Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/MikeTheWatchGuy/PySimpleGUI
This commit is contained in:
commit
eb3e21e8d1
6 changed files with 342 additions and 6 deletions
26
Demo_Keyboard.py
Normal file
26
Demo_Keyboard.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Recipe for getting keys, one at a time as they are released
|
||||
# If want to use the space bar, then be sure and disable the "default focus"
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.FlexForm('Realtime Keyboard Test', return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_focus=False) as form:
|
||||
text_elem = sg.Text('', size=(12,1))
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Press a key')],
|
||||
[text_elem],
|
||||
[sg.SimpleButton('OK')]]
|
||||
|
||||
form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = form.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'OK':
|
||||
print(button, 'exiting')
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(button)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
23
Demo_Keyboard_Realtime.py
Normal file
23
Demo_Keyboard_Realtime.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Recipe for getting a continuous stream of keys when using a non-blocking form
|
||||
# If want to use the space bar, then be sure and disable the "default focus"
|
||||
|
||||
with sg.FlexForm('Realtime Keyboard Test', return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_focus=False) as form:
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Hold down a key')],
|
||||
[sg.SimpleButton('OK')]]
|
||||
|
||||
form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'OK':
|
||||
print(button, value, 'exiting')
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
elif value is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
183
Demo_PDF_Viewer.py
Normal file
183
Demo_PDF_Viewer.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
|
|||
"""
|
||||
@created: 2018-08-19 18:00:00
|
||||
|
||||
@author: (c) 2018 Jorj X. McKie
|
||||
|
||||
Display a PyMuPDF Document using Tkinter
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Dependencies:
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
PyMuPDF, PySimpleGUI > v2.9.0, Tkinter with Tk v8.6+, Python 3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
License:
|
||||
--------
|
||||
GNU GPL V3+
|
||||
|
||||
Description
|
||||
------------
|
||||
Read filename from command line and start display with page 1.
|
||||
Pages can be directly jumped to, or buttons for paging can be used.
|
||||
For experimental / demonstration purposes, we have included options to zoom
|
||||
into the four page quadrants (top-left, bottom-right, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
We also interpret keyboard events to support paging by PageDown / PageUp
|
||||
keys as if the resp. buttons were clicked. Similarly, we do not include
|
||||
a 'Quit' button. Instead, the ESCAPE key can be used, or cancelling the form.
|
||||
|
||||
To improve paging performance, we are not directly creating pixmaps from
|
||||
pages, but instead from the fitz.DisplayList of the page. A display list
|
||||
will be stored in a list and looked up by page number. This way, zooming
|
||||
pixmaps and page re-visits will re-use a once-created display list.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import fitz
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
from binascii import hexlify
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
rc, fname = sg.GetFileBox('PDF Browser', 'PDF file to open', file_types=(("PDF Files", "*.pdf"),))
|
||||
if rc is False:
|
||||
sg.MsgBoxCancel('Cancelling')
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fname = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
|
||||
doc = fitz.open(fname)
|
||||
page_count = len(doc)
|
||||
|
||||
# storage for page display lists
|
||||
dlist_tab = [None] * page_count
|
||||
|
||||
title = "PyMuPDF display of '%s', pages: %i" % (fname, page_count)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_page(pno, zoom=0):
|
||||
"""Return a PNG image for a document page number. If zoom is other than 0, one of the 4 page quadrants are zoomed-in instead and the corresponding clip returned.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
dlist = dlist_tab[pno] # get display list
|
||||
if not dlist: # create if not yet there
|
||||
dlist_tab[pno] = doc[pno].getDisplayList()
|
||||
dlist = dlist_tab[pno]
|
||||
r = dlist.rect # page rectangle
|
||||
mp = r.tl + (r.br - r.tl) * 0.5 # rect middle point
|
||||
mt = r.tl + (r.tr - r.tl) * 0.5 # middle of top edge
|
||||
ml = r.tl + (r.bl - r.tl) * 0.5 # middle of left edge
|
||||
mr = r.tr + (r.br - r.tr) * 0.5 # middle of right egde
|
||||
mb = r.bl + (r.br - r.bl) * 0.5 # middle of bottom edge
|
||||
mat = fitz.Matrix(2, 2) # zoom matrix
|
||||
if zoom == 1: # top-left quadrant
|
||||
clip = fitz.Rect(r.tl, mp)
|
||||
elif zoom == 4: # bot-right quadrant
|
||||
clip = fitz.Rect(mp, r.br)
|
||||
elif zoom == 2: # top-right
|
||||
clip = fitz.Rect(mt, mr)
|
||||
elif zoom == 3: # bot-left
|
||||
clip = fitz.Rect(ml, mb)
|
||||
if zoom == 0: # total page
|
||||
pix = dlist.getPixmap(alpha=False)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pix = dlist.getPixmap(alpha=False, matrix=mat, clip=clip)
|
||||
return pix.getPNGData() # return the PNG image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
form = sg.FlexForm(title, return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_focus=False)
|
||||
|
||||
cur_page = 0
|
||||
data = get_page(cur_page) # show page 1 for start
|
||||
image_elem = sg.Image(data=data)
|
||||
goto = sg.InputText(str(cur_page + 1), size=(5, 1), do_not_clear=True)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Next'),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Prev'),
|
||||
sg.Text('Page:'),
|
||||
goto,
|
||||
],
|
||||
[
|
||||
sg.Text("Zoom:"),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Top-L'),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Top-R'),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Bot-L'),
|
||||
sg.ReadFormButton('Bot-R'),
|
||||
],
|
||||
[image_elem],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
my_keys = ("Next", "Next:34", "Prev", "Prior:33", "Top-L", "Top-R",
|
||||
"Bot-L", "Bot-R", "MouseWheel:Down", "MouseWheel:Up")
|
||||
zoom_buttons = ("Top-L", "Top-R", "Bot-L", "Bot-R")
|
||||
|
||||
old_page = 0
|
||||
old_zoom = 0 # used for zoom on/off
|
||||
# the zoom buttons work in on/off mode.
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = False
|
||||
if button is None and value is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if button in ("Escape:27"): # this spares me a 'Quit' button!
|
||||
break
|
||||
# print("hex(button)", hexlify(button.encode()))
|
||||
if button[0] == chr(13): # surprise: this is 'Enter'!
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cur_page = int(value[0]) - 1 # check if valid
|
||||
while cur_page < 0:
|
||||
cur_page += page_count
|
||||
except:
|
||||
cur_page = 0 # this guy's trying to fool me
|
||||
goto.Update(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
# goto.TKStringVar.set(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
|
||||
elif button in ("Next", "Next:34", "MouseWheel:Down"):
|
||||
cur_page += 1
|
||||
elif button in ("Prev", "Prior:33", "MouseWheel:Up"):
|
||||
cur_page -= 1
|
||||
elif button == "Top-L":
|
||||
zoom = 1
|
||||
elif button == "Top-R":
|
||||
zoom = 2
|
||||
elif button == "Bot-L":
|
||||
zoom = 3
|
||||
elif button == "Bot-R":
|
||||
zoom = 4
|
||||
|
||||
# sanitize page number
|
||||
if cur_page >= page_count: # wrap around
|
||||
cur_page = 0
|
||||
while cur_page < 0: # we show conventional page numbers
|
||||
cur_page += page_count
|
||||
|
||||
# prevent creating same data again
|
||||
if cur_page != old_page:
|
||||
zoom = old_zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = True
|
||||
|
||||
if button in zoom_buttons:
|
||||
if 0 < zoom == old_zoom:
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = True
|
||||
|
||||
if zoom != old_zoom:
|
||||
force_page = True
|
||||
|
||||
if force_page:
|
||||
data = get_page(cur_page, zoom)
|
||||
image_elem.Update(data=data)
|
||||
old_page = cur_page
|
||||
old_zoom = zoom
|
||||
|
||||
# update page number field
|
||||
if button in my_keys or not value[0]:
|
||||
goto.Update(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
# goto.TKStringVar.set(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
|
|
@ -867,6 +867,10 @@ class FlexForm:
|
|||
'''
|
||||
Display a user defined for and return the filled in data
|
||||
'''
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
>>>>>>> 531b32ab66746c9f4b6acd2ea8b6d113cb235827
|
||||
def __init__(self, title, default_element_size=(DEFAULT_ELEMENT_SIZE[0], DEFAULT_ELEMENT_SIZE[1]), auto_size_text=None, auto_size_buttons=None, scale=(None, None), location=(None, None), button_color=None, font=None, progress_bar_color=(None, None), background_color=None, is_tabbed_form=False, border_depth=None, auto_close=False, auto_close_duration=DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME, icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON, return_keyboard_events=False, use_default_focus=True, text_justification=None):
|
||||
self.AutoSizeText = auto_size_text if auto_size_text is not None else DEFAULT_AUTOSIZE_TEXT
|
||||
self.AutoSizeButtons = auto_size_buttons if auto_size_buttons is not None else DEFAULT_AUTOSIZE_BUTTONS
|
||||
|
|
@ -1034,6 +1038,10 @@ class FlexForm:
|
|||
return BuildResults(self, False, self)
|
||||
|
||||
def KeyboardCallback(self, event ):
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
>>>>>>> 531b32ab66746c9f4b6acd2ea8b6d113cb235827
|
||||
self.LastButtonClicked = None
|
||||
self.FormRemainedOpen = True
|
||||
if event.char != '':
|
||||
|
|
@ -1052,6 +1060,10 @@ class FlexForm:
|
|||
BuildResults(self, False, self)
|
||||
self.TKroot.quit()
|
||||
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
>>>>>>> 531b32ab66746c9f4b6acd2ea8b6d113cb235827
|
||||
|
||||
def _Close(self):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
@ -1814,6 +1826,10 @@ def StartupTK(my_flex_form):
|
|||
# root.bind('<Destroy>', MyFlexForm.DestroyedCallback())
|
||||
ConvertFlexToTK(my_flex_form)
|
||||
my_flex_form.SetIcon(my_flex_form.WindowIcon)
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
>>>>>>> 531b32ab66746c9f4b6acd2ea8b6d113cb235827
|
||||
if my_flex_form.ReturnKeyboardEvents and not my_flex_form.NonBlocking:
|
||||
root.bind("<KeyRelease>", my_flex_form.KeyboardCallback)
|
||||
root.bind("<MouseWheel>", my_flex_form.MouseWheelCallback)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,16 +6,28 @@
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# PySimpleGUI
|
||||
(Ver 2.9)
|
||||
|
||||
Lots of documentation available in addition to this Readme File.
|
||||
[Formatted ReadTheDocs Version of this Readme](http://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/)
|
||||
|
||||
[COOKBOOK documentation now online!](https://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cookbook/)
|
||||
|
||||
[Brief Tutorial on PySimpleGUI](https://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial/)
|
||||
|
||||
[See Wiki for latest news about development branch + new features](https://github.com/MikeTheWatchGuy/PySimpleGUI/wiki)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Super-simple GUI to grasp... Powerfully customizable.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a custom GUI in 5 lines of code.
|
||||
|
||||
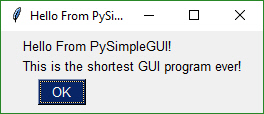
Can create a custom GUI in 1 line of code if desired.
|
||||
|
||||
Note - ***Python3*** is required to run PySimpleGUI. It takes advantage of some Python3 features that do not translate well into Python2.
|
||||
|
||||
Looking to take your Python code from the world of command lines and into the convenience of a GUI? Have a Raspberry **Pi** with a touchscreen that's going to waste because you don't have the time to learn a GUI SDK? Into Machine Learning and are sick of the command line? Look no further, **you've found your GUI package**.
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,6 +39,14 @@ Looking to take your Python code from the world of command lines and into the co
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Or how about a ***custom GUI*** in 1 line of code?
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
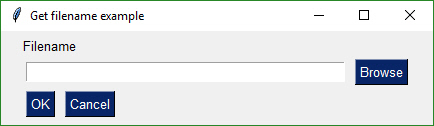
button, (filename,) = sg.FlexForm('Get filename example'). LayoutAndRead([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Build beautiful customized forms that fit your specific problem. Let PySimpleGUI solve your GUI problem while you solve the real problems. Do you really want to plod through the mountains of code required to program tkinter?
|
||||
|
||||
PySimpleGUI wraps tkinter so that you get all the same widgets as you would tkinter, but you interact with them in a **much** more friendly way.
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +55,8 @@ PySimpleGUI wraps tkinter so that you get all the same widgets as you would tkin
|
|||
|
||||
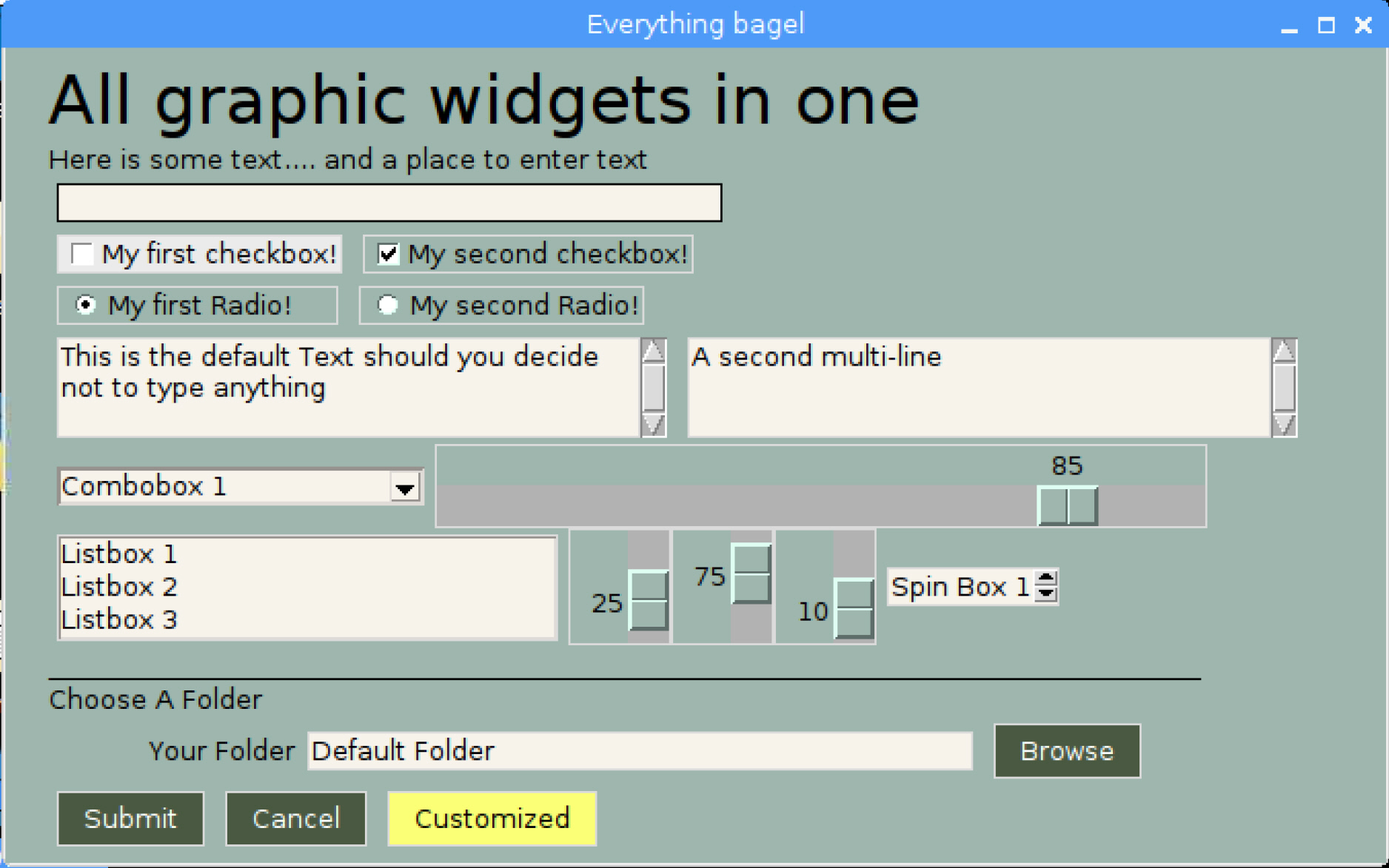
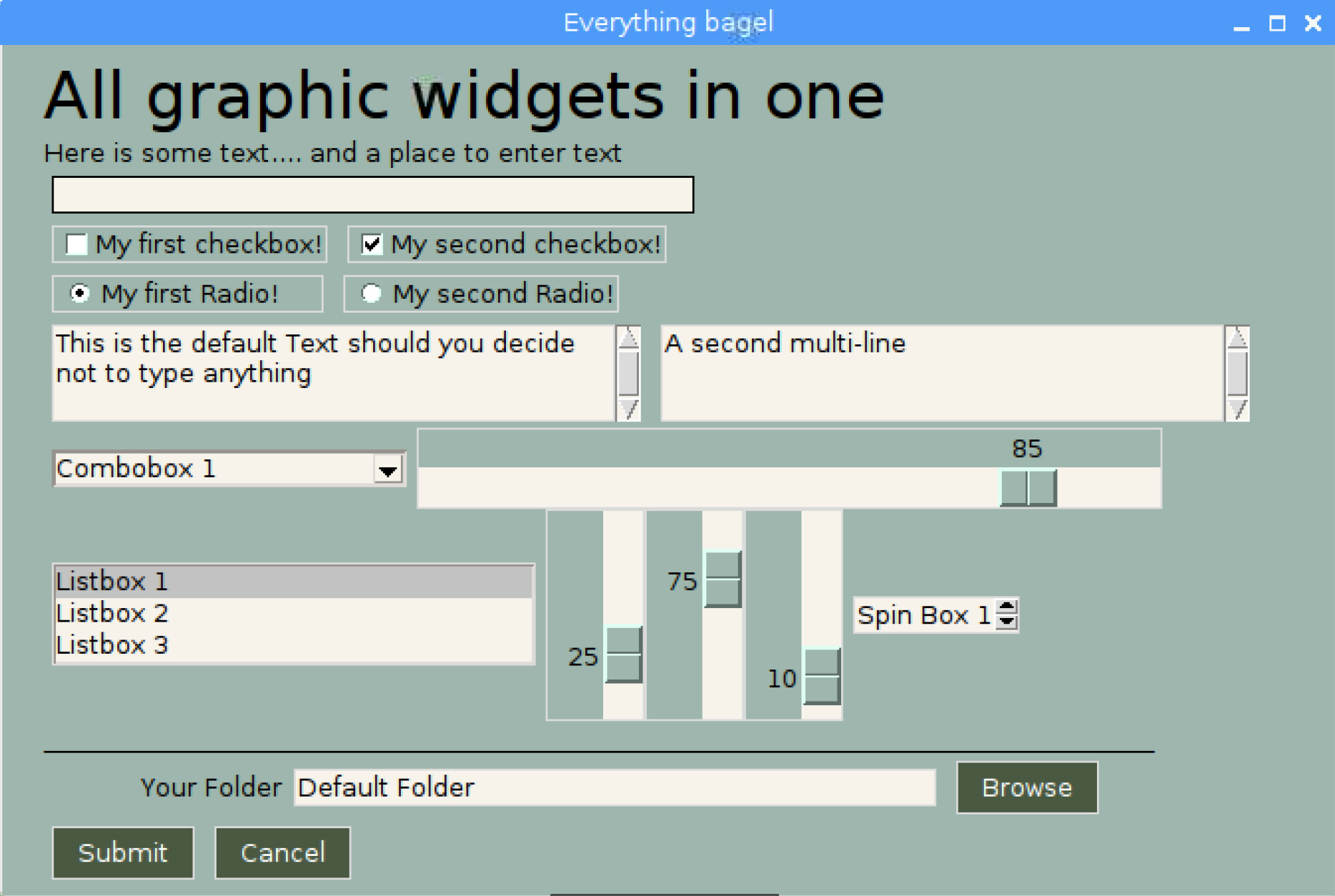
Perhaps you're looking for a way to interact with your **Raspberry Pi** in a more friendly way. The is the same form as above, except shown on a Pi.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to a primary GUI, you can add a Progress Meter to your code with ONE LINE of code. Slide this into any of your `for` loops and get a nice meter like this:
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,6 +69,7 @@ You can build an async media player GUI with custom buttons in 30 lines of code.
|
|||
|
||||
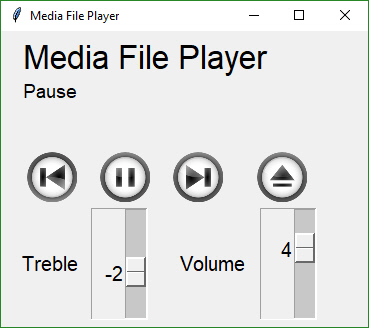
|
||||
|
||||
## Background
|
||||
I was frustrated by having to deal with the dos prompt when I had a powerful Windows machine right in front of me. Why is it SO difficult to do even the simplest of input/output to a window in Python??
|
||||
|
||||
There are a number of 'easy to use' Python GUIs, but they're **very** limiting. PySimpleGUI takes the best of packages like `EasyGUI`and `WxSimpleGUI` , both really handy but limited. The primary difference between these and `PySimpleGUI` is that in addition to getting the simple Message Boxes you also get the ability to **make your own forms** that are highly customizeable. Don't like the standard Message Box? Then make your own!
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,6 +82,8 @@ With a simple GUI, it becomes practical to "associate" .py files with the python
|
|||
|
||||
The `PySimpleGUI` package is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desired result be achieved in as little and as simple code as possible? This was the mantra used to create PySimpleGUI. How can it be done is a Python-like way?
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
Features of PySimpleGUI include:
|
||||
Text
|
||||
Single Line Input
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,6 +113,7 @@ The `PySimpleGUI` package is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desire
|
|||
Return values as dictionary
|
||||
Set focus
|
||||
Bind return key to buttons
|
||||
Group widgets into a column and place into form anywhere
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
An example of many widgets used on a single form. A little further down you'll find the TWENTY lines of code required to create this complex form. Try it if you don't believe it. Start Python, copy and paste the code below into the >>> prompt and hit enter. This will pop up...
|
||||
|
|
@ -143,6 +168,7 @@ You will see a number of different styles of buttons, data entry fields, etc, in
|
|||
- A row is a list of elements
|
||||
- Return values are a list of button presses and input values.
|
||||
- Return values can also be represented as a dictionary
|
||||
- The SDK calls collapse down into a single line of Python code that presents a custom GUI and returns values
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
|
|
@ -733,11 +759,19 @@ This is the definition of the FlexForm object:
|
|||
location=(None, None),
|
||||
button_color=None,Font=None,
|
||||
progress_bar_color=(None,None),
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
is_tabbed_form=False,
|
||||
border_depth=None,
|
||||
auto_close=False,
|
||||
auto_close_duration=DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME,
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON):
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON,
|
||||
return_keyboard_events=False,
|
||||
use_default_focus=True,
|
||||
text_justification=None):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter Descriptions. You will find these same parameters specified for each `Element` and some of them in `Row` specifications. The `Element` specified value will take precedence over the `Row` and `Form` values.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -748,11 +782,15 @@ Parameter Descriptions. You will find these same parameters specified for each
|
|||
location - (x,y) Location to place window in pixels
|
||||
button_color - Default color for buttons (foreground, background). Can be text or hex
|
||||
progress_bar_color - Foreground and background colors for progress bars
|
||||
background_color - Color of the window background
|
||||
is_tabbed_form - Bool. If True then form is a tabbed form
|
||||
border_depth - Amount of 'bezel' to put on input boxes, buttons, etc.
|
||||
auto_close - Bool. If True form will autoclose
|
||||
auto_close_duration - Duration in seconds before form closes
|
||||
icon - .ICO file that will appear on the Task Bar and end of Title Bar
|
||||
return_keyboard_events - if True key presses are returned as buttons
|
||||
use_default_focus - if True and no focus set, then automatically set a focus
|
||||
text_justification - Justification to use for Text Elements in this form
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Window Location
|
||||
|
|
@ -1111,7 +1149,7 @@ While it's possible to build forms using the Button Element directly, you should
|
|||
button_color=None,
|
||||
font=None)
|
||||
|
||||
Pre-made buttons include:
|
||||
These Pre-made buttons are some of the most important elements of all because they are used so much. If you find yourself needing to create a custom button often because it's not on this list, please post a request on GitHub. (hmmm Save already comes to mind). They include:
|
||||
|
||||
OK
|
||||
Ok
|
||||
|
|
@ -1600,8 +1638,14 @@ Valid values for the description string are:
|
|||
GreenMono
|
||||
BrownBlue
|
||||
BrightColors
|
||||
NeutralBlue
|
||||
Kayak
|
||||
SandyBeach
|
||||
TealMono
|
||||
|
||||
To see the latest list of color choices, take a look at the bottom of the `PySimpleGUI.py` file where you'll find the `ChangLookAndFeel` function.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also combine the `ChangeLookAndFeel` function with the `SetOptions` function to quickly modify one of the canned color schemes. Maybe you like the colors but was more depth to your bezels. You can dial in exactly what you want.
|
||||
|
||||
**ObjToString**
|
||||
Ever wanted to easily display an objects contents easily? Use ObjToString to get a nicely formatted recursive walk of your objects.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
50
readme.md
50
readme.md
|
|
@ -6,16 +6,28 @@
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# PySimpleGUI
|
||||
(Ver 2.9)
|
||||
|
||||
Lots of documentation available in addition to this Readme File.
|
||||
[Formatted ReadTheDocs Version of this Readme](http://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/)
|
||||
|
||||
[COOKBOOK documentation now online!](https://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cookbook/)
|
||||
|
||||
[Brief Tutorial on PySimpleGUI](https://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial/)
|
||||
|
||||
[See Wiki for latest news about development branch + new features](https://github.com/MikeTheWatchGuy/PySimpleGUI/wiki)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Super-simple GUI to grasp... Powerfully customizable.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a custom GUI in 5 lines of code.
|
||||
|
||||
Can create a custom GUI in 1 line of code if desired.
|
||||
|
||||
Note - ***Python3*** is required to run PySimpleGUI. It takes advantage of some Python3 features that do not translate well into Python2.
|
||||
|
||||
Looking to take your Python code from the world of command lines and into the convenience of a GUI? Have a Raspberry **Pi** with a touchscreen that's going to waste because you don't have the time to learn a GUI SDK? Into Machine Learning and are sick of the command line? Look no further, **you've found your GUI package**.
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,6 +39,14 @@ Looking to take your Python code from the world of command lines and into the co
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Or how about a ***custom GUI*** in 1 line of code?
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.FlexForm('Get filename example'). LayoutAndRead([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ])
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Build beautiful customized forms that fit your specific problem. Let PySimpleGUI solve your GUI problem while you solve the real problems. Do you really want to plod through the mountains of code required to program tkinter?
|
||||
|
||||
PySimpleGUI wraps tkinter so that you get all the same widgets as you would tkinter, but you interact with them in a **much** more friendly way.
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +55,8 @@ PySimpleGUI wraps tkinter so that you get all the same widgets as you would tkin
|
|||
|
||||
Perhaps you're looking for a way to interact with your **Raspberry Pi** in a more friendly way. The is the same form as above, except shown on a Pi.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to a primary GUI, you can add a Progress Meter to your code with ONE LINE of code. Slide this into any of your `for` loops and get a nice meter like this:
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,6 +69,7 @@ You can build an async media player GUI with custom buttons in 30 lines of code.
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Background
|
||||
I was frustrated by having to deal with the dos prompt when I had a powerful Windows machine right in front of me. Why is it SO difficult to do even the simplest of input/output to a window in Python??
|
||||
|
||||
There are a number of 'easy to use' Python GUIs, but they're **very** limiting. PySimpleGUI takes the best of packages like `EasyGUI`and `WxSimpleGUI` , both really handy but limited. The primary difference between these and `PySimpleGUI` is that in addition to getting the simple Message Boxes you also get the ability to **make your own forms** that are highly customizeable. Don't like the standard Message Box? Then make your own!
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,6 +82,8 @@ With a simple GUI, it becomes practical to "associate" .py files with the python
|
|||
|
||||
The `PySimpleGUI` package is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desired result be achieved in as little and as simple code as possible? This was the mantra used to create PySimpleGUI. How can it be done is a Python-like way?
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
Features of PySimpleGUI include:
|
||||
Text
|
||||
Single Line Input
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,6 +113,7 @@ The `PySimpleGUI` package is focused on the ***developer***. How can the desire
|
|||
Return values as dictionary
|
||||
Set focus
|
||||
Bind return key to buttons
|
||||
Group widgets into a column and place into form anywhere
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
An example of many widgets used on a single form. A little further down you'll find the TWENTY lines of code required to create this complex form. Try it if you don't believe it. Start Python, copy and paste the code below into the >>> prompt and hit enter. This will pop up...
|
||||
|
|
@ -143,6 +168,7 @@ You will see a number of different styles of buttons, data entry fields, etc, in
|
|||
- A row is a list of elements
|
||||
- Return values are a list of button presses and input values.
|
||||
- Return values can also be represented as a dictionary
|
||||
- The SDK calls collapse down into a single line of Python code that presents a custom GUI and returns values
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
|
|
@ -733,11 +759,19 @@ This is the definition of the FlexForm object:
|
|||
location=(None, None),
|
||||
button_color=None,Font=None,
|
||||
progress_bar_color=(None,None),
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
is_tabbed_form=False,
|
||||
border_depth=None,
|
||||
auto_close=False,
|
||||
auto_close_duration=DEFAULT_AUTOCLOSE_TIME,
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON):
|
||||
icon=DEFAULT_WINDOW_ICON,
|
||||
return_keyboard_events=False,
|
||||
use_default_focus=True,
|
||||
text_justification=None):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter Descriptions. You will find these same parameters specified for each `Element` and some of them in `Row` specifications. The `Element` specified value will take precedence over the `Row` and `Form` values.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -748,11 +782,15 @@ Parameter Descriptions. You will find these same parameters specified for each
|
|||
location - (x,y) Location to place window in pixels
|
||||
button_color - Default color for buttons (foreground, background). Can be text or hex
|
||||
progress_bar_color - Foreground and background colors for progress bars
|
||||
background_color - Color of the window background
|
||||
is_tabbed_form - Bool. If True then form is a tabbed form
|
||||
border_depth - Amount of 'bezel' to put on input boxes, buttons, etc.
|
||||
auto_close - Bool. If True form will autoclose
|
||||
auto_close_duration - Duration in seconds before form closes
|
||||
icon - .ICO file that will appear on the Task Bar and end of Title Bar
|
||||
return_keyboard_events - if True key presses are returned as buttons
|
||||
use_default_focus - if True and no focus set, then automatically set a focus
|
||||
text_justification - Justification to use for Text Elements in this form
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Window Location
|
||||
|
|
@ -1111,7 +1149,7 @@ While it's possible to build forms using the Button Element directly, you should
|
|||
button_color=None,
|
||||
font=None)
|
||||
|
||||
Pre-made buttons include:
|
||||
These Pre-made buttons are some of the most important elements of all because they are used so much. If you find yourself needing to create a custom button often because it's not on this list, please post a request on GitHub. (hmmm Save already comes to mind). They include:
|
||||
|
||||
OK
|
||||
Ok
|
||||
|
|
@ -1600,8 +1638,14 @@ Valid values for the description string are:
|
|||
GreenMono
|
||||
BrownBlue
|
||||
BrightColors
|
||||
NeutralBlue
|
||||
Kayak
|
||||
SandyBeach
|
||||
TealMono
|
||||
|
||||
To see the latest list of color choices, take a look at the bottom of the `PySimpleGUI.py` file where you'll find the `ChangLookAndFeel` function.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also combine the `ChangeLookAndFeel` function with the `SetOptions` function to quickly modify one of the canned color schemes. Maybe you like the colors but was more depth to your bezels. You can dial in exactly what you want.
|
||||
|
||||
**ObjToString**
|
||||
Ever wanted to easily display an objects contents easily? Use ObjToString to get a nicely formatted recursive walk of your objects.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue