figure_w, height=figure_h)
|
||||
|
||||
canvas.create_image(640 / 2, 480 / 2, image=photo)
|
||||
|
||||
figure_canvas_agg = FigureCanvasAgg(fig)
|
||||
figure_canvas_agg.draw()
|
||||
|
||||
tkagg.blit(photo, figure_canvas_agg.get_renderer()._renderer, colormode=2)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Tight Layout with Button States
|
||||
|
|
@ -809,10 +857,10 @@ In other GUI frameworks this program would be most likely "event driven" with ca
|
|||
layout = [[sg.T('User:', pad=((3,0),0)), sg.OptionMenu(values = ('User 1', 'User 2'), size=(20,1)), sg.T('0', size=(8,1))],
|
||||
[sg.T('Customer:', pad=((3,0),0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('Customer 1', 'Customer 2'), size=(20,1)), sg.T('1', size=(8,1))],
|
||||
[sg.T('Notes:', pad=((3,0),0)), sg.In(size=(44,1), background_color='white', text_color='black')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Start', button_color=('white', 'black'), key='Start'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Stop', button_color=('white', 'black'), key='Stop'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Reset', button_color=('white', 'firebrick3'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Submit', button_color=('white', 'springgreen4'), key='Submit')]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Start', button_color=('white', 'black'), key='Start'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Stop', button_color=('white', 'black'), key='Stop'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Reset', button_color=('white', 'firebrick3'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Submit', button_color=('white', 'springgreen4'), key='Submit')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Time Tracker", default_element_size=(12,1), text_justification='r', auto_size_text=False, auto_size_buttons=False,
|
||||
|
|
@ -973,10 +1021,10 @@ You can easily change colors to match your background by changing a couple of pa
|
|||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0,0), button_element_size=(12,1), auto_size_buttons=False)
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Combo(values=namesonly, size=(35,30), key='demofile'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Run', button_color=('white', '#00168B')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Program 1'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Program 2'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Program 3', button_color=('white', '#35008B')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Run', button_color=('white', '#00168B')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Program 1'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Program 2'),
|
||||
sg.Button('Program 3', button_color=('white', '#35008B')),
|
||||
sg.Button('EXIT', button_color=('white','firebrick3'))],
|
||||
[sg.T('', text_color='white', size=(50,1), key='output')]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1032,72 +1080,82 @@ Much of the code is handling the button states in a fancy way. It could be much
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Timer Desktop Widget Creates a floating timer that is always on top of other windows You move it by grabbing anywhere on the window Good example of how to do a non-blocking, polling program using PySimpleGUI Can be used to poll hardware when running on a Pi NOTE - you will get a warning message printed when you exit using exit button. It will look something like: invalid command name \"1616802625480StopMove\"
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- Create window ----------------
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='text')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Pause', key='button', button_color=('white', '#001480')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Reset', button_color=('white', '#007339'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), key='Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', no_titlebar=True, auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True, grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
if not paused:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
current_time = int(round(time.time() * 100)) - start_time
|
||||
else:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'button':
|
||||
button = window.FindElement(button).GetText()
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event is 'Reset':
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused_time = start_time
|
||||
elif event == 'Pause':
|
||||
paused = True
|
||||
paused_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Run')
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = start_time + int(round(time.time() * 100)) - paused_time
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Pause')
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Display timer in window --------
|
||||
window.FindElement('text').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((current_time // 100) // 60,
|
||||
(current_time // 100) % 60,
|
||||
current_time % 100))
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- After loop --------
|
||||
|
||||
# Broke out of main loop. Close the window.
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Timer Desktop Widget Creates a floating timer that is always on top of other windows You move it by grabbing anywhere on the window Good example of how to do a non-blocking, polling program using SimpleGUI Can be used to poll hardware when running on a Pi
|
||||
|
||||
While the timer ticks are being generated by PySimpleGUI's "timeout" mechanism, the actual value
|
||||
of the timer that is displayed comes from the system timer, time.time(). This guarantees an
|
||||
accurate time value is displayed regardless of the accuracy of the PySimpleGUI timer tick. If
|
||||
this design were not used, then the time value displayed would slowly drift by the amount of time
|
||||
it takes to execute the PySimpleGUI read and update calls (not good!)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE - you will get a warning message printed when you exit using exit button.
|
||||
It will look something like: invalid command name \"1616802625480StopMove\"
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- Create Form ----------------
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='text')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Pause', key='button', button_color=('white', '#001480')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Reset', button_color=('white', '#007339'), key='Reset'),
|
||||
sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), key='Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', no_titlebar=True, auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True, grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
if not paused:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=10)
|
||||
current_time = int(round(time.time() * 100)) - start_time
|
||||
else:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'button':
|
||||
event = window.FindElement(event).GetText()
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit': # ALWAYS give a way out of program
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event is 'Reset':
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused_time = start_time
|
||||
elif event == 'Pause':
|
||||
paused = True
|
||||
paused_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Run')
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = start_time + int(round(time.time() * 100)) - paused_time
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Pause')
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Display timer in window --------
|
||||
window.FindElement('text').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((current_time // 100) // 60,
|
||||
(current_time // 100) % 60,
|
||||
current_time % 100))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Desktop Floating Widget - CPU Utilization
|
||||
|
||||
Like the Timer widget above, this script can be kept running. You will need the package psutil installed in order to run this Recipe.
|
||||
Like the Timer widget above, this script can be kept running. You will need the package psutil installed in order to run this Recipe.
|
||||
|
||||
The spinner changes the number of seconds between reads. Note that you will get an error message printed when exiting because the window does not have have a titlebar. It's a known problem.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1105,39 +1163,42 @@ The spinner changes the number of seconds between reads. Note that you will get
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- Create Window ----------------
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='text')],
|
||||
[sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), pad=((15,0), 0)), sg.Spin([x+1 for x in range(10)], 1, key='spin')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', no_titlebar=True, auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True, grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
interval = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
except:
|
||||
interval = 1
|
||||
|
||||
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=interval)
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Display timer in window --------
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('text').Update(f'CPU {cpu_percent:02.0f}%')
|
||||
|
||||
# Broke out of main loop. Close the window.
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- Create Window ----------------
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Black')
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center', key='text')],
|
||||
[sg.Exit(button_color=('white', 'firebrick4'), pad=((15, 0), 0)),
|
||||
sg.Spin([x + 1 for x in range(10)], 1, key='spin')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Running Timer', no_titlebar=True, auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
interval = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
except:
|
||||
interval = 1
|
||||
|
||||
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=interval)
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Display timer in window --------
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('text').Update(f'CPU {cpu_percent:02.0f}%')
|
||||
|
||||
# Broke out of main loop. Close the window.
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Menus
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1145,7 +1206,7 @@ Menus are nothing more than buttons that live in a menu-bar. When you click on
|
|||
|
||||
Menu's are defined separately from the GUI window. To add one to your window, simply insert sg.Menu(menu_layout). The menu definition is a list of menu choices and submenus. They are a list of lists. Copy the Recipe and play with it. You'll eventually get when you're looking for.
|
||||
|
||||
If you double click the dashed line at the top of the list of choices, that menu will tear off and become a floating toolbar. How cool!
|
||||
If you double click the dashed line at the top of the list of choices, that menu will tear off and become a floating toolbar. How cool! To enable this feature, set the parameter `tearoff=True` in your call to `sg.Menu()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1164,7 +1225,7 @@ If you double click the dashed line at the top of the list of choices, that menu
|
|||
|
||||
# ------ GUI Defintion ------ #
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Menu(menu_def)],
|
||||
[sg.Menu(menu_def, )],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(60, 20))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1247,7 +1308,7 @@ tab2_layout = [[sg.T('This is inside tab 2')],
|
|||
[sg.In(key='in')]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout, tooltip='tip'), sg.Tab('Tab 2', tab2_layout)]], tooltip='TIP2')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Read')]]
|
||||
[sg.Button('Read')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,9 +24,9 @@
|
|||
|
||||
## Now supports both Python 2.7 & 3
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Announcements of Latest Developments](https://github.com/MikeTheWatchGuy/PySimpleGUI/issues/142)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -934,14 +935,10 @@ Isn't this what a Python programmer looking for a GUI wants? Something easy to w
|
|||
|
||||
### Two Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
All Window Read and ReadNonBlocking calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
All Window Read calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
All of the demo programs and the Cookbook recipes have this line of code for windows that are normal reads (not non-blocking). A similar line of code is used for non-blocking window reads:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't HAVE to write your reads in this way. You can name your variables however you want. But if you want to code them in a way that other programmers using PySimpleGUI are used to, then use these statements.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -970,6 +967,15 @@ To check for a closed window use this line of code:
|
|||
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
|
||||
Putting it all together we end up with an "event loop" that looks something like this:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### The 'values' Variable - Return values as a list
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1181,8 +1187,12 @@ You will find it ***much easier*** to write code using PySimpleGUI if you use an
|
|||
|
||||
## Synchronous windows
|
||||
The most common use of PySimpleGUI is to display and collect information from the user. The most straightforward way to do this is using a "blocking" GUI call. Execution is "blocked" while waiting for the user to close the GUI window/dialog box.
|
||||
You've already seen a number of examples above that use blocking windows. The call to look for that will show you non-blocking windows are calls to `ReadNonBlocking()`. You can read more about Async windows at the end of this document.
|
||||
You've already seen a number of examples above that use blocking windows. A truly non-blocking Read call looks like this:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about these async / non-blocking windows toward the end of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Window Object - Beginning a window
|
||||
|
|
@ -1287,12 +1297,12 @@ There are a few methods (functions) that you will see in this document that act
|
|||
window.Layout(layout) - Turns your definition of the Window into Window
|
||||
window.Finalize() - creates the tkinter objects for the Window. Normally you do not call this
|
||||
window.Read() - Read the Windows values and get the button / key that caused the Read to return. Can have an optional timeout
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking() - Same as Read but will return right away
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking() - NO LONGER USED!
|
||||
window.Refresh() - Use if updating elements and want to show the updates prior to the nex Read
|
||||
window.Fill(values_dict) - Fill each Element with entry from the dictionary passed in
|
||||
window.SaveToDisk(filename) - Save the Window's values to disk
|
||||
window.LoadFromDisk(filename) - Load the Window's values from disk
|
||||
window.Close() - To close your window, if a button hasn't already closed iit
|
||||
window.Close() - To close your window, if a button hasn't already closed it
|
||||
window.Disable() - Use to disable the window inpurt when opening another window on top of the primnary Window
|
||||
window.Enable() - Re-enable a Disabled window
|
||||
window.FindElement(key) - Returns the element that has a matching key value
|
||||
|
|
@ -2056,7 +2066,7 @@ The Types of buttons include:
|
|||
* Color Chooser
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Close window - Normal buttons like Submit, Cancel, Yes, No, etc, are "Close window" buttons. They cause the input values to be read and then the window is ***closed***, returning the values to the caller.
|
||||
Close window - Normal buttons like Submit, Cancel, Yes, No, do NOT close the window... they used to. Now to close a window you need to use a CloseButton / CButton.
|
||||
|
||||
Folder Browse - When clicked a folder browse dialog box is opened. The results of the Folder Browse dialog box are written into one of the input fields of the window.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2070,17 +2080,20 @@ Read window - This is a window button that will read a snapshot of all of the in
|
|||
|
||||
Realtime - This is another async window button. Normal button clicks occur after a button's click is released. Realtime buttons report a click the entire time the button is held down.
|
||||
|
||||
Most programs will use a combination of shortcut button calls (Submit, Cancel, etc), plain buttons that close the window, and ReadButton buttons that keep the window open but returns control back to the caller.
|
||||
Most programs will use a combination of shortcut button calls (Submit, Cancel, etc), normal Buttons which leave the windows open and CloseButtons that close the window when clicked.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes there are multiple names for the same function. This is simply to make the job of the programmer quicker and easier.
|
||||
Sometimes there are multiple names for the same function. This is simply to make the job of the programmer quicker and easier. Or they are old names that are no longer used but kept around so that existing programs don't break.
|
||||
|
||||
The 3 primary windows of PySimpleGUI buttons and their names are:
|
||||
The 4 primary windows of PySimpleGUI buttons and their names are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `Button` = `SimpleButton`
|
||||
2. `ReadButton` = `RButton` = `ReadFormButton` (old style... use ReadButton instead)
|
||||
1. `Button`= `ReadButton` = `RButton` = `ReadFormButton` (old style... use Button instead)
|
||||
2. `CloseButton` = `CButton`
|
||||
3. `RealtimeButton`
|
||||
4. `DummyButton`
|
||||
|
||||
You will find the long-form in the older programs.
|
||||
You will find the long-form names in the older programs. ReadButton for example.
|
||||
|
||||
In Oct 2018, the definition of Button changed. Previously Button would CLOSE the window when clicked. It has been changed so the Button calls will leave the window open in exactly the same way as a ReadButton. They are the same calls now. To enables windows to be closed using buttons, a new button was added... `CloseButton` or `CButton`.
|
||||
|
||||
The most basic Button element call to use is `Button`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2152,9 +2165,10 @@ These Pre-made buttons are some of the most important elements of all because th
|
|||
**IMPORT NOTE ABOUT SHORTCUT BUTTONS**
|
||||
Prior to release 3.11.0, these buttons closed the window. Starting with 3.11 they will not close the window. They act like RButtons (return the button text and do not close the window)
|
||||
|
||||
If you are having trouble with these buttons closing your window, please check your installed version of PySimpleGUI by typing `pip list` at a command promt. Prior to 3.11 these buttons close your window.
|
||||
If you are having trouble with these buttons closing your window, please check your installed version of PySimpleGUI by typing `pip list` at a command prompt. Prior to 3.11 these buttons close your window.
|
||||
|
||||
Using older versions, if you want a Submit() button that does not close the window, then you would instead use RButton('Submit'). Using the new version, if you want a Submit button that closes the window like the sold Submit() call did, you would write that as `CloseButton('Submit')` or `CButton('Submit')`
|
||||
|
||||
Using older versions, if you want a Submit() button that does not close the window, then you would instead use RButton('Submit')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2299,22 +2313,22 @@ window = sg.Window('Robotics Remote Control', auto_size_text=True).Layout(gui_ro
|
|||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
# You need to perform a Read or Refresh call on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it will apprear as if the program has locked up.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close() # Don't forget to close your window!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This loop will read button values and print them. When one of the Realtime buttons is clicked, the call to `window.ReadNonBlocking` will return a button name matching the name on the button that was depressed or the key if there was a key assigned to the button. It will continue to return values as long as the button remains depressed. Once released, the ReadNonBlocking will return None for buttons until a button is again clicked.
|
||||
This loop will read button values and print them. When one of the Realtime buttons is clicked, the call to `window.Read` will return a button name matching the name on the button that was depressed or the key if there was a key assigned to the button. It will continue to return values as long as the button remains depressed. Once released, the Read will return timeout events until a button is again clicked.
|
||||
|
||||
**File Types**
|
||||
The `FileBrowse` & `SaveAs` buttons have an additional setting named `file_types`. This variable is used to filter the files shown in the file dialog box. The default value for this setting is
|
||||
|
|
@ -2679,7 +2693,7 @@ Let me say up front that the Table Element has Beta status. The reason is that s
|
|||
|
||||
### Read return values from Table Element
|
||||
|
||||
The values returned from a `Window.Read` or `Window.ReadNonBlocking` call for the Tree Element are a list of row numbers that are currently highlighted.
|
||||
The values returned from a `Window.Read` call for the Tree Element are a list of row numbers that are currently highlighted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Update Call
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2947,7 +2961,7 @@ There are 2 ways to keep a window open after the user has clicked a button. One
|
|||
|
||||
The `RButton` Element creates a button that when clicked will return control to the user, but will leave the window open and visible. This button is also used in Non-Blocking windows. The difference is in which call is made to read the window. The normal `Read` call with no parameters will block, a call with a `timeout` value of zero will not block.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `InputText` and `MultiLine` Elements will be **cleared** when performing a `ReadNonBlocking`. If you do not want your input field to be cleared after a `ReadNonBlocking` then you can set the `do_not_clear` parameter to True when creating those elements. The clear is turned on and off on an element by element basis.
|
||||
Note that `InputText` and `MultiLine` Elements will be **cleared** when performing a `Read`. If you do not want your input field to be cleared after a `Read` then you can set the `do_not_clear` parameter to True when creating those elements. The clear is turned on and off on an element by element basis.
|
||||
|
||||
The reasoning behind this is that Persistent Windows are often "forms". When "submitting" a form you want to have all of the fields left blank so the next entry of data will start with a fresh window. Also, when implementing a "Chat Window" type of interface, after each read / send of the chat data, you want the input field cleared. Think of it as a Texting application. Would you want to have to clear your previous text if you want to send a second text?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2986,7 +3000,7 @@ Let's say you had a device that you want to "poll" every 100ms. The "easy way
|
|||
```python
|
||||
# YOU SHOULD NOT DO THIS....
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking() # DO NOT USE THIS CALL ANYMORE
|
||||
read_my_hardware() # process my device here
|
||||
time.sleep(.1) # sleep 1/10 second
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -3518,6 +3532,7 @@ A MikeTheWatchGuy production... entirely responsible for this code.... unless it
|
|||
| 3.10.1 & 1.2.1 | Oct 20, 2018
|
||||
| 3.10.3 & 1.2.3 | Oct 23, 2018
|
||||
| 3.11.0 & 1.11.0 | Oct 28, 2018
|
||||
| 3.12.0 & 1.12.0 | Oct 28, 2018
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Release Notes
|
||||
|
|
@ -3740,6 +3755,13 @@ Emergency patch release... going out same day as previous release
|
|||
* Shortcut buttons no longer close windows!
|
||||
* Added CloseButton, CButton that closes the windows
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.12.0 & 1.12.0
|
||||
* Changed Button to be the same as ReadButton which means it will no longer close the window
|
||||
* All shortcut buttons no longer close the window
|
||||
* Updating a table clears selected rows information in return values
|
||||
* Progress meter uses new CloseButton
|
||||
* Popups use new CloseButton
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Upcoming
|
||||
Make suggestions people! Future release features
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
76
readme.md
76
readme.md
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,9 +24,9 @@
|
|||
|
||||
## Now supports both Python 2.7 & 3
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Announcements of Latest Developments](https://github.com/MikeTheWatchGuy/PySimpleGUI/issues/142)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -934,14 +935,10 @@ Isn't this what a Python programmer looking for a GUI wants? Something easy to w
|
|||
|
||||
### Two Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
All Window Read and ReadNonBlocking calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
All Window Read calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
All of the demo programs and the Cookbook recipes have this line of code for windows that are normal reads (not non-blocking). A similar line of code is used for non-blocking window reads:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't HAVE to write your reads in this way. You can name your variables however you want. But if you want to code them in a way that other programmers using PySimpleGUI are used to, then use these statements.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -970,6 +967,15 @@ To check for a closed window use this line of code:
|
|||
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
|
||||
Putting it all together we end up with an "event loop" that looks something like this:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### The 'values' Variable - Return values as a list
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1181,8 +1187,12 @@ You will find it ***much easier*** to write code using PySimpleGUI if you use an
|
|||
|
||||
## Synchronous windows
|
||||
The most common use of PySimpleGUI is to display and collect information from the user. The most straightforward way to do this is using a "blocking" GUI call. Execution is "blocked" while waiting for the user to close the GUI window/dialog box.
|
||||
You've already seen a number of examples above that use blocking windows. The call to look for that will show you non-blocking windows are calls to `ReadNonBlocking()`. You can read more about Async windows at the end of this document.
|
||||
You've already seen a number of examples above that use blocking windows. A truly non-blocking Read call looks like this:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about these async / non-blocking windows toward the end of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Window Object - Beginning a window
|
||||
|
|
@ -1287,12 +1297,12 @@ There are a few methods (functions) that you will see in this document that act
|
|||
window.Layout(layout) - Turns your definition of the Window into Window
|
||||
window.Finalize() - creates the tkinter objects for the Window. Normally you do not call this
|
||||
window.Read() - Read the Windows values and get the button / key that caused the Read to return. Can have an optional timeout
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking() - Same as Read but will return right away
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking() - NO LONGER USED!
|
||||
window.Refresh() - Use if updating elements and want to show the updates prior to the nex Read
|
||||
window.Fill(values_dict) - Fill each Element with entry from the dictionary passed in
|
||||
window.SaveToDisk(filename) - Save the Window's values to disk
|
||||
window.LoadFromDisk(filename) - Load the Window's values from disk
|
||||
window.Close() - To close your window, if a button hasn't already closed iit
|
||||
window.Close() - To close your window, if a button hasn't already closed it
|
||||
window.Disable() - Use to disable the window inpurt when opening another window on top of the primnary Window
|
||||
window.Enable() - Re-enable a Disabled window
|
||||
window.FindElement(key) - Returns the element that has a matching key value
|
||||
|
|
@ -2056,7 +2066,7 @@ The Types of buttons include:
|
|||
* Color Chooser
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Close window - Normal buttons like Submit, Cancel, Yes, No, etc, are "Close window" buttons. They cause the input values to be read and then the window is ***closed***, returning the values to the caller.
|
||||
Close window - Normal buttons like Submit, Cancel, Yes, No, do NOT close the window... they used to. Now to close a window you need to use a CloseButton / CButton.
|
||||
|
||||
Folder Browse - When clicked a folder browse dialog box is opened. The results of the Folder Browse dialog box are written into one of the input fields of the window.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2070,17 +2080,20 @@ Read window - This is a window button that will read a snapshot of all of the in
|
|||
|
||||
Realtime - This is another async window button. Normal button clicks occur after a button's click is released. Realtime buttons report a click the entire time the button is held down.
|
||||
|
||||
Most programs will use a combination of shortcut button calls (Submit, Cancel, etc), plain buttons that close the window, and ReadButton buttons that keep the window open but returns control back to the caller.
|
||||
Most programs will use a combination of shortcut button calls (Submit, Cancel, etc), normal Buttons which leave the windows open and CloseButtons that close the window when clicked.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes there are multiple names for the same function. This is simply to make the job of the programmer quicker and easier.
|
||||
Sometimes there are multiple names for the same function. This is simply to make the job of the programmer quicker and easier. Or they are old names that are no longer used but kept around so that existing programs don't break.
|
||||
|
||||
The 3 primary windows of PySimpleGUI buttons and their names are:
|
||||
The 4 primary windows of PySimpleGUI buttons and their names are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `Button` = `SimpleButton`
|
||||
2. `ReadButton` = `RButton` = `ReadFormButton` (old style... use ReadButton instead)
|
||||
1. `Button`= `ReadButton` = `RButton` = `ReadFormButton` (old style... use Button instead)
|
||||
2. `CloseButton` = `CButton`
|
||||
3. `RealtimeButton`
|
||||
4. `DummyButton`
|
||||
|
||||
You will find the long-form in the older programs.
|
||||
You will find the long-form names in the older programs. ReadButton for example.
|
||||
|
||||
In Oct 2018, the definition of Button changed. Previously Button would CLOSE the window when clicked. It has been changed so the Button calls will leave the window open in exactly the same way as a ReadButton. They are the same calls now. To enables windows to be closed using buttons, a new button was added... `CloseButton` or `CButton`.
|
||||
|
||||
The most basic Button element call to use is `Button`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2152,9 +2165,10 @@ These Pre-made buttons are some of the most important elements of all because th
|
|||
**IMPORT NOTE ABOUT SHORTCUT BUTTONS**
|
||||
Prior to release 3.11.0, these buttons closed the window. Starting with 3.11 they will not close the window. They act like RButtons (return the button text and do not close the window)
|
||||
|
||||
If you are having trouble with these buttons closing your window, please check your installed version of PySimpleGUI by typing `pip list` at a command promt. Prior to 3.11 these buttons close your window.
|
||||
If you are having trouble with these buttons closing your window, please check your installed version of PySimpleGUI by typing `pip list` at a command prompt. Prior to 3.11 these buttons close your window.
|
||||
|
||||
Using older versions, if you want a Submit() button that does not close the window, then you would instead use RButton('Submit'). Using the new version, if you want a Submit button that closes the window like the sold Submit() call did, you would write that as `CloseButton('Submit')` or `CButton('Submit')`
|
||||
|
||||
Using older versions, if you want a Submit() button that does not close the window, then you would instead use RButton('Submit')
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2299,22 +2313,22 @@ window = sg.Window('Robotics Remote Control', auto_size_text=True).Layout(gui_ro
|
|||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Some place later in your code...
|
||||
# You need to perform a ReadNonBlocking on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it won't refresh.
|
||||
# You need to perform a Read or Refresh call on your window every now and then or
|
||||
# else it will apprear as if the program has locked up.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=0)
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.Close() # Don't forget to close your window!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This loop will read button values and print them. When one of the Realtime buttons is clicked, the call to `window.ReadNonBlocking` will return a button name matching the name on the button that was depressed or the key if there was a key assigned to the button. It will continue to return values as long as the button remains depressed. Once released, the ReadNonBlocking will return None for buttons until a button is again clicked.
|
||||
This loop will read button values and print them. When one of the Realtime buttons is clicked, the call to `window.Read` will return a button name matching the name on the button that was depressed or the key if there was a key assigned to the button. It will continue to return values as long as the button remains depressed. Once released, the Read will return timeout events until a button is again clicked.
|
||||
|
||||
**File Types**
|
||||
The `FileBrowse` & `SaveAs` buttons have an additional setting named `file_types`. This variable is used to filter the files shown in the file dialog box. The default value for this setting is
|
||||
|
|
@ -2679,7 +2693,7 @@ Let me say up front that the Table Element has Beta status. The reason is that s
|
|||
|
||||
### Read return values from Table Element
|
||||
|
||||
The values returned from a `Window.Read` or `Window.ReadNonBlocking` call for the Tree Element are a list of row numbers that are currently highlighted.
|
||||
The values returned from a `Window.Read` call for the Tree Element are a list of row numbers that are currently highlighted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Update Call
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2947,7 +2961,7 @@ There are 2 ways to keep a window open after the user has clicked a button. One
|
|||
|
||||
The `RButton` Element creates a button that when clicked will return control to the user, but will leave the window open and visible. This button is also used in Non-Blocking windows. The difference is in which call is made to read the window. The normal `Read` call with no parameters will block, a call with a `timeout` value of zero will not block.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `InputText` and `MultiLine` Elements will be **cleared** when performing a `ReadNonBlocking`. If you do not want your input field to be cleared after a `ReadNonBlocking` then you can set the `do_not_clear` parameter to True when creating those elements. The clear is turned on and off on an element by element basis.
|
||||
Note that `InputText` and `MultiLine` Elements will be **cleared** when performing a `Read`. If you do not want your input field to be cleared after a `Read` then you can set the `do_not_clear` parameter to True when creating those elements. The clear is turned on and off on an element by element basis.
|
||||
|
||||
The reasoning behind this is that Persistent Windows are often "forms". When "submitting" a form you want to have all of the fields left blank so the next entry of data will start with a fresh window. Also, when implementing a "Chat Window" type of interface, after each read / send of the chat data, you want the input field cleared. Think of it as a Texting application. Would you want to have to clear your previous text if you want to send a second text?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2986,7 +3000,7 @@ Let's say you had a device that you want to "poll" every 100ms. The "easy way
|
|||
```python
|
||||
# YOU SHOULD NOT DO THIS....
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking() # DO NOT USE THIS CALL ANYMORE
|
||||
read_my_hardware() # process my device here
|
||||
time.sleep(.1) # sleep 1/10 second
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -3518,6 +3532,7 @@ A MikeTheWatchGuy production... entirely responsible for this code.... unless it
|
|||
| 3.10.1 & 1.2.1 | Oct 20, 2018
|
||||
| 3.10.3 & 1.2.3 | Oct 23, 2018
|
||||
| 3.11.0 & 1.11.0 | Oct 28, 2018
|
||||
| 3.12.0 & 1.12.0 | Oct 28, 2018
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Release Notes
|
||||
|
|
@ -3740,6 +3755,13 @@ Emergency patch release... going out same day as previous release
|
|||
* Shortcut buttons no longer close windows!
|
||||
* Added CloseButton, CButton that closes the windows
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.12.0 & 1.12.0
|
||||
* Changed Button to be the same as ReadButton which means it will no longer close the window
|
||||
* All shortcut buttons no longer close the window
|
||||
* Updating a table clears selected rows information in return values
|
||||
* Progress meter uses new CloseButton
|
||||
* Popups use new CloseButton
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Upcoming
|
||||
Make suggestions people! Future release features
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue