LOTS of changes and new additions
Text justification for Text Elems NEW Image Element OutputFlush renamed to Refresh More shorthand functions - Combo, Dropdown, Drop, EasyPrint - output of stdout, stderr to a window
This commit is contained in:
parent
fb2fe90d37
commit
f331661a3a
3 changed files with 352 additions and 147 deletions
|
|
@ -1,19 +1,21 @@
|
||||||
import time
|
import time
|
||||||
|
from random import randint
|
||||||
|
import random
|
||||||
|
import string
|
||||||
import PySimpleGUI as SG
|
import PySimpleGUI as SG
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def SourceDestFolders():
|
def SourceDestFolders():
|
||||||
with SG.FlexForm('Demo Source / Destination Folders', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
with SG.FlexForm('Demo Source / Destination Folders', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Enter the Source and Destination folders')],
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Enter the Source and Destination folders')],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders')],
|
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Source')],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
|
||||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
(button, (source, dest)) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
button, (source, dest) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
||||||
if button == 'Submit':
|
if button == 'Submit':
|
||||||
# do something useful with the inputs
|
# do something useful with the inputs
|
||||||
SG.MsgBox('Submitted', 'The user entered source:', source, 'Destination folder:', dest)
|
SG.MsgBox('Submitted', 'The user entered source:', source, 'Destination folder:', dest, 'Using button', button)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
SG.MsgBoxError('Cancelled', 'User Cancelled')
|
SG.MsgBoxError('Cancelled', 'User Cancelled')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -33,9 +35,9 @@ def Everything_NoContextManager():
|
||||||
[SG.SimpleButton('Your very own button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
[SG.SimpleButton('Your very own button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
||||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
(button, (values)) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
button, (values) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'The results of the form are a lot of data! Get ready... ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'Here are the restults! There is one entry per input field ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def Everything():
|
def Everything():
|
||||||
|
|
@ -45,16 +47,18 @@ def Everything():
|
||||||
[SG.InputText()],
|
[SG.InputText()],
|
||||||
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
[SG.Checkbox('My first checkbox!'), SG.Checkbox('My second checkbox!', default=True)],
|
||||||
[SG.Radio('My first Radio!', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
[SG.Radio('My first Radio!', "RADIO1", default=True), SG.Radio('My second Radio!', "RADIO1")],
|
||||||
|
[SG.Spin(values=(1,2,3), initial_value=1, size=(2,1)), SG.T('Spinner 1', size=(20,1)),
|
||||||
|
SG.Spin(values=(1,2,3), initial_value=1, size=(2,1)),SG.T('Spinner 2')],
|
||||||
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
[SG.Multiline(default_text='This is the default Text should you decide not to type anything', scale=(2, 10))],
|
||||||
[SG.InputCombo(['choice 1', 'choice 2'], size=(20, 3))],
|
[SG.InputCombo(['choice 1', 'choice 2'], size=(20, 3))],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
[SG.Text('_' * 100, size=(70, 1))],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
[SG.Text('Choose Source and Destination Folders', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
[SG.Text('Source Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Source'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||||
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
[SG.Text('Destination Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False), SG.InputText('Dest'), SG.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||||
[SG.SimpleButton('Your very own button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
[SG.SimpleButton('Custom Button', button_color=('white', 'green'))],
|
||||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
(button, (values)) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
button, (values) = form.LayoutAndShow(layout)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'The results of the form are a lot of data! Get ready... ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
SG.MsgBox('Title', 'Typical message box', 'The results of the form are a lot of data! Get ready... ', 'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button), 'The values are', values)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -62,6 +66,26 @@ def ProgressMeter():
|
||||||
for i in range(1,10000):
|
for i in range(1,10000):
|
||||||
if not SG.EasyProgressMeter('My Meter', i+1, 10000): break
|
if not SG.EasyProgressMeter('My Meter', i+1, 10000): break
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def RunningTimer():
|
||||||
|
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||||
|
output_element = SG.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20))
|
||||||
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non-blocking GUI with updates')],
|
||||||
|
[output_element],
|
||||||
|
[SG.SimpleButton('Quit')]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||||
|
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||||
|
for i in range(1, 100):
|
||||||
|
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||||
|
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||||
|
if rc is None or rc[0] == 'Quit':
|
||||||
|
break
|
||||||
|
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Persistant form. Does not close when Send button is clicked.
|
# Persistant form. Does not close when Send button is clicked.
|
||||||
# Normally all Simple Buttons cause forms to close
|
# Normally all Simple Buttons cause forms to close
|
||||||
|
|
@ -70,7 +94,7 @@ def ChatBot():
|
||||||
form.AddRow(SG.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40, 1]))
|
form.AddRow(SG.Text('This is where standard out is being routed', size=[40, 1]))
|
||||||
form.AddRow(SG.Output(size=(80, 20)))
|
form.AddRow(SG.Output(size=(80, 20)))
|
||||||
form.AddRow(SG.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), SG.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.BLUES[0])), SG.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.GREENS[0])))
|
form.AddRow(SG.Multiline(size=(70, 5), enter_submits=True), SG.ReadFormButton('SEND', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.BLUES[0])), SG.SimpleButton('EXIT', button_color=(SG.YELLOWS[0], SG.GREENS[0])))
|
||||||
(button, value) = form.Read()
|
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||||
while True:
|
while True:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -78,22 +102,22 @@ def ChatBot():
|
||||||
print(value)
|
print(value)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
break
|
break
|
||||||
(button, value) = form.Read()
|
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager():
|
def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager():
|
||||||
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
||||||
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||||
output_element = SG.Text('',size=(8,2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red')
|
output_element = SG.Text('',size=(10,2), font=('Helvetica', 20), text_color='red', justification='center')
|
||||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('None blocking GUI with updates')],
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non blocking GUI with updates', justification='center')],
|
||||||
[output_element],
|
[output_element],
|
||||||
[SG.Quit()]]
|
[SG.T(' '*15), SG.Quit()]]
|
||||||
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for i in range(1,500):
|
for i in range(1,500):
|
||||||
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||||
rc = form.OutputFlush()
|
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||||
if rc is None: # if user closed the window using X
|
if rc is None: # if user closed the window using X
|
||||||
break
|
break
|
||||||
button, values = rc
|
button, values = rc
|
||||||
|
|
@ -117,11 +141,8 @@ def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm():
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for i in range(1,50000):
|
for i in range(1,50000):
|
||||||
output_element.Update(f'{(i/100)/60:02d}:{(i/100)%60:02d}.{i%100:02d}')
|
output_element.Update(f'{(i/100)/60:02d}:{(i/100)%60:02d}.{i%100:02d}')
|
||||||
rc = form.OutputFlush()
|
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||||
if rc is None: # if user closed the window using X
|
if rc is None or rc[0] == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
button, values = rc
|
|
||||||
if button == 'Quit':
|
|
||||||
break
|
break
|
||||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -129,40 +150,24 @@ def NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm():
|
||||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def NonBlockingScrolledPrintForm():
|
def DebugTest():
|
||||||
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
# SG.Print('How about we print a bunch of random numbers?', , size=(90,40))
|
||||||
form = SG.FlexForm('Scrolled Print', auto_size_text=True, font=('Courier New', 12))
|
for i in range (1,300):
|
||||||
output_element = SG.Output(size=(42,10))
|
SG.Print(i, randint(1, 1000), end='', sep='-')
|
||||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Scrolled print output')],
|
|
||||||
[output_element],
|
|
||||||
[SG.Quit()]]
|
|
||||||
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
|
||||||
form.Show(non_blocking=True) # Show a ;non-blocking form, returns immediately
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for i in range(1,50000):
|
|
||||||
print(f'{i} ', end="") # all print output will go to the scrolled text box
|
|
||||||
# must call OutputFlush on a periodic basis to keep GUI alive
|
|
||||||
rc = form.OutputFlush()
|
|
||||||
if rc is None: # if user closed the window using X
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
button, values = rc
|
|
||||||
if button == 'Quit': # if user cliced Quit button
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
else: # if the loop finished then need to close the form for the user
|
|
||||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# SG.PrintClose()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def main():
|
def main():
|
||||||
SG.SetOptions(border_width=4, element_padding=(4,6), font=("Helvetica", 10), button_color=('white', SG.BLUES[0]),
|
SG.SetOptions(border_width=1, element_padding=(4,6), font=("Helvetica", 10), button_color=('white', SG.BLUES[0]),
|
||||||
progress_meter_border_depth=4)
|
progress_meter_border_depth=0)
|
||||||
SourceDestFolders()
|
SourceDestFolders()
|
||||||
|
Everything()
|
||||||
|
NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager()
|
||||||
ProgressMeter()
|
ProgressMeter()
|
||||||
ChatBot()
|
ChatBot()
|
||||||
NonBlockingScrolledPrintForm()
|
DebugTest()
|
||||||
NonBlockingPeriodicUpdateForm_ContextManager()
|
|
||||||
Everything_NoContextManager()
|
|
||||||
Everything()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||||
main()
|
main()
|
||||||
|
exit(69)
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
257
PySimpleGUI.py
257
PySimpleGUI.py
|
|
@ -16,9 +16,10 @@ DEFAULT_MARGINS = (10,5) # Margins for each LEFT/RIGHT margin is
|
||||||
DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING = (5,3) # Padding between elements (row, col) in pixels
|
DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING = (5,3) # Padding between elements (row, col) in pixels
|
||||||
DEFAULT_AUTOSIZE_TEXT = False
|
DEFAULT_AUTOSIZE_TEXT = False
|
||||||
DEFAULT_FONT = ("Helvetica", 10)
|
DEFAULT_FONT = ("Helvetica", 10)
|
||||||
|
DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION = 'left'
|
||||||
DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH = 4
|
DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH = 4
|
||||||
DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME = 3 # time in seconds to show an autoclose form
|
DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME = 3 # time in seconds to show an autoclose form
|
||||||
|
DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE = (80,20)
|
||||||
MAX_SCROLLED_TEXT_BOX_HEIGHT = 50
|
MAX_SCROLLED_TEXT_BOX_HEIGHT = 50
|
||||||
#################### COLOR STUFF ####################
|
#################### COLOR STUFF ####################
|
||||||
BLUES = ("#082567","#0A37A3","#00345B")
|
BLUES = ("#082567","#0A37A3","#00345B")
|
||||||
|
|
@ -89,17 +90,18 @@ READ_FORM = 7
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------- Element types ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- Element types ------------------------- #
|
||||||
# class ElementType(Enum):
|
# class ElementType(Enum):
|
||||||
TEXT = 1
|
ELEM_TYPE_TEXT = 1
|
||||||
INPUT_TEXT = 20
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_TEXT = 20
|
||||||
INPUT_COMBO = 21
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO = 21
|
||||||
INPUT_RADIO = 5
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_RADIO = 5
|
||||||
INPUT_MULTILINE = 7
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE = 7
|
||||||
INPUT_CHECKBOX = 8
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX = 8
|
||||||
INPUT_SPIN = 9
|
ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN = 9
|
||||||
BUTTON = 3
|
ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON = 3
|
||||||
OUTPUT = 300
|
ELEM_TYPE_IMAGE = 30
|
||||||
PROGRESS_BAR = 200
|
ELEM_TYPE_OUTPUT = 300
|
||||||
BLANK = 100
|
ELEM_TYPE_PROGRESS_BAR = 200
|
||||||
|
ELEM_TYPE_BLANK = 100
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------- MsgBox Buttons Types ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- MsgBox Buttons Types ------------------------- #
|
||||||
MSG_BOX_YES_NO = 1
|
MSG_BOX_YES_NO = 1
|
||||||
|
|
@ -131,6 +133,7 @@ class Element():
|
||||||
self.TKIntVar = None
|
self.TKIntVar = None
|
||||||
self.TKText = None
|
self.TKText = None
|
||||||
self.TKEntry = None
|
self.TKEntry = None
|
||||||
|
self.TKImage = None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
self.ParentForm=None
|
self.ParentForm=None
|
||||||
self.TextInputDefault = None
|
self.TextInputDefault = None
|
||||||
|
|
@ -163,7 +166,7 @@ class InputText(Element):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, default_text ='', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, password_char=''):
|
def __init__(self, default_text ='', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, password_char=''):
|
||||||
self.DefaultText = default_text
|
self.DefaultText = default_text
|
||||||
self.PasswordCharacter = password_char
|
self.PasswordCharacter = password_char
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_TEXT, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_TEXT, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def ReturnKeyHandler(self, event):
|
def ReturnKeyHandler(self, event):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -171,7 +174,7 @@ class InputText(Element):
|
||||||
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
||||||
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
||||||
for element in row.Elements:
|
for element in row.Elements:
|
||||||
if element.Type == BUTTON:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
||||||
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
@ -187,7 +190,7 @@ class InputCombo(Element):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, values, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
def __init__(self, values, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
self.Values = values
|
self.Values = values
|
||||||
self.TKComboBox = None
|
self.TKComboBox = None
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_COMBO, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -207,7 +210,7 @@ class Radio(Element):
|
||||||
self.TKRadio = None
|
self.TKRadio = None
|
||||||
self.GroupID = group_id
|
self.GroupID = group_id
|
||||||
self.Value = None
|
self.Value = None
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_RADIO, scale, size, auto_size_text, font)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_RADIO, scale, size, auto_size_text, font)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -227,7 +230,7 @@ class Checkbox(Element):
|
||||||
self.Value = None
|
self.Value = None
|
||||||
self.TKCheckbox = None
|
self.TKCheckbox = None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_CHECKBOX, scale, size, auto_size_text, font)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX, scale, size, auto_size_text, font)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -248,7 +251,7 @@ class Spin(Element):
|
||||||
self.Values = values
|
self.Values = values
|
||||||
self.DefaultValue = initial_value
|
self.DefaultValue = initial_value
|
||||||
self.TKSpinBox = None
|
self.TKSpinBox = None
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_SPIN, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -265,7 +268,7 @@ class Multiline(Element):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, default_text='', enter_submits = False, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
def __init__(self, default_text='', enter_submits = False, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
self.DefaultText = default_text
|
self.DefaultText = default_text
|
||||||
self.EnterSubmits = enter_submits
|
self.EnterSubmits = enter_submits
|
||||||
super().__init__(INPUT_MULTILINE, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def ReturnKeyHandler(self, event):
|
def ReturnKeyHandler(self, event):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -273,7 +276,7 @@ class Multiline(Element):
|
||||||
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
||||||
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
||||||
for element in row.Elements:
|
for element in row.Elements:
|
||||||
if element.Type == BUTTON:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
||||||
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
@ -285,12 +288,13 @@ class Multiline(Element):
|
||||||
# Text #
|
# Text #
|
||||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||||
class Text(Element):
|
class Text(Element):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None):
|
def __init__(self, text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None, justification=None):
|
||||||
self.DisplayText = text
|
self.DisplayText = text
|
||||||
self.TextColor = text_color if text_color else 'black'
|
self.TextColor = text_color if text_color else 'black'
|
||||||
|
self.Justification = justification if justification else DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION
|
||||||
# self.Font = Font if Font else DEFAULT_FONT
|
# self.Font = Font if Font else DEFAULT_FONT
|
||||||
# i=1/0
|
# i=1/0
|
||||||
super().__init__(TEXT, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font if font else DEFAULT_FONT)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_TEXT, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font if font else DEFAULT_FONT)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def Update(self, NewValue):
|
def Update(self, NewValue):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -394,11 +398,12 @@ in the text pane.'''
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
sys.stdout = self.previous_stdout
|
sys.stdout = self.previous_stdout
|
||||||
|
sys.stderr = self.previous_stderr
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class Output(Element):
|
class Output(Element):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None)):
|
def __init__(self, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None)):
|
||||||
self.TKOut = None
|
self.TKOut = None
|
||||||
super().__init__(OUTPUT, scale, size)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_OUTPUT, scale, size)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -419,7 +424,7 @@ class Button(Element):
|
||||||
self.ButtonText = button_text
|
self.ButtonText = button_text
|
||||||
self.ButtonColor = button_color if button_color else DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR
|
self.ButtonColor = button_color if button_color else DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR
|
||||||
self.UserData = None
|
self.UserData = None
|
||||||
super().__init__(BUTTON, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON, scale, size, auto_size_text, font=font)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------- Button Callback ------- #
|
# ------- Button Callback ------- #
|
||||||
|
|
@ -478,7 +483,7 @@ class Button(Element):
|
||||||
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
# search through this form and find the first button that will exit the form
|
||||||
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
for row in MyForm.Rows:
|
||||||
for element in row.Elements:
|
for element in row.Elements:
|
||||||
if element.Type == BUTTON:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
if element.BType == CLOSES_WIN or element.BType == READ_FORM:
|
||||||
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
element.ButtonCallBack()
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
@ -506,7 +511,7 @@ class ProgressBar(Element):
|
||||||
self.BorderWidth = border_width if border_width else DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH
|
self.BorderWidth = border_width if border_width else DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH
|
||||||
self.Relief = relief if relief else DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_RELIEF
|
self.Relief = relief if relief else DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_RELIEF
|
||||||
self.BarExpired = False
|
self.BarExpired = False
|
||||||
super().__init__(PROGRESS_BAR, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_PROGRESS_BAR, scale, size, auto_size_text)
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def UpdateBar(self, current_count):
|
def UpdateBar(self, current_count):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -524,7 +529,7 @@ class ProgressBar(Element):
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
self.ParentForm.TKroot.update()
|
self.ParentForm.TKroot.update()
|
||||||
except:
|
except:
|
||||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
# _my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||||
return False
|
return False
|
||||||
return True
|
return True
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -535,6 +540,20 @@ class ProgressBar(Element):
|
||||||
pass
|
pass
|
||||||
super().__del__()
|
super().__del__()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||||
|
# Image #
|
||||||
|
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||||
|
class Image(Element):
|
||||||
|
def __init__(self, filename, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
|
self.Filename = filename
|
||||||
|
super().__init__(ELEM_TYPE_IMAGE, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
||||||
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
|
super().__del__()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||||
# Row CLASS #
|
# Row CLASS #
|
||||||
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
|
||||||
|
|
@ -589,6 +608,7 @@ class FlexForm:
|
||||||
self.RootNeedsDestroying = False
|
self.RootNeedsDestroying = False
|
||||||
self.Shown = False
|
self.Shown = False
|
||||||
self.ReturnValues = None
|
self.ReturnValues = None
|
||||||
|
self.ResultsBuilt = False
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------- Add ONE Row to Form ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- Add ONE Row to Form ------------------------- #
|
||||||
def AddRow(self, *args, auto_size_text=None):
|
def AddRow(self, *args, auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -663,31 +683,37 @@ class FlexForm:
|
||||||
self.TKroot.mainloop()
|
self.TKroot.mainloop()
|
||||||
if self.RootNeedsDestroying:
|
if self.RootNeedsDestroying:
|
||||||
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||||
|
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||||
return(BuildResults(self))
|
return(BuildResults(self))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def OutputFlush(self, Message=''):
|
def Refresh(self, Message=''):
|
||||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed: return None
|
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||||
|
return None
|
||||||
if Message:
|
if Message:
|
||||||
print(Message)
|
print(Message)
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
self.TKroot.update()
|
self.TKroot.update()
|
||||||
except:
|
except:
|
||||||
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
||||||
|
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||||
return(BuildResults(self))
|
return(BuildResults(self))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def Close(self):
|
def Close(self):
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
self.TKroot.update()
|
self.TKroot.update()
|
||||||
except: pass
|
except: pass
|
||||||
|
if not self.NonBlocking:
|
||||||
results = BuildResults(self)
|
results = BuildResults(self)
|
||||||
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
if self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||||
return results
|
return None
|
||||||
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
||||||
self.RootNeedsDestroying = True
|
self.RootNeedsDestroying = True
|
||||||
return results
|
return None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def CloseNonBlockingForm(self):
|
def CloseNonBlockingForm(self):
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||||
|
except: pass
|
||||||
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def OnClosingCallback(self):
|
def OnClosingCallback(self):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -735,6 +761,7 @@ class UberForm():
|
||||||
if not self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
if not self.TKrootDestroyed:
|
||||||
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
self.TKrootDestroyed = True
|
||||||
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
self.TKroot.destroy()
|
||||||
|
_my_windows.NumOpenWindows -= 1 * (_my_windows.NumOpenWindows != 0) # decrement if not 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __del__(self):
|
def __del__(self):
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
@ -750,12 +777,21 @@ def In(default_text ='', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=N
|
||||||
def Input(default_text ='', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
def Input(default_text ='', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
return InputText(default_text=default_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
return InputText(default_text=default_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------- TEXT Element lazy functions ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT COMBO Element lazy functions ------------------------- #
|
||||||
def Txt(display_text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None):
|
def Combo(values, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
return Text(display_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text, font=font, text_color=text_color)
|
return InputCombo(values=values, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def T(display_text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None):
|
def DropDown(values, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
return Text(display_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text, font=font, text_color=text_color)
|
return InputCombo(values=values, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def Drop(values, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None):
|
||||||
|
return InputCombo(values=values, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text)
|
||||||
|
# ------------------------- TEXT Element lazy functions ------------------------- #
|
||||||
|
def Txt(display_text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None, justification=None):
|
||||||
|
return Text(display_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text, font=font, text_color=text_color, justification=justification)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def T(display_text, scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, font=None, text_color=None, justification=None):
|
||||||
|
return Text(display_text, scale=scale, size=size, auto_size_text=auto_size_text, font=font, text_color=text_color, justification=justification)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ------------------------- FOLDER BROWSE Element lazy function ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- FOLDER BROWSE Element lazy function ------------------------- #
|
||||||
def FolderBrowse(target=(ThisRow, -1), button_text='Browse', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, button_color=None):
|
def FolderBrowse(target=(ThisRow, -1), button_text='Browse', scale=(None, None), size=(None, None), auto_size_text=None, button_color=None):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -815,28 +851,30 @@ def InitializeResults(form):
|
||||||
for row_num,row in enumerate(form.Rows):
|
for row_num,row in enumerate(form.Rows):
|
||||||
r = []
|
r = []
|
||||||
for element in row.Elements:
|
for element in row.Elements:
|
||||||
if element.Type == TEXT:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_TEXT:
|
||||||
r.append(None)
|
r.append(None)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_TEXT:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_IMAGE:
|
||||||
|
r.append(None)
|
||||||
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_TEXT:
|
||||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
||||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == BUTTON:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
r.append(False)
|
r.append(False)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == PROGRESS_BAR:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_PROGRESS_BAR:
|
||||||
r.append(None)
|
r.append(None)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
||||||
r.append(element.InitialState)
|
r.append(element.InitialState)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(element.InitialState)
|
return_vals.append(element.InitialState)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_RADIO:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_RADIO:
|
||||||
r.append(element.InitialState)
|
r.append(element.InitialState)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(element.InitialState)
|
return_vals.append(element.InitialState)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_COMBO:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO:
|
||||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_SPIN:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN:
|
||||||
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
r.append(element.TextInputDefault)
|
||||||
return_vals.append(None)
|
return_vals.append(None)
|
||||||
results.append(r)
|
results.append(r)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -870,38 +908,39 @@ def BuildResults(form):
|
||||||
input_values = []
|
input_values = []
|
||||||
for row_num,row in enumerate(form.Rows):
|
for row_num,row in enumerate(form.Rows):
|
||||||
for col_num, element in enumerate(row.Elements):
|
for col_num, element in enumerate(row.Elements):
|
||||||
if element.Type == INPUT_TEXT:
|
if element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_TEXT:
|
||||||
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||||
input_values.append(value)
|
input_values.append(value)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
||||||
value=element.TKIntVar.get()
|
value=element.TKIntVar.get()
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||||
input_values.append(value != 0)
|
input_values.append(value != 0)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_RADIO:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_RADIO:
|
||||||
RadVar=element.TKIntVar.get()
|
RadVar=element.TKIntVar.get()
|
||||||
this_rowcol = EncodeRadioRowCol(row_num,col_num)
|
this_rowcol = EncodeRadioRowCol(row_num,col_num)
|
||||||
value = RadVar == this_rowcol
|
value = RadVar == this_rowcol
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||||
input_values.append(value)
|
input_values.append(value)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == BUTTON:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
if results[row_num][col_num] is True:
|
if results[row_num][col_num] is True:
|
||||||
button_pressed_text = element.ButtonText
|
button_pressed_text = element.ButtonText
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = False
|
results[row_num][col_num] = False
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_COMBO:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO:
|
||||||
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||||
input_values.append(value)
|
input_values.append(value)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_SPIN:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN:
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
value=element.TKStringVar.get()
|
||||||
except:
|
except:
|
||||||
value = 0
|
value = 0
|
||||||
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
results[row_num][col_num] = value
|
||||||
input_values.append(value)
|
input_values.append(value)
|
||||||
elif element.Type == INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
elif element.Type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
value=element.TKText.get(1.0, tk.END)
|
value=element.TKText.get(1.0, tk.END)
|
||||||
|
if not form.NonBlocking:
|
||||||
element.TKText.delete('1.0', tk.END)
|
element.TKText.delete('1.0', tk.END)
|
||||||
except:
|
except:
|
||||||
value = None
|
value = None
|
||||||
|
|
@ -964,7 +1003,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
element_size = (int(element_size[0] * MyFlexForm.Scale[0]), int(element_size[1] * MyFlexForm.Scale[1]))
|
element_size = (int(element_size[0] * MyFlexForm.Scale[0]), int(element_size[1] * MyFlexForm.Scale[1]))
|
||||||
# ------------------------- TEXT element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- TEXT element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
element_type = element.Type
|
element_type = element.Type
|
||||||
if element_type == TEXT:
|
if element_type == ELEM_TYPE_TEXT:
|
||||||
display_text = element.DisplayText # text to display
|
display_text = element.DisplayText # text to display
|
||||||
if auto_size_text is False:
|
if auto_size_text is False:
|
||||||
width, height=element_size
|
width, height=element_size
|
||||||
|
|
@ -983,14 +1022,16 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
stringvar.set(display_text)
|
stringvar.set(display_text)
|
||||||
if auto_size_text:
|
if auto_size_text:
|
||||||
width = 0
|
width = 0
|
||||||
tktext_label = tk.Label(tk_row_frame,anchor=tk.NW, textvariable=stringvar, width=width, height=height, justify=tk.LEFT, bd=border_depth, fg=element.TextColor)
|
justify = tk.LEFT if element.Justification == 'left' else tk.CENTER if element.Justification == 'center' else tk.RIGHT
|
||||||
|
anchor = tk.NW if element.Justification == 'left' else tk.N if element.Justification == 'center' else tk.NE
|
||||||
|
tktext_label = tk.Label(tk_row_frame, textvariable=stringvar, width=width, height=height, justify=justify, bd=border_depth, fg=element.TextColor)
|
||||||
# tktext_label = tk.Label(tk_row_frame,anchor=tk.NW, text=display_text, width=width, height=height, justify=tk.LEFT, bd=border_depth)
|
# tktext_label = tk.Label(tk_row_frame,anchor=tk.NW, text=display_text, width=width, height=height, justify=tk.LEFT, bd=border_depth)
|
||||||
# Set wrap-length for text (in PIXELS) == PAIN IN THE ASS
|
# Set wrap-length for text (in PIXELS) == PAIN IN THE ASS
|
||||||
wraplen = tktext_label.winfo_reqwidth() # width of widget in Pixels
|
wraplen = tktext_label.winfo_reqwidth() # width of widget in Pixels
|
||||||
tktext_label.configure(anchor=tk.NW, font=font, wraplen=wraplen*2 ) # set wrap to width of widget
|
tktext_label.configure(anchor=anchor, font=font, wraplen=wraplen*2 ) # set wrap to width of widget
|
||||||
tktext_label.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
|
tktext_label.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
|
||||||
# ------------------------- BUTTON element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- BUTTON element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == BUTTON:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_BUTTON:
|
||||||
element.Location = (row_num, col_num)
|
element.Location = (row_num, col_num)
|
||||||
btext = element.ButtonText
|
btext = element.ButtonText
|
||||||
btype = element.BType
|
btype = element.BType
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1019,7 +1060,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
element.TKButton.focus_set()
|
element.TKButton.focus_set()
|
||||||
MyFlexForm.TKroot.focus_force()
|
MyFlexForm.TKroot.focus_force()
|
||||||
# ------------------------- INPUT (Single Line) element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT (Single Line) element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_TEXT:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_TEXT:
|
||||||
default_text = element.DefaultText
|
default_text = element.DefaultText
|
||||||
element.TKStringVar = tk.StringVar()
|
element.TKStringVar = tk.StringVar()
|
||||||
element.TKStringVar.set(default_text)
|
element.TKStringVar.set(default_text)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1031,7 +1072,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
focus_set = True
|
focus_set = True
|
||||||
element.TKEntry.focus_set()
|
element.TKEntry.focus_set()
|
||||||
# ------------------------- COMBO BOX (Drop Down) element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- COMBO BOX (Drop Down) element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_COMBO:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_COMBO:
|
||||||
max_line_len = max([len(str(l)) for l in element.Values])
|
max_line_len = max([len(str(l)) for l in element.Values])
|
||||||
if auto_size_text is False: width=element_size[0]
|
if auto_size_text is False: width=element_size[0]
|
||||||
else: width = max_line_len
|
else: width = max_line_len
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1041,7 +1082,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
element.TKCombo.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
element.TKCombo.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
element.TKCombo.current(0)
|
element.TKCombo.current(0)
|
||||||
# ------------------------- INPUT MULTI LINE element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT MULTI LINE element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_MULTILINE:
|
||||||
default_text = element.DefaultText
|
default_text = element.DefaultText
|
||||||
width, height = element_size
|
width, height = element_size
|
||||||
element.TKText = tk.scrolledtext.ScrolledText(tk_row_frame, width=width, height=height, wrap='word', bd=border_depth,font=font)
|
element.TKText = tk.scrolledtext.ScrolledText(tk_row_frame, width=width, height=height, wrap='word', bd=border_depth,font=font)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1053,7 +1094,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
focus_set = True
|
focus_set = True
|
||||||
element.TKText.focus_set()
|
element.TKText.focus_set()
|
||||||
# ------------------------- INPUT CHECKBOX element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT CHECKBOX element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_CHECKBOX:
|
||||||
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
||||||
default_value = element.InitialState
|
default_value = element.InitialState
|
||||||
element.TKIntVar = tk.IntVar()
|
element.TKIntVar = tk.IntVar()
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1061,7 +1102,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
element.TKCheckbutton = tk.Checkbutton(tk_row_frame, anchor=tk.NW, text=element.Text, width=width, variable=element.TKIntVar, bd=border_depth, font=font)
|
element.TKCheckbutton = tk.Checkbutton(tk_row_frame, anchor=tk.NW, text=element.Text, width=width, variable=element.TKIntVar, bd=border_depth, font=font)
|
||||||
element.TKCheckbutton.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
element.TKCheckbutton.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
# ------------------------- PROGRESS BAR element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- PROGRESS BAR element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == PROGRESS_BAR:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_PROGRESS_BAR:
|
||||||
# save this form because it must be 'updated' (refreshed) solely for the purpose of updating bar
|
# save this form because it must be 'updated' (refreshed) solely for the purpose of updating bar
|
||||||
width = element_size[0]
|
width = element_size[0]
|
||||||
fnt = tkinter.font.Font()
|
fnt = tkinter.font.Font()
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1079,7 +1120,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
s = ttk.Style()
|
s = ttk.Style()
|
||||||
element.TKProgressBar.TKCanvas.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
element.TKProgressBar.TKCanvas.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
# ------------------------- INPUT RADIO BUTTON element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT RADIO BUTTON element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_RADIO:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_RADIO:
|
||||||
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
||||||
default_value = element.InitialState
|
default_value = element.InitialState
|
||||||
ID = element.GroupID
|
ID = element.GroupID
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1097,7 +1138,7 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
variable=element.TKIntVar, value=value, bd=border_depth, font=font)
|
variable=element.TKIntVar, value=value, bd=border_depth, font=font)
|
||||||
element.TKRadio.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
element.TKRadio.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
# ------------------------- INPUT SPIN Box element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- INPUT SPIN Box element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == INPUT_SPIN:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_INPUT_SPIN:
|
||||||
width, height = element_size
|
width, height = element_size
|
||||||
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
width = 0 if auto_size_text else element_size[0]
|
||||||
element.TKStringVar = tk.StringVar()
|
element.TKStringVar = tk.StringVar()
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1106,9 +1147,21 @@ def ConvertFlexToTK(MyFlexForm):
|
||||||
element.TKSpinBox.configure(font=font) # set wrap to width of widget
|
element.TKSpinBox.configure(font=font) # set wrap to width of widget
|
||||||
element.TKSpinBox.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
element.TKSpinBox.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
# ------------------------- OUTPUT element ------------------------- #
|
# ------------------------- OUTPUT element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
elif element_type == OUTPUT:
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_OUTPUT:
|
||||||
width, height = element_size
|
width, height = element_size
|
||||||
element.TKOut = TKOutput(tk_row_frame, width=width, height=height, bd=border_depth)
|
element.TKOut = TKOutput(tk_row_frame, width=width, height=height, bd=border_depth)
|
||||||
|
element.TKOut.pack(side=tk.LEFT,padx=element.Pad[0], pady=element.Pad[1])
|
||||||
|
# ------------------------- IMAGE Box element ------------------------- #
|
||||||
|
elif element_type == ELEM_TYPE_IMAGE:
|
||||||
|
photo = tk.PhotoImage(file=element.Filename)
|
||||||
|
if element_size == (None, None) or element_size == None or element_size == MyFlexForm.DefaultElementSize:
|
||||||
|
width, height = photo.width(), photo.height()
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
width, height = element_size
|
||||||
|
tktext_label = tk.Label(tk_row_frame, image=photo, width=width, height=height, bd=border_depth)
|
||||||
|
tktext_label.image = photo
|
||||||
|
# tktext_label.configure(anchor=tk.NW, image=photo)
|
||||||
|
tktext_label.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
|
||||||
#............................DONE WITH ROW pack the row of widgets ..........................#
|
#............................DONE WITH ROW pack the row of widgets ..........................#
|
||||||
# done with row, pack the row of widgets
|
# done with row, pack the row of widgets
|
||||||
tk_row_frame.grid(row=row_num+2, sticky=tk.W, padx=DEFAULT_MARGINS[0])
|
tk_row_frame.grid(row=row_num+2, sticky=tk.W, padx=DEFAULT_MARGINS[0])
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1619,9 +1672,66 @@ def GetComplimentaryHex(color):
|
||||||
comp_color = 0xFFFFFF ^ color
|
comp_color = 0xFFFFFF ^ color
|
||||||
# convert the color back to hex by prefixing a #
|
# convert the color back to hex by prefixing a #
|
||||||
comp_color = "#%06X" % comp_color
|
comp_color = "#%06X" % comp_color
|
||||||
# return the result
|
|
||||||
return comp_color
|
return comp_color
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# ======================== EasyPrint =====#
|
||||||
|
# ===================================================#
|
||||||
|
_easy_print_data = None # global variable... I'm cheating
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class DebugWin():
|
||||||
|
def __init__(self, size=(None, None)):
|
||||||
|
# Show a form that's a running counter
|
||||||
|
win_size = size if size !=(None, None) else DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE
|
||||||
|
self.form = FlexForm('Debug Window', auto_size_text=True, font=('Courier New', 12))
|
||||||
|
self.output_element = Output(size=win_size)
|
||||||
|
self.form_rows = [[Text('EasyPrint Output')],
|
||||||
|
[self.output_element],
|
||||||
|
[Quit()]]
|
||||||
|
self.form.AddRows(self.form_rows)
|
||||||
|
self.form.Show(non_blocking=True) # Show a ;non-blocking form, returns immediately
|
||||||
|
return
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def Print(self, *args, end=None, sep=None):
|
||||||
|
sepchar = sep if sep is not None else ' '
|
||||||
|
endchar = end if end is not None else '\n'
|
||||||
|
print(*args, sep=sepchar, end=endchar)
|
||||||
|
# for a in args:
|
||||||
|
# msg = str(a)
|
||||||
|
# print(msg, end="", sep=sepchar)
|
||||||
|
# print(1, 2, 3, sep='-')
|
||||||
|
# if end is None:
|
||||||
|
# print("")
|
||||||
|
self.form.Refresh()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def Close(self):
|
||||||
|
self.form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||||
|
self.form.__del__()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def Print(*args, size=(None,None), end=None, sep=None):
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint(*args, size=size, end=end, sep=sep)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def PrintClose():
|
||||||
|
EasyPrintClose()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def eprint(*args, size=(None,None), end=None, sep=None):
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint(*args, size=size, end=end, sep=sep)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def EasyPrint(*args, size=(None,None), end=None, sep=None):
|
||||||
|
if 'easy_print_data' not in EasyPrint.__dict__: # use a function property to save DebugWin object (static variable)
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint.easy_print_data = DebugWin(size=size)
|
||||||
|
if EasyPrint.easy_print_data is None:
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint.easy_print_data = DebugWin(size=size)
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint.easy_print_data.Print(*args, end=end, sep=sep)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def EasyPrintClose():
|
||||||
|
if 'easy_print_data' in EasyPrint.__dict__:
|
||||||
|
if EasyPrint.easy_print_data is not None:
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint.easy_print_data.Close()
|
||||||
|
EasyPrint.easy_print_data = None
|
||||||
|
# del EasyPrint.easy_print_data
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ======================== Scrolled Text Box =====#
|
# ======================== Scrolled Text Box =====#
|
||||||
# ===================================================#
|
# ===================================================#
|
||||||
def ScrolledTextBox(*args, button_color=None, yes_no=False, auto_close=False, auto_close_duration=None, height=None):
|
def ScrolledTextBox(*args, button_color=None, yes_no=False, auto_close=False, auto_close_duration=None, height=None):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1733,7 +1843,7 @@ def SetGlobalIcon(icon):
|
||||||
# ===================================================#
|
# ===================================================#
|
||||||
def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), margins=(None,None), element_padding=(None,None),
|
def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), margins=(None,None), element_padding=(None,None),
|
||||||
auto_size_text=None, font=None, border_width=None, autoclose_time=None, message_box_line_width=None,
|
auto_size_text=None, font=None, border_width=None, autoclose_time=None, message_box_line_width=None,
|
||||||
progress_meter_border_depth=None):
|
progress_meter_border_depth=None, text_justification=None, debug_win_size=(None,None)):
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_SIZE
|
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_SIZE
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_MARGINS # Margins for each LEFT/RIGHT margin is first term
|
global DEFAULT_MARGINS # Margins for each LEFT/RIGHT margin is first term
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING # Padding between elements (row, col) in pixels
|
global DEFAULT_ELEMENT_PADDING # Padding between elements (row, col) in pixels
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1744,6 +1854,8 @@ def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), ma
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR
|
global DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR
|
||||||
global MESSAGE_BOX_LINE_WIDTH
|
global MESSAGE_BOX_LINE_WIDTH
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH
|
global DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH
|
||||||
|
global DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION
|
||||||
|
global DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE
|
||||||
global _my_windows
|
global _my_windows
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if icon:
|
if icon:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1784,16 +1896,15 @@ def SetOptions(icon=None, button_color=(None,None), element_size=(None,None), ma
|
||||||
if progress_meter_border_depth != None:
|
if progress_meter_border_depth != None:
|
||||||
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH = progress_meter_border_depth
|
DEFAULT_PROGRESS_BAR_BORDER_WIDTH = progress_meter_border_depth
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if text_justification != None:
|
||||||
|
DEFAULT_TEXT_JUSTIFICATION = text_justification
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if debug_win_size != (None,None):
|
||||||
|
DEFAULT_DEBUG_WINDOW_SIZE = debug_win_size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return True
|
return True
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ============================== SetButtonColor =====#
|
|
||||||
# Sets the defaul button color #
|
|
||||||
# ===================================================#
|
|
||||||
def SetButtonColor(foreground, background):
|
|
||||||
global DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
DEFAULT_BUTTON_COLOR = (foreground, background)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# ============================== sprint ======#
|
# ============================== sprint ======#
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
127
readme.md
127
readme.md
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||||
|
[](http://pepy.tech/project/pysimplegui)
|
||||||
# PySimpleGUI
|
# PySimpleGUI
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This really is a simple GUI, but also powerfully customizable.
|
This really is a simple GUI, but also powerfully customizable.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -9,9 +9,17 @@ This really is a simple GUI, but also powerfully customizable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
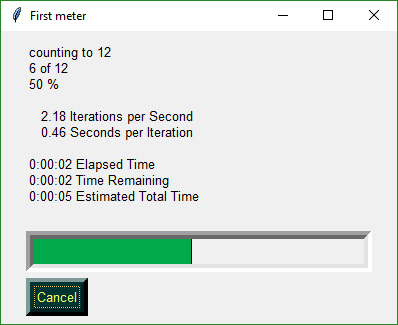
Add a Progress Meter to your code with ONE LINE of code
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
EasyProgressMeter('My meter title', current_value, max value)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I was frustrated by having to deal with the dos prompt when I had a powerful Windows machine right in front of me. Why is it SO difficult to do even the simplest of input/output to a window in Python??
|
I was frustrated by having to deal with the dos prompt when I had a powerful Windows machine right in front of me. Why is it SO difficult to do even the simplest of input/output to a window in Python??
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are a number of 'easy to use' Python GUIs, but they're quite limiting. PySimpleGUI tried to take the best of packages like `EasyGUI`(no longer maintained) and `WxSimpleGUI` (a great package, but was too limited for my application). `PySimpleGUI` provides similar single-call-message-box solutions as you'll see.
|
There are a number of 'easy to use' Python GUIs, but they're **very** limiting. PySimpleGUI takes the best of packages like `EasyGUI`(no longer maintained) and `WxSimpleGUI` (a great package, but limited). The difference between these and PySimpleGUI is that in addition to getting those simple Message Boxes you also get the ability to make your own forms that are highly customizeable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Every call has optional parameters so that you can change the look and feel. Don't like the button color? It's easy to change by adding a button_color parameter to your widget.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
GUI Packages with more functionality, like QT and WxPython, require configuring and can take a ***week*** to get *reasonably familiar* with the interfaces.
|
GUI Packages with more functionality, like QT and WxPython, require configuring and can take a ***week*** to get *reasonably familiar* with the interfaces.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -19,14 +27,6 @@ With a simple GUI, it becomes practical to "associate" .py files with the python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `PySimpleGUI` solution is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desired result be achieved in as little and as simple code as possible? This was the mantra used to create PySimpleGUI. How can it be done is a Python-like way?
|
The `PySimpleGUI` solution is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desired result be achieved in as little and as simple code as possible? This was the mantra used to create PySimpleGUI. How can it be done is a Python-like way?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
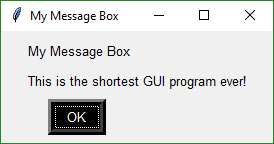
You can add a GUI to your command line with a single line of code. With 3 or 4 lines of code you can add a fully customized GUI. And for you Machine Learning folks out there, a **single line** progress meter call that you can drop into any loop to get a graphic like this one:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Features of PySimpleGUI include:
|
Features of PySimpleGUI include:
|
||||||
Text
|
Text
|
||||||
Single Line Input
|
Single Line Input
|
||||||
|
|
@ -241,6 +241,12 @@ With a little trickery you can provide a way to break out of your loop using the
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This is the FUN part of the programming of this GUI. In order to really get the most out of the API, you should be using an IDE that supports auto complete or will show you the definition of the function. This will make customizing go smoother.
|
This is the FUN part of the programming of this GUI. In order to really get the most out of the API, you should be using an IDE that supports auto complete or will show you the definition of the function. This will make customizing go smoother.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This first section on custom forms is for your typical, blocking, non-persistant form. By this I mean, when you "show" the form, the function will not return until the user has clicked a button or closed the window. When this happens, the form's window will be automatically closed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Two other types of forms exist.
|
||||||
|
1. Persistent form - rather than closing on button clicks, the show form function returns and the form continues to be visible. This is good for applications like a chat window.
|
||||||
|
2. Asynchronous form - the trickiest of the lot. Great care must be exercised. Examples are an MP3 player or status dashboard. Async forms are updated (refreshed) on a periodic basis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It's both not enjoyable nor helpful to immediately jump into tweaking each and every little thing available to you. Let's start with a basic Browse for a file and do something with it.
|
It's both not enjoyable nor helpful to immediately jump into tweaking each and every little thing available to you. Let's start with a basic Browse for a file and do something with it.
|
||||||
# Copy these design patterns!
|
# Copy these design patterns!
|
||||||
## Pattern 1 - With Context Manager
|
## Pattern 1 - With Context Manager
|
||||||
|
|
@ -249,7 +255,7 @@ It's both not enjoyable nor helpful to immediately jump into tweaking each and e
|
||||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
||||||
[SG.InputText(), SG.FileBrowse()],
|
[SG.InputText(), SG.FileBrowse()],
|
||||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||||
(button, (source_filename, )) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
button, (source_filename, ) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Pattern 2 - No Context Manager
|
## Pattern 2 - No Context Manager
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -257,7 +263,7 @@ It's both not enjoyable nor helpful to immediately jump into tweaking each and e
|
||||||
form_rows = [[SG.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
||||||
[SG.InputText(), SG.FileBrowse()],
|
[SG.InputText(), SG.FileBrowse()],
|
||||||
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
[SG.Submit(), SG.Cancel()]]
|
||||||
(button, (source_filename,)) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
button, (source_filename,) = form.LayoutAndShow(form_rows)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
These 2 design patters both produce this custom form:
|
These 2 design patters both produce this custom form:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -266,7 +272,7 @@ These 2 design patters both produce this custom form:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It's important to use the "with" context manager so that resources are freed as quickly as possible, using the currently executing thread. PySimpleGUI uses `tkinter`. `tkinter` is very picky about who releases objects and when. The `with` takes care of disposing of everything properly for you.
|
It's important to use the "with" context manager so that resources are freed as quickly as possible, using the currently executing thread. PySimpleGUI uses `tkinter`. `tkinter` is very picky about who releases objects and when. The `with` takes care of disposing of everything properly for you.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The second design pattern is not context manager based. There are times when the context manager hides errors. If you are struggling with an unknown error, try modifying the code to run without a context manager.
|
The second design pattern is not context manager based. If you are struggling with an unknown error, try modifying the code to run without a context manager. To do so, you simple remove the with, stick the form on the front of that statement, and un-indent the with-block code.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You will use these design patterns or code templates for all of your "normal" (blocking) types of input forms. Copy it and modify it to suit your needs. This is the quickest way to get your code up and running with PySimpleGUI. This is the most basic / normal of the design patterns.
|
You will use these design patterns or code templates for all of your "normal" (blocking) types of input forms. Copy it and modify it to suit your needs. This is the quickest way to get your code up and running with PySimpleGUI. This is the most basic / normal of the design patterns.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -480,7 +486,16 @@ The most basic element is the Text element. It simply displays text. Many of t
|
||||||
size=(None, None),
|
size=(None, None),
|
||||||
auto_size_text=None,
|
auto_size_text=None,
|
||||||
font=None,
|
font=None,
|
||||||
text_color=None)
|
text_color=None,
|
||||||
|
justification=None)
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Text - The text that's displayed
|
||||||
|
size - Element's size
|
||||||
|
auto_size_text - Bool. Change width to match size of text
|
||||||
|
font - Font name and size to use
|
||||||
|
text_color - text color
|
||||||
|
justification - Justification for the text. String - 'left', 'right', 'center'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Some commonly used elements have 'shorthand' versions of the functions to make the code more compact. The functions `T` and `Txt` are the same as calling `Text`.
|
Some commonly used elements have 'shorthand' versions of the functions to make the code more compact. The functions `T` and `Txt` are the same as calling `Text`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -814,7 +829,7 @@ Each of the tabs of the form is in fact a form. The same steps are taken to cre
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Global Settings
|
## Global Settings
|
||||||
**Global Settings**
|
**Global Settings**
|
||||||
You can set the global settings using the function `PySimpleGUI.SetOptions`. Each option has an optional parameter that's used to set it.
|
Let's have some fun customizing! Make PySimpleGUI look the way you want it to look. You can set the global settings using the function `PySimpleGUI.SetOptions`. Each option has an optional parameter that's used to set it.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SetOptions(icon=None,
|
SetOptions(icon=None,
|
||||||
button_color=(None,None),
|
button_color=(None,None),
|
||||||
|
|
@ -825,7 +840,8 @@ You can set the global settings using the function `PySimpleGUI.SetOptions`. Ea
|
||||||
font=None, border_width=None,
|
font=None, border_width=None,
|
||||||
autoclose_time=None,
|
autoclose_time=None,
|
||||||
message_box_line_width=None,
|
message_box_line_width=None,
|
||||||
progress_meter_border_depth=None):
|
progress_meter_border_depth=None,
|
||||||
|
text_justification=None):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Explanation of parameters
|
Explanation of parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -840,6 +856,7 @@ Explanation of parameters
|
||||||
autoclose_time - time in seconds for autoclose boxes
|
autoclose_time - time in seconds for autoclose boxes
|
||||||
message_box_line_width - number of characers in a line of text in message boxes
|
message_box_line_width - number of characers in a line of text in message boxes
|
||||||
progress_meter_border_depth - amount of border around raised or lowered progress meters
|
progress_meter_border_depth - amount of border around raised or lowered progress meters
|
||||||
|
text_justification - justification to use on Text Elements. Values are strings - 'left', 'right', 'center'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
These settings apply to all forms `SetOptions`. The Row options and Element options will take precedence over these settings. Settings can be thought of as levels of settings with the Form-level being the highest and the Element-level the lowest. Thus the levels are:
|
These settings apply to all forms `SetOptions`. The Row options and Element options will take precedence over these settings. Settings can be thought of as levels of settings with the Form-level being the highest and the Element-level the lowest. Thus the levels are:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -851,7 +868,55 @@ These settings apply to all forms `SetOptions`. The Row options and Element opt
|
||||||
Each lower level overrides the settings of the higher level
|
Each lower level overrides the settings of the higher level
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Asynchronous (Non-Blocking) Forms
|
## Asynchronous (Non-Blocking) Forms
|
||||||
While the majority of GUIs are a simple exercise to "collect input values and return with them", there are instances where we want to continue executing while the form is open. These are "asynchronous" forms and require special options, new SDK calls, and **great care**.
|
So you want to be a wizard do ya? Well go boldly! While the majority of GUIs are a simple exercise to "collect input values and return with them", there are instances where we want to continue executing while the form is open. These are "asynchronous" forms and require special options, new SDK calls, and **great care**. With asynchronous forms the form is shown, user input is read, but your code keeps right on chugging. YOUR responsibility is to call `PySimpleGUI.refresh` on a periodic basis. Once a second or more will produce a reasonably snappy GUI.
|
||||||
|
When do you use a non-blocking form? A couple of examples are
|
||||||
|
* A media file player like an MP3 player
|
||||||
|
* A status dashboard that's periodically updated
|
||||||
|
* Progress Meters - when you want to make your own progress meters
|
||||||
|
* Output using print to a scrolled text element. Good for debugging.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We're going to build an app that does the latter. It's going to update our form with a running clock.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The basic flow and functions you will be calling are:
|
||||||
|
Setup
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
form = FlexForm()
|
||||||
|
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||||
|
form.Show(non_blocking = True)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Periodic refresh
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
form.Refresh()
|
||||||
|
If you need to close the form
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Rather than the usual `form.LayoutAndShow()` call, we're manually adding the rows (doing the layout) and then showing the form. After the form is shown, you simply call `form.Refresh()` every now and then.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
When you are ready to close the form (assuming the form wasn't closed by the user or a button click) you simply call `form.CloseNonBlockingForm()`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example - Running timer that updates**
|
||||||
|
We're going to make a form and update one of the elements of that form every .01 seconds. Here's the entire code to do that.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
with SG.FlexForm('Running Timer', auto_size_text=True) as form:
|
||||||
|
output_element = SG.Text('', size=(8, 2), font=('Helvetica', 20))
|
||||||
|
form_rows = [[SG.Text('Non-blocking GUI with updates')],
|
||||||
|
[output_element],
|
||||||
|
[SG.SimpleButton('Quit')]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
form.AddRows(form_rows)
|
||||||
|
form.Show(non_blocking=True)
|
||||||
|
for i in range(1, 100):
|
||||||
|
output_element.Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i/100), 60), i%100))
|
||||||
|
rc = form.Refresh()
|
||||||
|
if rc is None or rc[0] == 'Quit':
|
||||||
|
break
|
||||||
|
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||||
|
What we have here is the same sequence of function calls as in the description. Get a form, add rows to it, show the form, and then refresh it every now and then.
|
||||||
|
The new thing in this example is the call use of the Update method for the Text Element. The first thing we do inside the loop is "update" the text element that we made earlier. This changes the value of the text field on the form. The new value will be displayed when `form.Refreshu()` is called. That's it... this example follows the async design pattern well.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Sample Applications
|
## Sample Applications
|
||||||
|
|
@ -874,12 +939,14 @@ sprint
|
||||||
Call `sprint` with as many parameters as you want and it'll print them all out in a `ScrolledTextBox`. This is simply a function pointing to `PySimpleGUI.ScrolledTextBox`.
|
Call `sprint` with as many parameters as you want and it'll print them all out in a `ScrolledTextBox`. This is simply a function pointing to `PySimpleGUI.ScrolledTextBox`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
---
|
||||||
## Known Issues
|
# Known Issues
|
||||||
While not an "issue" this is a ***stern warning***
|
While not an "issue" this is a ***stern warning***
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## **Do not attempt** to call `PySimpleGUI` from multiple threads! It's `tkinter` based and `tkinter` has issues with multiple threads
|
## **Do not attempt** to call `PySimpleGUI` from multiple threads! It's `tkinter` based and `tkinter` has issues with multiple threads
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Progress Meters** - the visual graphic portion of the meter may be off. May return to the native tkinter progress meter solution in the future. Right now a "custom" progress meter is used. On the bright side, the statistics shown are extremely accurate and can tell you something about the performance of your code.
|
**Progress Meters** - the visual graphic portion of the meter may be off. May return to the native tkinter progress meter solution in the future. Right now a "custom" progress meter is used. On the bright side, the statistics shown are extremely accurate and can tell you something about the performance of your code.
|
||||||
|
**Async Forms** - these include the 'easy' forms (EasyProgressMeter and EasyPrint/Print). If you start overlapping having Async forms open with normal forms then things get a littler squirrelly. Still tracking down the issues and am making it more solid every day possible. You'll know there's an issue when you see blank form.
|
||||||
|
**EasyPrint** - EasyPrint is a new feature that's pretty awesome. You print and the output goes to a window, with a scroll bar, that you can copy and paste from. Being a new feature, it's got some potential problems. There are known interaction problems with other GUI windows. For example, closing a Print window can also close other windows you have open. For now, don't close your debug print window until other windows are closed too.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Contributing
|
## Contributing
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -892,6 +959,7 @@ A MikeTheWatchGuy production... entirely responsible for this code.... unless it
|
||||||
| 1.0.21 | July 13, 2018 - Readme updates |
|
| 1.0.21 | July 13, 2018 - Readme updates |
|
||||||
| 2.0.0 | July 16, 2018 - ALL optional parameters renamed from CamelCase to all_lower_case
|
| 2.0.0 | July 16, 2018 - ALL optional parameters renamed from CamelCase to all_lower_case
|
||||||
| 2.1.1 | July 18, 2018 - Global settings exposed, fixes
|
| 2.1.1 | July 18, 2018 - Global settings exposed, fixes
|
||||||
|
| 2.2.0| July 20, 2018 - Image Elements, Print output
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Code Condition
|
## Code Condition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -915,7 +983,28 @@ For non-commercial individual, the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL 3) a
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* Jorj McKie was the motivator behind the entire project. His wxsimpleGUI concepts sparked PySimpleGUI into existence
|
* Jorj McKie was the motivator behind the entire project. His wxsimpleGUI concepts sparked PySimpleGUI into existence
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## How Do I
|
||||||
|
Finally, I must thank the fine folks at How Do I.
|
||||||
|
https://github.com/gleitz/howdoi
|
||||||
|
Their utility has forever changed the way and pace in which I can program. I urge you to try the HowDoI.py application here on GitHub. Trust me, **it's going to be worth the effort!**
|
||||||
|
Here are the steps to run that application
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Install howdoi:
|
||||||
|
pip install howdoi
|
||||||
|
Test your install:
|
||||||
|
python -m howdoi howdoi.py
|
||||||
|
To run it:
|
||||||
|
Python HowDoI.py
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The pip command is all there is to the setup.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The way HowDoI works is that it uses your search term to look through stack overflow posts. It finds the best answer, gets the code from the answer, and presents it as a response. It gives you the correct answer OFTEN. It's a miracle that it work SO well.
|
||||||
|
For Python questions, I simply start my query with 'Python'. Let's say you forgot how to reverse a list in Python. When you run HowDoI and ask this question, this is what you'll see.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In the hands of a competent programmer, this tool is **amazing**. It's a must-try kind of program that has completely changed my programming process. I'm not afraid of asking for help! You just have to be smart about using what you find.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The PySimpleGUI window that the results are shown in is an 'input' field which means you can copy and paste the results right into your code.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue