2.3 Release
Large change to ReadMe and Recipes. Some functions renamed or a new name was created, leaving legacy name in place... for now. As long as docs steer people in the direction of the new names it'll be ok
This commit is contained in:
parent
f6f02b6f2b
commit
f3bee1687e
3 changed files with 626 additions and 371 deletions
181
Demo Recipes.py
181
Demo Recipes.py
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ import random
|
|||
import string
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as SG
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# A simple blocking form. Your best starter-form
|
||||
def SourceDestFolders():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Demo Source / Destination Folders', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Enter the Source and Destination folders')],
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,161 +12,158 @@ def SourceDestFolders():
|
|||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (source, dest) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
||||
button, (source, dest) = form.LayoutAndRead(form_rows)
|
||||
if button == 'Submit':
|
||||
# do something useful with the inputs
|
||||
SG.MsgBox('Submitted', 'The user entered source:', source, 'Destination folder:', dest, 'Using button', button)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
SG.MsgBoxError('Cancelled', 'User Cancelled')
|
||||
|
||||
# YOUR BEST STARTING POINT
|
||||
# This is a form showing you all of the basic Elements (widgets)
|
||||
# Some have a few of the optional parameters set, but there are more to choose from
|
||||
# You want to use the context manager because it will free up resources when you are finished
|
||||
# Use this especially if you are runningm multi-threaded
|
||||
# Where you free up resources is really important to tkinter
|
||||
def Everything():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)) as form:
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[SG.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25), text_color='blue')],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[SG.InputText()],
|
||||
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text shoulsd you decide not to type anything',
|
||||
scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[SG.InputCombo(['Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'], size=(20, 3)),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(35, 20), default_value=85)],
|
||||
[SG.Listbox(values=['Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'], size=(30, 6)),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=10)],
|
||||
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Dest'),
|
||||
SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel(), SG.SimpleButton('Customized', button_color=('white', 'green'))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'The results of the form are a lot of data! Get ready... ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should you decide not to use a context manager, then try this form as your starting point
|
||||
# Be aware that tkinter, which this is based on, is picky about who frees up resources, especially if
|
||||
# you are running multithreaded
|
||||
def Everything_NoContextManager():
|
||||
form = SG.FlexForm('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1))
|
||||
layout = [[SG.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25), text_color='blue')],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[SG.InputText()],
|
||||
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio!', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[SG.InputCombo(['choice 1', 'choice 2'], size=(20, 3))],
|
||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text shoulsd you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[SG.InputCombo(['Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'], size=(20, 3)), SG.Slider(range=(1,100), orientation='h', size=(35,20), default_value=85)],
|
||||
[SG.Listbox(values=['Listbox 1','Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'], size=(30,6)),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1,100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=10)],
|
||||
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.SimpleButton('Your very own button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1), text_color='red')],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel(), SG.SimpleButton('Customized', button_color=('white', 'green'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (values) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
del(form)
|
||||
|
||||
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'Here are the restults! There is one entry per input field ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def Everything():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)) as form:
|
||||
layout = [[SG.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25), text_color='blue')],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[SG.InputText()],
|
||||
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio!', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[SG.Spin(values=(1,2,3), initial_value=1, size=(2,1)), SG.T('Spinner 1', size=(20,1)),
|
||||
SG.Spin(values=(1,2,3), initial_value=1, size=(2,1)),SG.T('Spinner 2')],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[SG.InputCombo(['choice 1', 'choice 2'], size=(20, 3))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.SimpleButton('Custom Button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (values) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'The results of the form are a lot of data! Get ready... ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
def ProgressMeter():
|
||||
for i in range(1,10000):
|
||||
if not SG.EasyProgressMeter('My Meter', i+1, 10000): break
|
||||
# SG.Print(i)
|
||||
|
||||
def RunningTimer():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||
output_element = SG.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20))
|
||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non-blocking GUI with updates')],
|
||||
[output_element],
|
||||
[SG.SimpleButton('Quit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||
for i in range(1, 100):
|
||||
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||
if rc is None or rc[0] == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Persistant form. Does not close when Send button is clicked.
|
||||
# Normally all Simple Buttons cause forms to close
|
||||
# Blocking form that doesn't close
|
||||
def ChatBot():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Chat Window', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30, 2)) as form:
|
||||
form.AddRow(SG.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40, 1]))
|
||||
form.AddRow(SG.Output(size=(80, 20)))
|
||||
form.AddRow(SG.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), SG.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.BLUES[0])), SG.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.GREENS[0])))
|
||||
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[(SG.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40, 1]))],
|
||||
[SG.Output(size=(80, 20))],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), SG.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.BLUES[0])), SG.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.GREENS[0]))]]
|
||||
# notice this is NOT the usual LayoutAndRead call because you don't yet want to read the form
|
||||
# if you call LayoutAndRead from here, then you will miss the first button click
|
||||
form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'SEND':
|
||||
print(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Shows a form that's a running counter
|
||||
# this is the basic design pattern if you can keep your reading of the
|
||||
# form within the 'with' block. If your read occurs far away in your code from the form creation
|
||||
# then you will want to use the NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm example
|
||||
def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager():
|
||||
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||
output_element = SG.Text('',size=(10,2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red', justification='center')
|
||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates', justification='center')],
|
||||
[output_element],
|
||||
text_element = SG.Text('',size=(10,2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red', justification='center')
|
||||
layout = [[SG.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates', justification='center')],
|
||||
[text_element],
|
||||
[SG.T(' '*15), SG.Quit()]]
|
||||
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||
form.LayoutAndRead(layout, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1,500):
|
||||
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||
if rc is None: # if user closed the window using X
|
||||
break
|
||||
button, values = rc
|
||||
if button == 'Quit':
|
||||
text_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Use this context-manager-free version if your read of the form occurs far away in your code
|
||||
# from the form creation (call to LayoutAndRead)
|
||||
def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm():
|
||||
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
||||
form = SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True)
|
||||
output_element = SG.Text('',size=(8,2), font=('Helvetica', 20))
|
||||
text_element = SG.Text('',size=(10,2), font=('Helvetica', 20), justification='center')
|
||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates')],
|
||||
[output_element],
|
||||
[SG.Quit()]]
|
||||
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||
[text_element],
|
||||
[SG.T(' ' * 15), SG.Quit()]]
|
||||
form.LayoutAndRead(form_rows, non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1,50000):
|
||||
output_element.Update(f'{(i/100)/60:02d}:{(i/100)%60:02d}.{i%100:02d}')
|
||||
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||
if rc is None or rc[0] == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
text_element.Update(f'{(i//100)//60:02d}:{(i//100)%60:02d}.{i%100:02d}')
|
||||
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||
|
||||
del(form)
|
||||
|
||||
def DebugTest():
|
||||
# SG.Print('How about we print a bunch of random numbers?', , size=(90,40))
|
||||
for i in range (1,300):
|
||||
SG.Print(i, randint(1, 1000), end='', sep='-')
|
||||
|
||||
# SG.PrintClose()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
SG.SetOptions(border_width=1, element_padding=(4,6), font=("Helvetica", 10), button_color=('white', SG.BLUES[0]),
|
||||
progress_meter_border_depth=0)
|
||||
SourceDestFolders()
|
||||
# SG.SetOptions(border_width=1, font=("Helvetica", 10), button_color=('white', SG.BLUES[0]), slider_border_width=1)
|
||||
Everything_NoContextManager()
|
||||
Everything()
|
||||
NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager()
|
||||
NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm()
|
||||
ChatBot()
|
||||
Everything()
|
||||
ProgressMeter()
|
||||
SourceDestFolders()
|
||||
ChatBot()
|
||||
DebugTest()
|
||||
SG.MsgBox('Done with all recipes')
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
220
PySimpleGUI.py
220
PySimpleGUI.py
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING = (5,3) # Padding between elements (row, col) in
|
|||
DEFAULT_AUTOSIZE_TEXT = False
|
||||
DEFAULT_FONT = ("Helvetica", 10)
|
||||
DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION = 'left'
|
||||
DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH = 4
|
||||
DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH = 1
|
||||
DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME = 3 # time in seconds to show an autoclose form
|
||||
DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE = (80,20)
|
||||
MAX_SCROLLED_TEXT_BOX_HEIGHT = 50
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,8 @@ NICE_BUTTON_COLORS = ((GREENS[3], TANS[0]), ('#000000','#FFFFFF'),('#FFFFFF', '#
|
|||
# DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = (YELLOWS[0], PURPLES[0]) # (Text, Background) or (Color "on", Color) as a way to remember
|
||||
# DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = (GREENS[3], TANS[0]) # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
# DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = (YELLOWS[0], GREENS[4]) # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = ('white', 'black') # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = ('white', BLUES[0]) # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
# DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = ('white', 'black') # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
# DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = (YELLOWS[0], PURPLES[2]) # Foreground, Background (None, None) == System Default
|
||||
DEFAULT_ERROR_BUTTON_COLOR =("#FFFFFF", "#FF0000")
|
||||
DEFAULT_CANCEL_BUTTON_COLOR = (GREENS[3], TANS[0])
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,21 +44,35 @@ DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_COLOR = (GREENS[3], GREENS[3]) # a nice green progress
|
|||
# DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_COLOR = (BLUES[0], BLUES[0]) # a nice green progress bar
|
||||
# DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_COLOR = (PURPLES[1],PURPLES[0]) # a nice purple progress bar
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_SIZE = (35,25) # Size of Progress Bar (characters for length, pixels for width)
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH=2
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH=1
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_RELIEF = tk.SUNKEN
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_STYLE = 'default'
|
||||
DEFAULT_METER_ORIENTATION = 'Horizontal'
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_ORIENTATION = 'vertical'
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_BORDER_WIDTH=1
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_RELIEF = tk.SUNKEN
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE = tk.SINGLE
|
||||
SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE = tk.MULTIPLE
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE = 'multiple'
|
||||
SELECT_MODE_BROWSE = tk.BROWSE
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_BROWSE = 'browse'
|
||||
SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED = tk.EXTENDED
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED = 'extended'
|
||||
SELECT_MODE_SINGLE = tk.SINGLE
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_SINGLE = 'single'
|
||||
|
||||
# DEFAULT_METER_ORIENTATION = 'Vertical'
|
||||
# ----====----====----==== Constants the user should NOT f-with ====----====----====----#
|
||||
ThisRow = 555666777 # magic number
|
||||
# Progress Bar Relief Choices
|
||||
# -relief
|
||||
RAISED='raised'
|
||||
SUNKEN='sunken'
|
||||
FLAT='flat'
|
||||
RIDGE='ridge'
|
||||
GROOVE='groove'
|
||||
SOLID = 'solid'
|
||||
RELIEF_RAISED= 'raised'
|
||||
RELIEF_SUNKEN= 'sunken'
|
||||
RELIEF_FLAT= 'flat'
|
||||
RELIEF_RIDGE= 'ridge'
|
||||
RELIEF_GROOVE= 'groove'
|
||||
RELIEF_SOLID = 'solid'
|
||||
|
||||
PROGRESS_BAR_STYLES = ('default','winnative', 'clam', 'alt', 'classic', 'vista', 'xpnative')
|
||||
# DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON = ''
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,6 +114,8 @@ ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX = 8
|
|||
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN = 9
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON = 3
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_IMAGE = 30
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SLIDER = 10
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_LISTBOX = 11
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_OUTPUT = 300
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_PROGRESS_BAR = 200
|
||||
ELEM_TYPE_BLANK = 100
|
||||
|
|
@ -200,6 +217,37 @@ class InputCombo(Element):
|
|||
pass
|
||||
super().__del__()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
# Combo #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
class Listbox(Element):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, values, select_mode=None, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None):
|
||||
self.Values = values
|
||||
self.TKListBox = None
|
||||
if select_mode == LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_BROWSE:
|
||||
self.SelectMode = SELECT_MODE_BROWSE
|
||||
elif select_mode == LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED:
|
||||
self.SelectMode = SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED
|
||||
elif select_mode == LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE:
|
||||
self.SelectMode = SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE
|
||||
elif select_mode == LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_SINGLE:
|
||||
self.SelectMode = SELECT_MODE_SINGLE
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.SelectMode = DEFAULT_LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE
|
||||
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_LISTBOX, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text, font=font)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.TKListBox.__del__()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
super().__del__()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
# Radio #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
|
|
@ -361,11 +409,6 @@ class TKProgressBar():
|
|||
# New Type of Widget that's a Text Widget in disguise #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
class TKOutput(tk.Frame):
|
||||
''' Demonstrate python interpreter output in Tkinter Text widget
|
||||
type python expression in the entry, hit DoIt and see the results
|
||||
in the text pane.'''
|
||||
# previous_stderr = None
|
||||
# previous_stdout = None
|
||||
def __init__(self, parent, width, height, bd):
|
||||
tk.Frame.__init__(self, parent)
|
||||
self.output = tk.Text(parent, width=width, height=height, bd=bd)
|
||||
|
|
@ -552,6 +595,23 @@ class Image(Element):
|
|||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
super().__del__()
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
# Slider #
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
class Slider(Element):
|
||||
def __init__(self, range=(None,None), default_value=None, orientation=None, border_width=None, relief=None, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), font=None):
|
||||
self.TKScale = None
|
||||
self.Range = (1,10) if range == (None, None) else range
|
||||
self.DefaultValue = 5 if default_value is None else default_value
|
||||
self.Orientation = orientation if orientation else DEFAULT_SLIDER_ORIENTATION
|
||||
self.BorderWidth = border_width if border_width else DEFAULT_SLIDER_BORDER_WIDTH
|
||||
self.Relief = relief if relief else DEFAULT_SLIDER_RELIEF
|
||||
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SLIDER, scale=scale, size=size, font=font)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
super().__del__()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||
|
|
@ -629,9 +689,17 @@ class FlexForm:
|
|||
for row in rows:
|
||||
self.AddRow(*row)
|
||||
|
||||
def LayoutAndShow(self,rows):
|
||||
def Layout(self,rows):
|
||||
self.AddRows(rows)
|
||||
self.Show()
|
||||
|
||||
def LayoutAndShow(self,rows, non_blocking=False):
|
||||
self.AddRows(rows)
|
||||
self.Show(non_blocking=non_blocking)
|
||||
return self.ReturnValues
|
||||
|
||||
def LayoutAndRead(self,rows, non_blocking=False):
|
||||
self.AddRows(rows)
|
||||
self.Show(non_blocking=non_blocking)
|
||||
return self.ReturnValues
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------------------- ShowForm THIS IS IT! ------------------------- #
|
||||
|
|
@ -676,27 +744,41 @@ class FlexForm:
|
|||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def Read(self):
|
||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed: return None
|
||||
if not self.TKrootDestroyed and not self.Shown:
|
||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
if not self.Shown:
|
||||
self.Show()
|
||||
elif not self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.TKroot.mainloop()
|
||||
if self.RootNeedsDestroying:
|
||||
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||
return(BuildResults(self))
|
||||
return BuildResults(self)
|
||||
|
||||
def Refresh(self, Message=''):
|
||||
def ReadNonBlocking(self, Message=''):
|
||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
if Message:
|
||||
print(Message)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.TKroot.update()
|
||||
rc = self.TKroot.update()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||
return(BuildResults(self))
|
||||
return BuildResults(self)
|
||||
|
||||
# LEGACY version of ReadNonBlocking
|
||||
def Refresh(self, Message=''):
|
||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
if Message:
|
||||
print(Message)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
rc = self.TKroot.update()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||
return BuildResults(self)
|
||||
|
||||
def Close(self):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
@ -874,8 +956,14 @@ def InitializeResults(form):
|
|||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO:
|
||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_LISTBOX:
|
||||
r.append(None)
|
||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN:
|
||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||
r.append(element.DefaultValue)
|
||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SLIDER:
|
||||
r.append(element.DefaultValue)
|
||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||
results.append(r)
|
||||
form.Results=results
|
||||
|
|
@ -930,6 +1018,11 @@ def BuildResults(form):
|
|||
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||
input_values.append(value)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_LISTBOX:
|
||||
items=element.TKListbox.curselection()
|
||||
value = [element.Values[int(item)] for item in items]
|
||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||
input_values.append(value)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
||||
|
|
@ -937,6 +1030,13 @@ def BuildResults(form):
|
|||
value = 0
|
||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||
input_values.append(value)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SLIDER:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
value=element.TKIntVar.get()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
value = 0
|
||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||
input_values.append(value)
|
||||
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
value=element.TKText.get(1.0, tk.END)
|
||||
|
|
@ -947,7 +1047,7 @@ def BuildResults(form):
|
|||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||
input_values.append(value)
|
||||
|
||||
return_value = (button_pressed_text,input_values)
|
||||
return_value = button_pressed_text,input_values
|
||||
form.ReturnValues = return_value
|
||||
form.ResultsBuilt = True
|
||||
return return_value
|
||||
|
|
@ -957,6 +1057,8 @@ def BuildResults(form):
|
|||
# ===================================== TK CODE STARTS HERE ====================================================== #
|
||||
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #
|
||||
def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||
def CharWidthInPixels():
|
||||
return tkinter.font.Font().measure('A') # single character width
|
||||
master = MyFlexForm.TKroot
|
||||
# only set title on non-tabbed forms
|
||||
if not MyFlexForm.IsTabbedForm:
|
||||
|
|
@ -1081,6 +1183,18 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
|||
element.TKCombo['values'] = element.Values
|
||||
element.TKCombo.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||
element.TKCombo.current(0)
|
||||
# ------------------------- LISTBOX (Drop Down) element ------------------------- #
|
||||
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_LISTBOX:
|
||||
max_line_len = max([len(str(l)) for l in element.Values])
|
||||
if auto_size_text is False: width=element_size[0]
|
||||
else: width = max_line_len
|
||||
|
||||
element.TKStringVar = tk.StringVar()
|
||||
element.TKListbox= tk.Listbox(tk_row_frame, height=element_size[1], width=width, selectmode=element.SelectMode, font=font)
|
||||
for item in element.Values:
|
||||
element.TKListbox.insert(tk.END, item)
|
||||
element.TKListbox.selection_set(0,0)
|
||||
element.TKListbox.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||
# ------------------------- INPUT MULTI LINE element ------------------------- #
|
||||
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
||||
default_text = element.DefaultText
|
||||
|
|
@ -1162,6 +1276,21 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
|||
tktext_label.image = photo
|
||||
# tktext_label.configure(anchor=tk.NW, image=photo)
|
||||
tktext_label.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
|
||||
# ------------------------- SLIDER Box element ------------------------- #
|
||||
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SLIDER:
|
||||
slider_length = element_size[0] * CharWidthInPixels()
|
||||
slider_width = element_size[1]
|
||||
element.TKIntVar = tk.IntVar()
|
||||
element.TKIntVar.set(element.DefaultValue)
|
||||
if element.Orientation[0] == 'v':
|
||||
range_from = element.Range[1]
|
||||
range_to = element.Range[0]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
range_from = element.Range[0]
|
||||
range_to = element.Range[1]
|
||||
tkscale = tk.Scale(tk_row_frame, orient=element.Orientation, variable=element.TKIntVar, from_=range_from, to_=range_to, length=slider_length, width=slider_width , bd=element.BorderWidth, relief=element.Relief, font=font)
|
||||
# tktext_label.configure(anchor=tk.NW, image=photo)
|
||||
tkscale.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
|
||||
#............................DONE WITH ROW pack the row of widgets ..........................#
|
||||
# done with row, pack the row of widgets
|
||||
tk_row_frame.grid(row=row_num+2, sticky=tk.W, padx=DEFAULT_MARGINS[0])
|
||||
|
|
@ -1520,7 +1649,6 @@ def ProgressMeterUpdate(bar, value, *args):
|
|||
if bar.BarExpired: return False
|
||||
message, w, h = ConvertArgsToSingleString(*args)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
bar.TextToDisplay = message
|
||||
bar.CurrentValue = value
|
||||
rc = bar.UpdateBar(value)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1529,8 +1657,8 @@ def ProgressMeterUpdate(bar, value, *args):
|
|||
bar.ParentForm.Close()
|
||||
if bar.ParentForm.RootNeedsDestroying:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
bar.ParentForm.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||
bar.ParentForm.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||
except: pass
|
||||
bar.ParentForm.RootNeedsDestroying = False
|
||||
bar.ParentForm.__del__()
|
||||
|
|
@ -1841,9 +1969,12 @@ def SetGlobalIcon(icon):
|
|||
# ============================== SetOptions =========#
|
||||
# Sets the icon to be used by default #
|
||||
# ===================================================#
|
||||
def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), margins=(None,None), element_padding=(None,None),
|
||||
auto_size_text=None, font=None, border_width=None, autoclose_time=None, message_box_line_width=None,
|
||||
def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), margins=(None,None),
|
||||
element_padding=(None,None),auto_size_text=None, font=None, border_width=None,
|
||||
slider_border_width=None, slider_relief=None, slider_orientation=None,
|
||||
autoclose_time=None, message_box_line_width=None,
|
||||
progress_meter_border_depth=None, text_justification=None, debug_win_size=(None,None)):
|
||||
|
||||
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_SIZE
|
||||
global DEFAULT_MARGINS # Margins for each LEFT/RIGHT margin is first term
|
||||
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING # Padding between elements (row, col) in pixels
|
||||
|
|
@ -1856,6 +1987,9 @@ def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), ma
|
|||
global DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH
|
||||
global DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION
|
||||
global DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE
|
||||
global DEFAULT_SLIDER_BORDER_WIDTH
|
||||
global DEFAULT_SLIDER_RELIEF
|
||||
global DEFAULT_SLIDER_ORIENTATION
|
||||
global _my_windows
|
||||
|
||||
if icon:
|
||||
|
|
@ -1896,6 +2030,15 @@ def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), ma
|
|||
if progress_meter_border_depth != None:
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH = progress_meter_border_depth
|
||||
|
||||
if slider_border_width != None:
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_BORDER_WIDTH = slider_border_width
|
||||
|
||||
if slider_orientation != None:
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_ORIENTATION = slider_orientation
|
||||
|
||||
if slider_relief != None:
|
||||
DEFAULT_SLIDER_RELIEF = slider_relief
|
||||
|
||||
if text_justification != None:
|
||||
DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION = text_justification
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1904,12 +2047,21 @@ def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), ma
|
|||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ============================== sprint ======#
|
||||
# ============================== sprint ======#fddddddddddddddddddddddd
|
||||
# Is identical to the Scrolled Text Box #
|
||||
# Provides a crude 'print' mechanism but in a #
|
||||
# GUI environment #
|
||||
# ============================================#
|
||||
sprint=ScrolledTextBox
|
||||
|
||||
# Converts an object's contents into a nice printable string. Great for dumping debug data
|
||||
def ObjToString_old(obj):
|
||||
return str(obj.__class__) + '\n' + '\n'.join(
|
||||
(repr(item) + ' = ' + repr(obj.__dict__[item]) for item in sorted(obj.__dict__)))
|
||||
|
||||
def ObjToString(obj, extra=' '):
|
||||
return str(obj.__class__) + '\n' + '\n'.join(
|
||||
(extra + (str(item) + ' = ' +
|
||||
(ObjToString(obj.__dict__[item], extra + ' ') if hasattr(obj.__dict__[item], '__dict__') else str(
|
||||
obj.__dict__[item])))
|
||||
for item in sorted(obj.__dict__)))
|
||||
192
readme.md
192
readme.md
|
|
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
[](http://pepy.tech/project/pysimplegui) since Jul 11, 2018
|
||||
# PySimpleGUI
|
||||
(Ver 2.3)
|
||||
|
||||
This really is a simple GUI, but also powerfully customizable.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -345,32 +346,40 @@ If you have a SINGLE value being returned, it is written this way:
|
|||
## All Widgets / Elements
|
||||
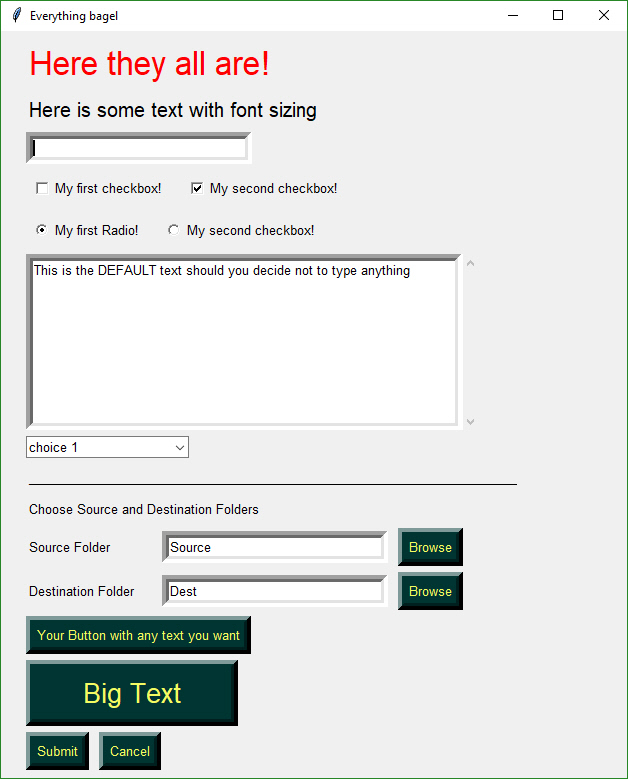
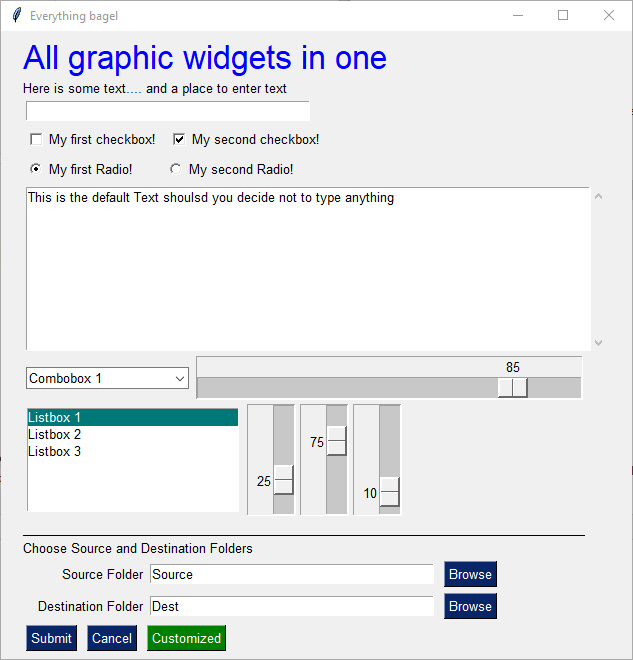
This code utilizes as many of the elements in one form as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
with FlexForm('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30,1)) as form:
|
||||
layout = [[Text('Here they all are!', size=(30,1), font=("Helvetica", 25), text_color='red')],
|
||||
[Text('Here is some text with font sizing', font=("Helvetica", 15))],
|
||||
[InputText()],
|
||||
[Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[Radio('My first Radio!', "RADIO1", default=True), Radio('My second checkbox!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[Multiline(DefaultText='This is the DEFAULT text should you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[InputCombo(['choice 1', 'choice 2'], size=(20, 3))],
|
||||
[Text('_' * 90, size=(60, 1))],
|
||||
[Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35,1))],
|
||||
[Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), InputText('Source'), FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), InputText('Dest'), FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SimpleButton('Your Button with any text you want')],
|
||||
[SimpleButton('Big Text', size=(12,1), font=("Helvetica", 20))],
|
||||
[Submit(), Cancel()]]
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)) as form:
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[SG.Text('All graphic widgets in one form!', size=(30, 1), font=("Helvetica", 25), text_color='blue')],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[SG.InputText()],
|
||||
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio! ', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text shoulsd you decide not to type anything',
|
||||
scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||
[SG.InputCombo(['Combobox 1', 'Combobox 2'], size=(20, 3)),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='h', size=(35, 20), default_value=85)],
|
||||
[SG.Listbox(values=['Listbox 1', 'Listbox 2', 'Listbox 3'], size=(30, 6)),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
SG.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(10, 20), default_value=10)],
|
||||
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Dest'),
|
||||
SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel(), SG.SimpleButton('Customized', button_color=('white', 'green'))]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
(button, (values)) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||
button, values = form.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
MsgBox('Results', 'You clicked {}'.format(button),'The values returned from form', values , font = ("Helvetica", 15))
|
||||
MsgBox('Results', 'You clicked {}'.format(button),'The values returned from form', values , font = ("Helvetica", 15))
|
||||
|
||||
This is a somewhat complex form with quite a bit of custom sizing to make things line up well. This is code you only have to write once. When looking at the code, remember that what you're seeing is a list of lists. Each row contains a list of Graphical Elements that are used to create the form.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
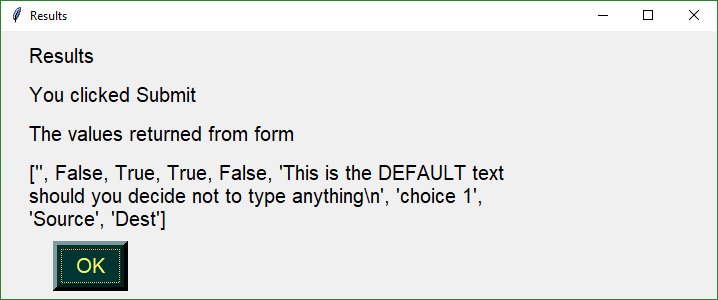
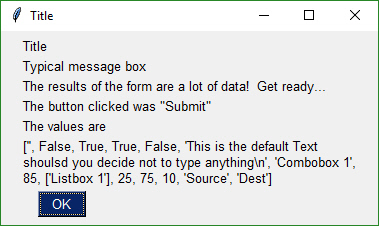
Clicking the Submit button caused the form call to return. The call to MsgBox resulted in this dialog box.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(button, (values)) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||
|
|
@ -437,6 +446,10 @@ Sizes can be set at the element level, or in this case, the size variables apply
|
|||
|
||||
In addition to `size` there is a `scale` option. `scale` will take the Element's size and scale it up or down depending on the scale value. `scale=(1,1)` doesn't change the Element's size. `scale=(2,1)` will set the Element's size to be twice as wide as the size setting.
|
||||
|
||||
There are a couple of widgets where one of the size values is in pixels rather than characters. This is true for Progress Meters and Sliders. The second parameter is the 'height' in pixels.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### FlexForm - form-level variables overview
|
||||
A summary of the variables that can be changed when a FlexForm is created
|
||||
|
|
@ -466,6 +479,8 @@ A summary of the variables that can be changed when a FlexForm is created
|
|||
Close form
|
||||
Checkboxes
|
||||
Radio Buttons
|
||||
Listbox
|
||||
Slider
|
||||
Multi-line Text Input
|
||||
Scroll-able Output
|
||||
Progress Bar
|
||||
|
|
@ -608,6 +623,68 @@ Also known as a drop-down list. Only required parameter is the list of choices.
|
|||
size - (width, height) of element in characters
|
||||
auto_size_text - Bool. True if size should fit the text length
|
||||
|
||||
#### Listbox Element
|
||||
The standard listbox like you'll find in most GUIs. Note that the return values from this element will be a ***list of results, not a single result***. This is because the user can select more than 1 item from the list (if you set the right mode).
|
||||
|
||||
Listbox(values,
|
||||
select_mode=None,
|
||||
scale=(None, None),
|
||||
size=(None, None),
|
||||
auto_size_text=None,
|
||||
font=None)
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
values - Choices to be displayed. List of strings
|
||||
select_mode - Defines how to list is to operate.
|
||||
Choices include constants or strings:
|
||||
Constants version:
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_BROWSE
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_EXTENDED
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_MULTIPLE
|
||||
LISTBOX_SELECT_MODE_SINGLE - the default
|
||||
Strings version:
|
||||
'browse'
|
||||
'extended'
|
||||
'multiple'
|
||||
'single'
|
||||
scale - Amount to scale size by
|
||||
size - (width, height) of element in characters
|
||||
auto_size_text - Bool. True if size should fit the text length
|
||||
|
||||
The `select_mode` option can be a string or a constant value defined as a variable. Generally speaking strings are used for these kinds of options.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Slider Element
|
||||
Sliders have a couple of slider-specific settings as well as appearance settings. Examples include the `orientation` and `range` settings.
|
||||
|
||||
Slider(range=(None,None),
|
||||
default_value=None,
|
||||
orientation=None,
|
||||
border_width=None,
|
||||
relief=None,
|
||||
scale=(None, None),
|
||||
size=(None, None),
|
||||
font=None):
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
range - (min, max) slider's range
|
||||
default_value - default setting (within range)
|
||||
orientation - 'horizontal' or 'vertical' ('h' or 'v' work)
|
||||
border_width - how deep the widget looks
|
||||
relief - relief style. Values are same as progress meter relief values. Can be a constant or a string:
|
||||
RELIEF_RAISED= 'raised'
|
||||
RELIEF_SUNKEN= 'sunken'
|
||||
RELIEF_FLAT= 'flat'
|
||||
RELIEF_RIDGE= 'ridge'
|
||||
RELIEF_GROOVE= 'groove'
|
||||
RELIEF_SOLID = 'solid'
|
||||
scale - Amount to scale size by
|
||||
size - (width, height) of element in characters
|
||||
auto_size_text - Bool. True if size should fit the text
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Radio Button Element
|
||||
Creates one radio button that is assigned to a group of radio buttons. Only 1 of the buttons in the group can be selected at any one time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -812,21 +889,25 @@ The Output Element is a re-direction of Stdout. Anything "printed" will be disp
|
|||
|
||||
Here's a complete solution for a chat-window using an Async form with an Output Element
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as g
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as SG
|
||||
# Blocking form that doesn't close
|
||||
def ChatBot():
|
||||
with SG.FlexForm('Chat Window', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30, 2)) as form:
|
||||
layout = [[(SG.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40, 1]))],
|
||||
[SG.Output(size=(80, 20))],
|
||||
[SG.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), SG.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.BLUES[0])), SG.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.GREENS[0]))]]
|
||||
# notice this is NOT the usual LayoutAndRead call because you don't yet want to read the form
|
||||
# if you call LayoutAndRead from here, then you will miss the first button click
|
||||
form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'SEND':
|
||||
print(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
with g.FlexForm('Chat Window', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30, 2)) as form:
|
||||
form.AddRow(g.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40,1]))
|
||||
form.AddRow(g.Output(size=(80, 20)))
|
||||
form.AddRow(g.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), g.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(g.YELLOWS[0], g.BLUES[0])), g.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(g.YELLOWS[0], g.GREENS[0])))
|
||||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and printing it --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = form.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'SEND':
|
||||
print(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('Exiting the form now')
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Tabbed Forms
|
||||
|
|
@ -848,11 +929,16 @@ Let's have some fun customizing! Make PySimpleGUI look the way you want it to l
|
|||
margins=(None,None),
|
||||
element_padding=(None,None),
|
||||
auto_size_text=None,
|
||||
font=None, border_width=None,
|
||||
font=None,
|
||||
border_width=None,
|
||||
slider_border_width=None,
|
||||
slider_relief=None,
|
||||
slider_orientation=None,
|
||||
autoclose_time=None,
|
||||
message_box_line_width=None,
|
||||
progress_meter_border_depth=None,
|
||||
text_justification=None):
|
||||
text_justification=None,
|
||||
debug_win_size=(None,None):
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation of parameters
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -864,10 +950,14 @@ Explanation of parameters
|
|||
auto_size_text - autosize the elements to fit their text
|
||||
font - font used for elements
|
||||
border_width - amount of bezel or border around sunken or raised elements
|
||||
slider_border_width - changes the way sliders look
|
||||
slider_relief - changes the way sliders look
|
||||
slider_orientation - changes orientation of slider
|
||||
autoclose_time - time in seconds for autoclose boxes
|
||||
message_box_line_width - number of characers in a line of text in message boxes
|
||||
progress_meter_border_depth - amount of border around raised or lowered progress meters
|
||||
text_justification - justification to use on Text Elements. Values are strings - 'left', 'right', 'center'
|
||||
debug_win_size - size of the Print output window
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
These settings apply to all forms `SetOptions`. The Row options and Element options will take precedence over these settings. Settings can be thought of as levels of settings with the Form-level being the highest and the Element-level the lowest. Thus the levels are:
|
||||
|
|
@ -879,7 +969,7 @@ These settings apply to all forms `SetOptions`. The Row options and Element opt
|
|||
Each lower level overrides the settings of the higher level
|
||||
|
||||
## Asynchronous (Non-Blocking) Forms
|
||||
So you want to be a wizard do ya? Well go boldly! While the majority of GUIs are a simple exercise to "collect input values and return with them", there are instances where we want to continue executing while the form is open. These are "asynchronous" forms and require special options, new SDK calls, and **great care**. With asynchronous forms the form is shown, user input is read, but your code keeps right on chugging. YOUR responsibility is to call `PySimpleGUI.refresh` on a periodic basis. Once a second or more will produce a reasonably snappy GUI.
|
||||
So you want to be a wizard do ya? Well go boldly! While the majority of GUIs are a simple exercise to "collect input values and return with them", there are instances where we want to continue executing while the form is open. These are "asynchronous" forms and require special options, new SDK calls, and **great care**. With asynchronous forms the form is shown, user input is read, but your code keeps right on chugging. YOUR responsibility is to call `PySimpleGUI.ReadNonBlocking` on a periodic basis. Once a second or more will produce a reasonably snappy GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
When do you use a non-blocking form? A couple of examples are
|
||||
* A media file player like an MP3 player
|
||||
|
|
@ -887,11 +977,11 @@ When do you use a non-blocking form? A couple of examples are
|
|||
* Progress Meters - when you want to make your own progress meters
|
||||
* Output using print to a scrolled text element. Good for debugging.
|
||||
|
||||
Word of warning... version 2.2, the currently released, and upcoming version 2.3 differ in the return code for the `Refresh` call. Previously the function returned 2 values, except when the form is closed using the "X" which returned a single value of `None`. The *new* way is that Refresh always returns 2 values. If the user closed the form with the "X" then the return values will be None, None. You will want to key off the second value to catch this case.
|
||||
Word of warning... version 2.2, the currently released, and upcoming version 2.3 differ in the return code for the `ReadNonBlocking` call. Previously the function returned 2 values, except when the form is closed using the "X" which returned a single value of `None`. The *new* way is that `ReadNonBlocking` always returns 2 values. If the user closed the form with the "X" then the return values will be None, None. You will want to key off the second value to catch this case.
|
||||
The proper code to check if the user has exited the form will be a polling-loop that looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = form.Refresh()
|
||||
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -906,12 +996,12 @@ Setup
|
|||
|
||||
Periodic refresh
|
||||
|
||||
form.Refresh()
|
||||
form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
If you need to close the form
|
||||
|
||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than the usual `form.LayoutAndShow()` call, we're manually adding the rows (doing the layout) and then showing the form. After the form is shown, you simply call `form.Refresh()` every now and then.
|
||||
Rather than the usual `form.LayoutAndShow()` call, we're manually adding the rows (doing the layout) and then showing the form. After the form is shown, you simply call `form.ReadNonBlocking()` every now and then.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are ready to close the form (assuming the form wasn't closed by the user or a button click) you simply call `form.CloseNonBlockingForm()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -928,7 +1018,7 @@ We're going to make a form and update one of the elements of that form every .01
|
|||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||
for i in range(1, 100):
|
||||
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||
button, values = form.Refresh()
|
||||
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
|
@ -937,7 +1027,7 @@ We're going to make a form and update one of the elements of that form every .01
|
|||
|
||||
What we have here is the same sequence of function calls as in the description. Get a form, add rows to it, show the form, and then refresh it every now and then.
|
||||
|
||||
The new thing in this example is the call use of the Update method for the Text Element. The first thing we do inside the loop is "update" the text element that we made earlier. This changes the value of the text field on the form. The new value will be displayed when `form.Refresh()` is called.
|
||||
The new thing in this example is the call use of the Update method for the Text Element. The first thing we do inside the loop is "update" the text element that we made earlier. This changes the value of the text field on the form. The new value will be displayed when `form.ReadNonBlocking()` is called.
|
||||
|
||||
Note the `else` statement on the for loop. This is needed because we're about to exit the loop while the form is still open. The user has not closed the form using the X nor a button so it's up to the caller to close the form using `CloseNonBlockingForm`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -984,7 +1074,7 @@ While not an "issue" this is a ***stern warning***
|
|||
|
||||
A MikeTheWatchGuy production... entirely responsible for this code.... unless it causes you trouble in which case I'm not at all responsible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Versioning
|
||||
## Versions
|
||||
|Version | Description |
|
||||
|--|--|
|
||||
| 1.0.9 | July 10, 2018 - Initial Release |
|
||||
|
|
@ -992,7 +1082,22 @@ A MikeTheWatchGuy production... entirely responsible for this code.... unless it
|
|||
| 2.0.0 | July 16, 2018 - ALL optional parameters renamed from CamelCase to all_lower_case
|
||||
| 2.1.1 | July 18, 2018 - Global settings exposed, fixes
|
||||
| 2.2.0| July 20, 2018 - Image Elements, Print output
|
||||
| 2.3.0 | July XX, 2018 - Changed form.Read return codes, Slider Elements, Listbox element
|
||||
| 2.3.0 | July XX, 2018 - Changed form.Read return codes, Slider Elements, Listbox element. Renamed some methods but left legacy calls in place for now.
|
||||
|
||||
### Release Notes
|
||||
2.3 - Sliders, Listbox's and Image elements (oh my!) This Readme is being updated with Listbox and Image elements. If you want to use them, they behave as one would expect. Note use of pixels in some parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
If using Progress Meters, avoid cancelling them when you have another window open. It could lead to future windows being blank. It's being worked on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Upcoming
|
||||
Make suggestions people! Future release features
|
||||
|
||||
Button images. Ability to replace boring rectangular buttons with your own images.
|
||||
|
||||
Columns. How multiple columns would be specified in the SDK interface are still being designed.
|
||||
|
||||
Progress Meters - Replace custom meter with tkinter meter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Code Condition
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1044,3 +1149,4 @@ The PySimpleGUI window that the results are shown in is an 'input' field which m
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue