Renamed return value from Read call from button to event... EVERYWHERE
This commit is contained in:
parent
43526e0182
commit
c79a8772cc
86 changed files with 7992 additions and 12709 deletions
|
|
@ -13,14 +13,14 @@ menu_def = [['&File', ['&Open', '&Save', 'E&xit', 'Properties']],
|
|||
['&Help', '&About...'], ]
|
||||
|
||||
# ------ Column Definition ------ #
|
||||
column1 = [[sg.Text('Column 1', background_color='#F7F3EC', justification='center', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
column1 = [[sg.Text('Column 1', background_color='lightblue', justification='center', size=(10, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin(values=('Spin Box 1', '2', '3'), initial_value='Spin Box 3')]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Menu(menu_def, tearoff=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('All graphic widgets in one Window!', size=(30, 1), justification='center', font=("Helvetica", 25), relief=sg.RELIEF_RIDGE, text_color='midnightblue')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('(Almost) All widgets in one Window!', size=(30, 1), justification='center', font=("Helvetica", 25), relief=sg.RELIEF_RIDGE)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Here is some text.... and a place to enter text')],
|
||||
[sg.InputText('This is my text')],
|
||||
[sg.Frame(layout=[
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,21 +36,19 @@ layout = [
|
|||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=25),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=75),
|
||||
sg.Slider(range=(1, 100), orientation='v', size=(5, 20), default_value=10),
|
||||
sg.Column(column1, background_color='#F7F3EC')]])],
|
||||
sg.Column(column1, background_color='lightblue')]])],
|
||||
[sg.Text('_' * 80)],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Choose A Folder', size=(35, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Your Folder', size=(15, 1), auto_size_text=False, justification='right'),
|
||||
sg.InputText('Default Folder'), sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(tooltip='Click to submit this form'), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
[sg.Submit(tooltip='Click to submit this form'), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup('Title',
|
||||
'The results of the window.',
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button),
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(event),
|
||||
'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ Turn off padding in order to get a really tight looking layout.
|
|||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('Dark')
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('User:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('User 1', 'User 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
sg.T('0', size=(8, 1))],
|
||||
[sg.T('Customer:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('Customer 1', 'Customer 2'), size=(20, 1)),
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,15 +23,20 @@ layout = [[sg.T('User:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.OptionMenu(values=('User 1', 'User
|
|||
sg.ReadButton('Submit', button_color=('gray60', 'springgreen4')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Exit', button_color=('white', '#00406B'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Time Tracker", default_element_size=(12, 1), text_justification='r', auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False, no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Borderless Window",
|
||||
default_element_size=(12, 1),
|
||||
text_justification='r',
|
||||
auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False,
|
||||
no_titlebar=True,
|
||||
grab_anywhere=True,
|
||||
default_button_element_size=(12, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ window.FindElement('submit').Update(disabled=True)
|
|||
|
||||
recording = have_data = False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
winsound.PlaySound("ButtonClick.wav", 1)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,22 +30,22 @@ for key, state in {'_Start_': False, '_Stop_': True, '_Reset_': True, '_Submit_'
|
|||
|
||||
recording = have_data = False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
if button == '_Start_':
|
||||
if event == '_Start_':
|
||||
for key, state in {'_Start_':True, '_Stop_':False, '_Reset_':False, '_Submit_':True}.items():
|
||||
window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=state)
|
||||
recording = True
|
||||
elif button == '_Stop_' and recording:
|
||||
elif event == '_Stop_' and recording:
|
||||
[window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=value) for key,value in {'_Start_':False, '_Stop_':True, '_Reset_':False, '_Submit_':False}.items()]
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
have_data = True
|
||||
elif button == '_Reset_':
|
||||
elif event == '_Reset_':
|
||||
[window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=value) for key,value in {'_Start_':False, '_Stop_':True, '_Reset_':True, '_Submit_':True}.items()]
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
have_data = False
|
||||
elif button is '_Submit_' and have_data:
|
||||
elif event is '_Submit_' and have_data:
|
||||
[window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=value) for key,value in {'_Start_':False, '_Stop_':True, '_Reset_':True, '_Submit_':False}.items()]
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,5 +11,5 @@ layout = [[sg.T('Calendar Test')],
|
|||
[sg.Ok(key=1)]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Calendar', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
b,v = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.Popup(v['input'])
|
||||
event,values = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.Popup(values['input'])
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,10 +15,10 @@ window = sg.Window('Canvas test').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
|||
cir = window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas.create_oval(50, 50, 100, 100)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Blue':
|
||||
if event is 'Blue':
|
||||
window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill = "Blue")
|
||||
elif button is 'Red':
|
||||
elif event is 'Red':
|
||||
window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill = "Red")
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,12 +21,12 @@ window = sg.Window('Chat window', default_element_size=(30, 2), font=('Helvetica
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is 'SEND':
|
||||
(event, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is 'SEND':
|
||||
query = value['query'].rstrip()
|
||||
# EXECUTE YOUR COMMAND HERE
|
||||
print('The command you entered was {}'.format(query))
|
||||
elif button is None or button is 'EXIT': # quit if exit button or X
|
||||
elif event is None or event == 'EXIT': # quit if exit button or X
|
||||
break
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,8 +32,8 @@ def ChatBotWithHistory():
|
|||
command_history = []
|
||||
history_offset = 0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is 'SEND':
|
||||
(event, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is 'SEND':
|
||||
query = value['query'].rstrip()
|
||||
# EXECUTE YOUR COMMAND HERE
|
||||
print('The command you entered was {}'.format(query))
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,17 +41,17 @@ def ChatBotWithHistory():
|
|||
history_offset = len(command_history)-1
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update('') # manually clear input because keyboard events blocks clear
|
||||
window.FindElement('history').Update('\n'.join(command_history[-3:]))
|
||||
elif button is None or button is 'EXIT': # quit if exit button or X
|
||||
elif event is None or event is 'EXIT': # quit if exit event or X
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif 'Up' in button and len(command_history):
|
||||
elif 'Up' in event and len(command_history):
|
||||
command = command_history[history_offset]
|
||||
history_offset -= 1 * (history_offset > 0) # decrement is not zero
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update(command)
|
||||
elif 'Down' in button and len(command_history):
|
||||
elif 'Down' in event and len(command_history):
|
||||
history_offset += 1 * (history_offset < len(command_history)-1) # increment up to end of list
|
||||
command = command_history[history_offset]
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update(command)
|
||||
elif 'Escape' in button:
|
||||
elif 'Escape' in event:
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update('')
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -66,8 +66,8 @@ window = sg.Window('Chat Window', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(30,
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, (value,) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is not 'SEND':
|
||||
event, (value,) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is not 'SEND':
|
||||
break
|
||||
string = value.rstrip()
|
||||
print(' '+string)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1689,12 +1689,12 @@ def main():
|
|||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Button('Many buttons', button_color=('white', '#0e6251'), key='Many buttons'), sg.ColorChooserButton( 'Chooser', target=(3,0), key='Chooser'), sg.Quit(),],
|
||||
]
|
||||
# [g.Multiline(DefaultText=str(printable), Size=(30,20))]]
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Color Demo', auto_size_buttons=False).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Color Demo', auto_size_buttons=False).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
# ------- OUTPUT results portion ------- #
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or button is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
elif button == 'Many buttons':
|
||||
elif event == 'Many buttons':
|
||||
show_all_colors_on_buttons()
|
||||
|
||||
drop_down_value = values['listbox']
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -673,12 +673,21 @@ color_map = {
|
|||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(button_element_size=(12,1), element_padding=(0,0), auto_size_buttons=False, border_width=1, tooltip_time=100)
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Hover mouse to see RGB value, click for white & black text', text_color='blue', font='Any 15', relief=sg.RELIEF_SUNKEN, justification='center', size=(100,1), background_color='light green', pad=(0,(0,20))),]]
|
||||
#start layout with the tittle
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Hover mouse to see RGB value, click for white & black text',
|
||||
text_color='blue',
|
||||
font='Any 15',
|
||||
relief=sg.RELIEF_SUNKEN,
|
||||
justification='center',
|
||||
size=(100,1),
|
||||
background_color='light green',
|
||||
pad=(0,(0,20))),]]
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Create primary color viewer window by building rows and appending to layout --
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
# -- Create primary color viewer window --
|
||||
for i, color in enumerate(color_map):
|
||||
row.append(sg.RButton(color, button_color=('black', color), key=color, tooltip=color_map[color]))
|
||||
if (i+1) % 15 == 0:
|
||||
if (i+1) % 15 == 0: # every 15 buttons make a new row
|
||||
layout.append(row)
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -686,9 +695,9 @@ window = sg.Window('Color Viewer', grab_anywhere=False, font=('any 9')).Layout(l
|
|||
|
||||
# -- Event loop --
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
if b is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# -- Create a secondary window that shows white and black text on chosen color
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(b, button_color=('white', b), tooltip=color_map[b]), sg.DummyButton(b, button_color=('black', b), tooltip=color_map[b])] ]
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('white', event), tooltip=color_map[event]), sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('black', event), tooltip=color_map[event])] ]
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
|
@ -105,9 +105,9 @@ window = sg.Window('Color Viewer', grab_anywhere=False, font=('any 9')).Layout(l
|
|||
|
||||
# -- Event loop --
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
if b is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# -- Create a secondary window that shows white and black text on chosen color
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(b, button_color=('white', b)), sg.DummyButton(b, button_color=('black', b))] ]
|
||||
layout2 =[[sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('white', event)), sg.DummyButton(event, button_color=('black', event))]]
|
||||
sg.Window('Buttons with white and black text', keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout2).ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ layout = [[sg.Listbox(values=('Listbox Item 1', 'Listbox Item 2', 'Listbox Item
|
|||
[sg.OK()]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Display the window and get values
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line form with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line form with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ def GetFilesToCompare():
|
|||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('File Compare')
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(form_rows).Read()
|
||||
return button, values
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(form_rows).Read()
|
||||
return event, values
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
button, values = GetFilesToCompare()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -173,16 +173,16 @@ old_page = 0
|
|||
old_zoom = False
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None and (value is None or value['PageNumber'] is None):
|
||||
event, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None and (value is None or value['PageNumber'] is None):
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button in quit_buttons:
|
||||
if event in quit_buttons:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
zoom_pressed = False
|
||||
zoom = False
|
||||
|
||||
if button in enter_buttons:
|
||||
if event in enter_buttons:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cur_page = int(value['PageNumber']) - 1 # check if valid
|
||||
while cur_page < 0:
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,19 +190,19 @@ while True:
|
|||
except:
|
||||
cur_page = 0 # this guy's trying to fool me
|
||||
|
||||
elif button in next_buttons:
|
||||
elif event in next_buttons:
|
||||
cur_page += 1
|
||||
elif button in prev_buttons:
|
||||
elif event in prev_buttons:
|
||||
cur_page -= 1
|
||||
elif button == Up:
|
||||
elif event == Up:
|
||||
zoom = (clip_pos, 0, -1)
|
||||
elif button == Down:
|
||||
elif event == Down:
|
||||
zoom = (clip_pos, 0, 1)
|
||||
elif button == Left:
|
||||
elif event == Left:
|
||||
zoom = (clip_pos, -1, 0)
|
||||
elif button == Right:
|
||||
elif event == Right:
|
||||
zoom = (clip_pos, 1, 0)
|
||||
elif button == "Zoom":
|
||||
elif event == "Zoom":
|
||||
zoom_pressed = True
|
||||
zoom = (clip_pos, 0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -228,7 +228,7 @@ while True:
|
|||
old_zoom = zoom_pressed or zoom
|
||||
|
||||
# update page number field
|
||||
if button in my_keys:
|
||||
if event in my_keys:
|
||||
goto.Update(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ else:
|
|||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -------------------------------------#
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,8 +35,8 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ]]
|
|||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------------------------------------------------------------#
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,6 +53,6 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ]]
|
|||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,19 +44,19 @@ def Launcher():
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and executing appropriate program --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is 'EXIT' or button is None:
|
||||
(event, values) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'EXIT' or event is None:
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
if button is 'Program 1':
|
||||
if event == 'Program 1':
|
||||
print('Run your program 1 here!')
|
||||
elif button is 'Program 2':
|
||||
elif event == 'Program 2':
|
||||
print('Run your program 2 here!')
|
||||
elif button is 'Run':
|
||||
file = value['demofile']
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
file = values['demofile']
|
||||
print('Launching %s'%file)
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('python', os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, file))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
|
||||
def ExecuteCommandSubprocess(command, *args, wait=False):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,8 +54,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
prev_x, prev_y = 0, 0
|
||||
while True: # the Event Loop
|
||||
time.sleep(.5)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None: # always give ths user a way out
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None: # always give ths user a way out
|
||||
break
|
||||
# do CPU measurement and graph it
|
||||
current_cpu = int(g_cpu_percent*10)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -62,10 +62,10 @@ def main():
|
|||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
g_interval = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,10 +25,10 @@ window = sg.Window('CPU Meter',
|
|||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
interval = int(values['_spin_'])
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,25 +32,25 @@ start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
|||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
if not paused:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
current_time = int(round(time.time() * 100)) - start_time
|
||||
else:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'button':
|
||||
button = window.FindElement(button).GetText()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'button':
|
||||
event = window.FindElement(event).GetText()
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Reset':
|
||||
if event is 'Reset':
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused_time = start_time
|
||||
elif button == 'Pause':
|
||||
elif event == 'Pause':
|
||||
paused = True
|
||||
paused_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Run')
|
||||
elif button == 'Run':
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = start_time + int(round(time.time() * 100)) - paused_time
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,35 +12,34 @@ sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
|||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.T('Notes:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.In(size=(44, 1), background_color='white', text_color='black', key='notes')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Output:', pad=((3, 0), 0)), sg.T('', size=(44, 1), text_color='white', key='output')],
|
||||
[sg.CBox('Checkbox:', default=True, pad=((3, 0), 0), key='cbox'), sg.Listbox((1,2,3,4),size=(8,3),key='listbox'),
|
||||
sg.Radio('Radio 1', default=True, group_id='1', key='radio1'), sg.Radio('Radio 2', default=False, group_id='1', key='radio2')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin((1,2,3,4),1, key='spin'), sg.OptionMenu((1,2,3,4), key='option'), sg.Combo(values=(1,2,3,4),key='combo')],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline('Multiline', size=(20,3), key='multi')],
|
||||
[sg.Slider((1,10), size=(20,20), orientation='h', key='slider')],
|
||||
[sg.CBox('Checkbox:', default=True, pad=((3, 0), 0), disabled=True, key='cbox'), sg.Listbox((1,2,3,4),size=(8,3),disabled=True, key='listbox'),
|
||||
sg.Radio('Radio 1', default=True, group_id='1', disabled=True, key='radio1'), sg.Radio('Radio 2', default=False, group_id='1', disabled=True, key='radio2')],
|
||||
[sg.Spin((1,2,3,4),1,disabled=True, key='spin'), sg.OptionMenu((1,2,3,4),disabled=True, key='option'), sg.Combo(values=(1,2,3,4),disabled=True,key='combo')],
|
||||
[sg.Multiline('Multiline', size=(20,3),disabled=True, key='multi')],
|
||||
[sg.Slider((1,10), size=(20,20), orientation='h', disabled=True, key='slider')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Enable', button_color=('white', 'black')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Disable', button_color=('white', 'black')),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Reset', button_color=('white', '#9B0023'), key='reset'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Values', button_color=('white', 'springgreen4')),
|
||||
sg.Button('Exit', button_color=('white', '#00406B'))]]
|
||||
sg.Button('Exit', disabled=True, button_color=('white', '#00406B'), key='exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("Disable Elements Demo", default_element_size=(12, 1), text_justification='r', auto_size_text=False,
|
||||
auto_size_buttons=False, keep_on_top=True, grab_anywhere=False,
|
||||
default_button_element_size=(12, 1)).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
key_list = 'cbox', 'listbox', 'radio1', 'radio2', 'spin', 'option', 'combo', 'reset', 'notes', 'multi', 'slider'
|
||||
key_list = 'cbox', 'listbox', 'radio1', 'radio2', 'spin', 'option', 'combo', 'reset', 'notes', 'multi', 'slider', 'exit'
|
||||
|
||||
for key in key_list: window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=True) # don't do this kind of for-loop
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button == 'Disable':
|
||||
elif event == 'Disable':
|
||||
for key in key_list: window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
elif button == 'Enable':
|
||||
elif event == 'Enable':
|
||||
for key in key_list: window.FindElement(key).Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
elif button == 'Values':
|
||||
elif event == 'Values':
|
||||
sg.Popup(values, keep_on_top=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,17 +46,17 @@ def Everything():
|
|||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button is 'SaveSettings':
|
||||
if event is 'SaveSettings':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('Save Settings', save_as=True, no_window=True)
|
||||
window.SaveToDisk(filename)
|
||||
# save(values)
|
||||
elif button is 'LoadSettings':
|
||||
elif event is 'LoadSettings':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('Load Settings', no_window=True)
|
||||
window.LoadFromDisk(filename)
|
||||
# load(form)
|
||||
elif button in ['Exit', None]:
|
||||
elif event in ['Exit', None]:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ sz = fontSize
|
|||
window = sg.Window("Font size selector", grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
sz_spin = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
sz_slider = int(values['slider'])
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
34
Demo_Font_String.py
Normal file
34
Demo_Font_String.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('This is my sample text',size=(20,1), key='_text_') ],
|
||||
[sg.CB('Bold', key='_bold_', change_submits=True),
|
||||
sg.CB('Italics', key='_italics_', change_submits=True),
|
||||
sg.CB('Underline', key='_underline_', change_submits=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Slider((6,50), default_value=12, size=(14,20), orientation='h', key='_slider_', change_submits=True),
|
||||
sg.Text('Font size')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Font string = '), sg.Text('', size=(25,1), key='_fontstring_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Font string builder').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
text_elem = window.FindElement('_text_')
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
font_string = 'Helvitica '
|
||||
font_string += str(values['_slider_'])
|
||||
if values['_bold_']:
|
||||
font_string += ' bold'
|
||||
if values['_italics_']:
|
||||
font_string += ' italic'
|
||||
if values['_underline_']:
|
||||
font_string += ' underline'
|
||||
text_elem.Update(font=font_string)
|
||||
window.FindElement('_fontstring_').Update('"'+font_string+'"')
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
|
@ -9,11 +9,11 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Filename', )],
|
|||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(
|
||||
event, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').LayoutAndRead(
|
||||
[[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
|
||||
#===== Add a click me button for fun and SHOW the window ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== =====#
|
||||
window.AddRow(sg.Button('Click ME!'))
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Show() # show it!
|
||||
event, values = window.Read() # show it!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,17 +16,18 @@ point = graph.DrawPoint((75,75), 10, color='green')
|
|||
oval = graph.DrawOval((25,300), (100,280), fill_color='purple', line_color='purple' )
|
||||
rectangle = graph.DrawRectangle((25,300), (100,280), line_color='purple' )
|
||||
line = graph.DrawLine((0,0), (100,100))
|
||||
|
||||
arc = graph.DrawArc((0,0), (400,400), 160, 10, style='arc' ,arc_color='blue')
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Blue':
|
||||
if event is 'Blue':
|
||||
graph.TKCanvas.itemconfig(circle, fill = "Blue")
|
||||
elif button is 'Red':
|
||||
elif event is 'Red':
|
||||
graph.TKCanvas.itemconfig(circle, fill = "Red")
|
||||
elif button is 'Move':
|
||||
elif event is 'Move':
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(point, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(circle, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(oval, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(rectangle, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(arc, 10,10)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
while True:
|
||||
time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if g_response_time is None or prev_response_time == g_response_time:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ for y in range(-100, 101, 20):
|
|||
|
||||
# Draw Graph
|
||||
for x in range(-100,100):
|
||||
y = math.sin(x/20)*50
|
||||
y = math.sin(x/30)*50
|
||||
graph.DrawCircle((x,y), 1, line_color='red', fill_color='red')
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -45,9 +45,9 @@ def main():
|
|||
graph_value = 250
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
graph_offset = random.randint(-10, 10)
|
||||
graph_value = graph_value + graph_offset
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -41,26 +41,26 @@ def HowDoI():
|
|||
command_history = []
|
||||
history_offset = 0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is 'SEND':
|
||||
query = value['query'].rstrip()
|
||||
print(query)
|
||||
QueryHowDoI(query, value['Num Answers'], value['full text']) # send the string to HowDoI
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'SEND':
|
||||
query = values['query'].rstrip()
|
||||
# print(query)
|
||||
QueryHowDoI(query, values['Num Answers'], values['full text']) # send the string to HowDoI
|
||||
command_history.append(query)
|
||||
history_offset = len(command_history)-1
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update('') # manually clear input because keyboard events blocks clear
|
||||
window.FindElement('history').Update('\n'.join(command_history[-3:]))
|
||||
elif button is None or button is 'EXIT': # if exit button or closed using X
|
||||
elif event == None or event == 'EXIT': # if exit button or closed using X
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif 'Up' in button and len(command_history): # scroll back in history
|
||||
elif 'Up' in event and len(command_history): # scroll back in history
|
||||
command = command_history[history_offset]
|
||||
history_offset -= 1 * (history_offset > 0) # decrement is not zero
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update(command)
|
||||
elif 'Down' in button and len(command_history): # scroll forward in history
|
||||
elif 'Down' in event and len(command_history): # scroll forward in history
|
||||
history_offset += 1 * (history_offset < len(command_history)-1) # increment up to end of list
|
||||
command = command_history[history_offset]
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update(command)
|
||||
elif 'Escape' in button: # clear currently line
|
||||
elif 'Escape' in event: # clear currently line
|
||||
window.FindElement('query').Update('')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -88,22 +88,22 @@ window.Layout(layout) # Shows form on screen
|
|||
i=0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# read the form
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
# perform button and keyboard operations
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button in ('Next', 'MouseWheel:Down', 'Down:40', 'Next:34'):
|
||||
elif event in ('Next', 'MouseWheel:Down', 'Down:40', 'Next:34'):
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
if i >= num_files:
|
||||
i -= num_files
|
||||
filename = os.path.join(folder, fnames[i])
|
||||
elif button in ('Prev', 'MouseWheel:Up', 'Up:38', 'Prior:33'):
|
||||
elif event in ('Prev', 'MouseWheel:Up', 'Up:38', 'Prior:33'):
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
if i < 0:
|
||||
i = num_files + i
|
||||
filename = os.path.join(folder, fnames[i])
|
||||
elif button == 'listbox': # something from the listbox
|
||||
elif event == 'listbox': # something from the listbox
|
||||
f = values["listbox"][0] # selected filename
|
||||
filename = os.path.join(folder, f) # read this file
|
||||
i = fnames.index(f) # update running index
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,14 +16,14 @@ window = sg.Window("Keyboard Test", return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_foc
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
text_elem = window.FindElement('text')
|
||||
if button in ("OK", None):
|
||||
print(button, "exiting")
|
||||
if event in ("OK", None):
|
||||
print(event, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if len(button) == 1:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(value='%s - %s' % (button, ord(button)))
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(button)
|
||||
if len(event) == 1:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(value='%s - %s' % (event, ord(event)))
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,15 +11,15 @@ layout = [[sg.Text("Hold down a key")],
|
|||
window = sg.Window("Realtime Keyboard Test", return_keyboard_events=True, use_default_focus=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == "OK":
|
||||
print(button, value, "exiting")
|
||||
if event == "OK":
|
||||
print(event, values, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
if len(button) == 1:
|
||||
print('%s - %s'%(button, ord(button)))
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
if len(event) == 1:
|
||||
print('%s - %s' % (event, ord(event)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
elif value is None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
elif values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,15 +29,15 @@ window = sg.Window('Keypad', default_button_element_size=(5, 2), auto_size_butto
|
|||
# Loop forever reading the form's values, updating the Input field
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read() # read the form
|
||||
if button is None: # if the X button clicked, just exit
|
||||
event, values = window.Read() # read the form
|
||||
if event is None: # if the X button clicked, just exit
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'Clear': # clear keys if clear button
|
||||
if event == 'Clear': # clear keys if clear button
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
elif button in '1234567890':
|
||||
elif event in '1234567890':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input'] # get what's been entered so far
|
||||
keys_entered += button # add the new digit
|
||||
elif button == 'Submit':
|
||||
keys_entered += event # add the new digit
|
||||
elif event == 'Submit':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input']
|
||||
window.FindElement('out').Update(keys_entered) # output the final string
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -39,8 +39,8 @@ window = sg.Window('My new window', default_element_size=(12, 1), auto_size_text
|
|||
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit':
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
break
|
||||
if value is None:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -90,16 +90,16 @@ class PlayerGUI():
|
|||
if 'window' not in locals() or window is None: # if the widnow has been destoyed don't mess with it
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_EXIT
|
||||
self.TextElem.Update(DisplayString)
|
||||
button, (values) = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, (values) = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None:
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_EXIT
|
||||
if button == 'PAUSE':
|
||||
if event == 'PAUSE':
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_PAUSE
|
||||
elif button == 'EXIT':
|
||||
elif event == 'EXIT':
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_EXIT
|
||||
elif button == 'NEXT':
|
||||
elif event == 'NEXT':
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_NEXT
|
||||
elif button == 'Restart Song':
|
||||
elif event == 'Restart Song':
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_RESTART_SONG
|
||||
return PLAYER_COMMAND_NONE
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -52,8 +52,8 @@ def CustomMeter():
|
|||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -112,4 +112,4 @@ window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI', for
|
|||
fig_photo = draw_figure(window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas, fig)
|
||||
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,8 +36,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
|
||||
dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
slider_elem.Update(i)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,8 +26,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
canvas = canvas_elem.TKCanvas
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
def PyplotScatterWithLegend():
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -886,10 +886,10 @@ canvas_elem = window.FindElement('canvas')
|
|||
multiline_elem= window.FindElement('multiline')
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
if button is None or button is 'Exit':
|
||||
if event is None or event is 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -662,8 +662,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
|
||||
run_a_ping_and_graph()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -96,8 +96,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
run_a_ping_and_graph()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -57,12 +57,12 @@ def MediaPlayerGUI():
|
|||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while(True):
|
||||
# Read the form (this call will not block)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if button:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(button)
|
||||
if event:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
MediaPlayerGUI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -43,19 +43,19 @@ def TestMenus():
|
|||
|
||||
# ------ Loop & Process button menu choices ------ #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
return
|
||||
print('Button = ', button)
|
||||
print('Event = ', event)
|
||||
# ------ Process menu choices ------ #
|
||||
if button == 'About...':
|
||||
window.Hide()
|
||||
if event == 'About...':
|
||||
# window.Hide()
|
||||
sg.Popup('About this program','Version 1.0', 'PySimpleGUI rocks...', grab_anywhere=True)
|
||||
window.UnHide()
|
||||
elif button == 'Open':
|
||||
# window.UnHide()
|
||||
elif event == 'Open':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('file to open', no_window=True)
|
||||
print(filename)
|
||||
elif button == 'Properties':
|
||||
elif event == 'Properties':
|
||||
SecondForm()
|
||||
|
||||
TestMenus()
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ def StatusOutputExample():
|
|||
i=0
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'LED On':
|
||||
if event == 'LED On':
|
||||
print('Turning on the LED')
|
||||
elif button == 'LED Off':
|
||||
elif event == 'LED Off':
|
||||
print('Turning off the LED')
|
||||
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -40,8 +40,8 @@ def main():
|
|||
# ---===--- LOOP through video file by frame --- #
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
while vidFile.isOpened():
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
ret, frame = vidFile.read()
|
||||
if not ret: # if out of data stop looping
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ else:
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import cv2 as cv
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import io
|
||||
from sys import exit as exit
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,30 +20,41 @@ def main():
|
|||
# define the window layout
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('OpenCV Demo', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(filename='', key='image')],
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 1), pad=((200, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
[sg.ReadButton('Record', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('Stop', size=(10, 1), font='Any 14'),
|
||||
sg.ReadButton('Exit', size=(10, 1), font='Helvetica 14'),
|
||||
sg.RButton('About', size=(10,1), font='Any 14')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# create the window and show it without the plot
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Demo Application - OpenCV Integration',
|
||||
location=(800,400))
|
||||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
window.Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
# ---===--- Event LOOP Read and display frames, operate the GUI --- #
|
||||
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
elif button == 'About':
|
||||
elif event == 'Record':
|
||||
recording = True
|
||||
elif event == 'Stop':
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
img = Image.new('RGB', (640, 480), (255, 255, 255))
|
||||
bio = io.BytesIO() # a binary memory resident stream
|
||||
img.save(bio, format='PNG') # save image as png to it
|
||||
imgbytes = bio.getvalue()
|
||||
window.FindElement('image').Update(data=imgbytes)
|
||||
elif event == 'About':
|
||||
sg.PopupNoWait('Made with PySimpleGUI',
|
||||
'www.PySimpleGUI.org',
|
||||
'Check out how the video keeps playing behind this window.',
|
||||
'I finally figured out how to display frames from a webcam.',
|
||||
'ENJOY! Go make something really cool with this... please!',
|
||||
keep_on_top=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if recording:
|
||||
ret, frame = cap.read()
|
||||
|
||||
gray = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -124,20 +124,20 @@ old_zoom = 0 # used for zoom on/off
|
|||
# the zoom buttons work in on/off mode.
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = False
|
||||
if button is None and value is None:
|
||||
if event is None and values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if button in ("Escape:27",): # this spares me a 'Quit' button!
|
||||
if event in ("Escape:27",): # this spares me a 'Quit' button!
|
||||
break
|
||||
# print("hex(button)", hexlify(button.encode()))
|
||||
if button[0] == chr(13): # surprise: this is 'Enter'!
|
||||
if event[0] == chr(13): # surprise: this is 'Enter'!
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cur_page = int(value[0]) - 1 # check if valid
|
||||
cur_page = int(values[0]) - 1 # check if valid
|
||||
while cur_page < 0:
|
||||
cur_page += page_count
|
||||
except:
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,17 +145,17 @@ while True:
|
|||
goto.Update(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
# goto.TKStringVar.set(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
|
||||
elif button in ("Next", "Next:34", "MouseWheel:Down"):
|
||||
elif event in ("Next", "Next:34", "MouseWheel:Down"):
|
||||
cur_page += 1
|
||||
elif button in ("Prev", "Prior:33", "MouseWheel:Up"):
|
||||
elif event in ("Prev", "Prior:33", "MouseWheel:Up"):
|
||||
cur_page -= 1
|
||||
elif button == "Top-L":
|
||||
elif event == "Top-L":
|
||||
zoom = 1
|
||||
elif button == "Top-R":
|
||||
elif event == "Top-R":
|
||||
zoom = 2
|
||||
elif button == "Bot-L":
|
||||
elif event == "Bot-L":
|
||||
zoom = 3
|
||||
elif button == "Bot-R":
|
||||
elif event == "Bot-R":
|
||||
zoom = 4
|
||||
|
||||
# sanitize page number
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ while True:
|
|||
zoom = old_zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = True
|
||||
|
||||
if button in zoom_buttons:
|
||||
if event in zoom_buttons:
|
||||
if 0 < zoom == old_zoom:
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
force_page = True
|
||||
|
|
@ -184,6 +184,6 @@ while True:
|
|||
old_zoom = zoom
|
||||
|
||||
# update page number field
|
||||
if button in my_keys or not value[0]:
|
||||
if event in my_keys or not values[0]:
|
||||
goto.Update(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
# goto.TKStringVar.set(str(cur_page + 1))
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
136
Demo_PNG_Thumbnail_Viewer.py
Normal file
136
Demo_PNG_Thumbnail_Viewer.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from sys import exit as exit
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import io
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
thumbnails = {}
|
||||
|
||||
ROWS = 8
|
||||
COLUMNS = 8
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(border_width=0)
|
||||
# Get the folder containing the images from the user
|
||||
# folder = 'A:/TEMP/pdfs'
|
||||
folder = sg.PopupGetFolder('Image folder to open')
|
||||
if folder is None:
|
||||
sg.PopupCancel('Cancelling')
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
def image_file_to_bytes(filename, size):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
image = Image.open(filename)
|
||||
image.thumbnail(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
|
||||
bio = io.BytesIO() # a binary memory resident stream
|
||||
image.save(bio, format='PNG') # save image as png to it
|
||||
imgbytes = bio.getvalue()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
imgbytes = None
|
||||
return imgbytes
|
||||
|
||||
def set_image_to_blank(key):
|
||||
img = Image.new('RGB', (100, 100), (255, 255, 255))
|
||||
img.thumbnail((1, 1), Image.ANTIALIAS)
|
||||
bio = io.BytesIO()
|
||||
img.save(bio, format='PNG')
|
||||
imgbytes = bio.getvalue()
|
||||
window.FindElement(key).Update(image_data=imgbytes)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# get list of PNG files in folder
|
||||
png_files = [os.path.join(folder, f) for f in os.listdir(folder) if '.png' in f]
|
||||
filenames_only = [f for f in os.listdir(folder) if '.png' in f]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(png_files) == 0:
|
||||
sg.Popup('No PNG images in folder')
|
||||
exit(0)
|
||||
|
||||
# define menu layout
|
||||
menu = [['&File', ['&Open Folder', 'E&xit']], ['&Help', ['&About',]]]
|
||||
|
||||
buttons = []
|
||||
for display_index in range(ROWS):
|
||||
row = []
|
||||
for j in range(COLUMNS):
|
||||
row.append(sg.RButton('',border_width=0,button_color=sg.COLOR_SYSTEM_DEFAULT, key=(display_index, j)))
|
||||
buttons.append(row)
|
||||
|
||||
col_buttons = [[]]
|
||||
|
||||
# define layout, show and read the window
|
||||
col = [[sg.Text(png_files[0], size=(80, 3), key='filename')],
|
||||
[sg.Image(data=image_file_to_bytes(png_files[0], (500,500)), key='image')],]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Menu(menu)], [sg.Column(buttons), sg.Column([[sg.Slider((len(png_files),0),default_value=0,size=(38,20),orientation='v', key='_slider_', change_submits=True)]]), sg.Column(col)]]
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Image Browser',
|
||||
return_keyboard_events=True,
|
||||
use_default_focus=False ).Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
# -------========= Event Loop =========--------
|
||||
display_index=0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
for x in range(ROWS): # update thumbnails
|
||||
for y in range(COLUMNS):
|
||||
cur_index = display_index + (x * 4) + y
|
||||
if cur_index < len(png_files):
|
||||
filename = png_files[cur_index]
|
||||
if filename not in thumbnails:
|
||||
imgbytes = image_file_to_bytes(filename, (100,100))
|
||||
thumbnails[filename] = imgbytes
|
||||
else:
|
||||
imgbytes = thumbnails[filename]
|
||||
button_elem = window.FindElement(key=(x,y))
|
||||
button_elem.Update(image_data=imgbytes)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
set_image_to_blank((x,y))
|
||||
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
display_index = values['_slider_']
|
||||
# --------------------- Button & Keyboard ---------------------
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event in ('MouseWheel:Down', 'Down:40',) and display_index < len(png_files)-1:
|
||||
display_index += 4
|
||||
elif event in ('MouseWheel:Up', 'Up:38',) and display_index > 0:
|
||||
display_index -= 4
|
||||
elif event in ('Prior:33', 'Prev'):
|
||||
display_index -= 16
|
||||
elif event in ('Next:34', 'Next'):
|
||||
display_index += 16
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('_slider_').Update(display_index)
|
||||
# ----------------- Menu choices -----------------
|
||||
if event == 'Open Folder':
|
||||
newfolder = sg.PopupGetFolder('New folder', no_window=True)
|
||||
if newfolder is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
folder = newfolder
|
||||
png_files = [os.path.join(folder, f) for f in os.listdir(folder) if '.png' in f]
|
||||
filenames_only = [f for f in os.listdir(folder) if '.png' in f]
|
||||
display_index = 0
|
||||
thumbnail = {}
|
||||
for j in range(ROWS):
|
||||
for i in range(COLUMNS):
|
||||
set_image_to_blank((i,j))
|
||||
# img = Image.new('RGB', (1,1), (255,255,255))
|
||||
# img.thumbnail((1,1), Image.ANTIALIAS)
|
||||
# bio = io.BytesIO()
|
||||
# img.save(bio, format='PNG')
|
||||
# imgbytes = bio.getvalue()
|
||||
# [window.FindElement((i,j)).Update(image_data=imgbytes) for j in range(ROWS) for i in range(COLUMNS)]
|
||||
elif event == 'About':
|
||||
sg.Popup('Demo PNG Viewer Program', 'Please give PySimpleGUI a try!')
|
||||
elif type(event) is tuple:
|
||||
x, y = event
|
||||
image_index = display_index + (x * 4) + y
|
||||
if image_index < len(png_files):
|
||||
filename = png_files[image_index]
|
||||
imgbytes = image_file_to_bytes(filename, (500, 500))
|
||||
window.FindElement('image').Update(data=imgbytes)
|
||||
window.FindElement('filename').Update(filename)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -42,21 +42,21 @@ window = sg.Window('Image Browser', return_keyboard_events=True, location=(0,0),
|
|||
i=0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
# --------------------- Button & Keyboard ---------------------
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button in ('Next', 'MouseWheel:Down', 'Down:40', 'Next:34') and i < len(png_files)-1:
|
||||
elif event in ('Next', 'MouseWheel:Down', 'Down:40', 'Next:34') and i < len(png_files)-1:
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
elif button in ('Prev', 'MouseWheel:Up', 'Up:38', 'Prior:33') and i > 0:
|
||||
elif event in ('Prev', 'MouseWheel:Up', 'Up:38', 'Prior:33') and i > 0:
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
elif button == 'Exit':
|
||||
elif event == 'Exit':
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
filename = folder + '/' + values['listbox'][0] if button == 'Read' else png_files[i]
|
||||
filename = folder + '/' + values['listbox'][0] if event == 'Read' else png_files[i]
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------------- Menu choices -----------------
|
||||
if button == 'Open Folder':
|
||||
if event == 'Open Folder':
|
||||
newfolder = sg.PopupGetFolder('New folder', no_window=True)
|
||||
if newfolder is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ while True:
|
|||
window.FindElement('listbox').Update(values=filenames_only)
|
||||
window.Refresh()
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
elif button == 'About':
|
||||
elif event == 'About':
|
||||
sg.Popup('Demo PNG Viewer Program', 'Please give PySimpleGUI a try!')
|
||||
|
||||
# update window with new image
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,9 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
desc_text = """
|
||||
Text( text
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,6 +25,7 @@ Shortcuts: Txt, T
|
|||
desc_inputtext = """
|
||||
InputText( default_text =''
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
password_char=''
|
||||
justification=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,6 +61,7 @@ desc_inputoptionmenu = """
|
|||
InputOptionMenu(values
|
||||
default_value=None
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
text_color=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,6 +97,7 @@ CheckBox( text
|
|||
background_color=None
|
||||
text_color=None
|
||||
change_submits=False
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
key=None
|
||||
pad=None
|
||||
tooltip=None)
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,6 +109,7 @@ desc_radio = """
|
|||
Radio( text
|
||||
group_id
|
||||
default=False
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -114,6 +123,7 @@ Radio( text
|
|||
desc_spin = """
|
||||
Spin( values
|
||||
initial_value=None
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
change_submits=False
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -128,6 +138,7 @@ Spin( values
|
|||
desc_multiline = """
|
||||
MultiLine( default_text=''
|
||||
enter_submits = False
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
autoscroll=False
|
||||
size=(None,None)
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -157,6 +168,7 @@ Button( button_text=''
|
|||
tooltip=None
|
||||
file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.*"),)
|
||||
initial_folder=None
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
image_filename=None
|
||||
image_size=(None, None)
|
||||
image_subsample=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,6 +276,7 @@ Slider( range=(None,None)
|
|||
border_width=None
|
||||
relief=None
|
||||
change_submits=False
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
font=None
|
||||
background_color=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -277,6 +290,7 @@ Slider( range=(None,None)
|
|||
desc_spin = """
|
||||
Spin( values
|
||||
initial_value=None
|
||||
disabled=False
|
||||
change_submits=False
|
||||
size=(None, None)
|
||||
auto_size_text=None
|
||||
|
|
@ -414,7 +428,7 @@ tab_progressbar = [[sg.Column([[sg.Text(desc_progressbar, font=('Consolas 12'))]
|
|||
tab_optionmenu = [[sg.Column([[sg.OptionMenu([1,2,3,4,5], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_inputoptionmenu, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_combo = [[sg.Column([[sg.Combo([1,2,3,4,5], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_inputoptionmenu, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_frame = [[sg.Column([[sg.Frame('Frame',[[sg.T(' ')]], size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_frame, font=('Consolas 12'))]])]]
|
||||
tab_column = [[sg.Column([[]],size=(15,1))],[sg.Text(desc_column, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_column = [[sg.Text(desc_column, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_graph = [[sg.Text(desc_graph, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_tab = [[sg.Text(desc_tab, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
tab_tabgroup = [[sg.Text(desc_tabgroup, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
|
|
@ -423,16 +437,25 @@ tab_table = [[sg.Text(desc_table, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
|||
tab_window = [[sg.Text(desc_window, font=('Consolas 12'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Window',tab_window),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Text',tab_text), sg.Tab('InputText', tab_input), sg.Tab('Checkbox', tab_checkbox),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Radio',tab_radio), sg.Tab('Listbox', tab_listbox), sg.Tab('Slider', tab_slider),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Spinner',tab_spinner), sg.Tab('Multiline', tab_multiline),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Text',tab_text),
|
||||
sg.Tab('InputText', tab_input),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Checkbox', tab_checkbox),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Radio',tab_radio),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Listbox', tab_listbox),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Slider', tab_slider),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Spinner',tab_spinner),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Multiline', tab_multiline),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Output', tab_output),
|
||||
sg.Tab('ProgressBar', tab_progressbar),
|
||||
sg.Tab('OptionMenu', tab_optionmenu), sg.Tab('Frame', tab_frame),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Combo', tab_combo), sg.Tab('Column', tab_column),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Graph', tab_graph), sg.Tab('Image', tab_image),
|
||||
sg.Tab('OptionMenu', tab_optionmenu),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Combo', tab_combo),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Image', tab_image),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Table', tab_table),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Tab', tab_tab), sg.Tab('TabGroup', tab_tabgroup),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Graph', tab_graph),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Frame', tab_frame),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Column', tab_column),
|
||||
sg.Tab('Tab', tab_tab),
|
||||
sg.Tab('TabGroup', tab_tabgroup),
|
||||
]], tab_location='lefttop', title_color='blue', selected_title_color='red')]]
|
||||
|
||||
# layout = [[sg.Text('The PySimpleGUI SDK Quick Reference Guide', font='Any 15', relief=sg.RELIEF_RAISED)],
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,8 +467,8 @@ window = sg.Window('PySimpleGUI SDK Quick Reference',
|
|||
font='Any 12').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
element = values['_in_'][0]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,8 +30,8 @@ def HashGeneratorGUI():
|
|||
text_justification='r', return_keyboard_events=True, grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
password = values['password']
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -41,13 +41,13 @@ layout = [[sg.T('Raspberry Pi LEDs')],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Raspberry Pi GUI', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if button is 'Switch LED':
|
||||
if event is 'Switch LED':
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(SwitchLED())
|
||||
elif button is 'Flash LED':
|
||||
elif event is 'Flash LED':
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('LED is Flashing')
|
||||
window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
FlashLED()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -40,13 +40,13 @@ def RemoteControlExample():
|
|||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(button)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(event)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update('')
|
||||
# if user clicked quit button OR closed the form using the X, then break out of loop
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,13 +73,13 @@ def RemoteControlExample_NoGraphics():
|
|||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(button)
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update(event)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
window.FindElement('status').Update('')
|
||||
# if user clicked quit button OR closed the form using the X, then break out of loop
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -638,8 +638,8 @@ prev_x, prev_y = canvas_left, canvas_bottom
|
|||
while True:
|
||||
time.sleep(.2)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if g_response_time is None or prev_response_time == g_response_time:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
14
Demo_Pong.py
14
Demo_Pong.py
|
|
@ -155,19 +155,19 @@ def pong():
|
|||
bat2.draw()
|
||||
|
||||
# ------------- Read the form, get keypresses -------------
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
# ------------- If quit -------------
|
||||
if button is None and values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
if event is None and values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
# ------------- Keypresses -------------
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
if button.startswith('Up'):
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
if event.startswith('Up'):
|
||||
bat2.up(2)
|
||||
elif button.startswith('Down'):
|
||||
elif event.startswith('Down'):
|
||||
bat2.down(2)
|
||||
elif button == 'w':
|
||||
elif event == 'w':
|
||||
bat1.up(1)
|
||||
elif button == 's':
|
||||
elif event == 's':
|
||||
bat1.down(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if ball1.checkwin():
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,8 +22,8 @@ def PopupDropDown(title, text, values):
|
|||
window = sg.Window(title).Layout([[sg.Text(text)],
|
||||
[sg.DropDown(values, key='_drop')],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
return None if button != 'OK' else values['_drop']
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
return None if event != 'OK' else values['_drop']
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------------------- Calling your PopupDropDown function -----------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,6 +5,12 @@ if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
|||
else:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
|
||||
from PySimpleGUI import Print as print
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
print('test')
|
||||
sg.PopupGetFile('Get file', save_as=True,file_types=(("ALL Files", "*.jpg")))
|
||||
|
||||
# Here, have some windows on me....
|
||||
[sg.PopupNoWait('No-wait Popup', location=(500+100*x,500)) for x in range(10)]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,16 +37,16 @@ def DemoOneLineProgressMeter():
|
|||
sg.T('Delay'), sg.In(default_text='10', key='TimeOuter', size=(5,1), do_not_clear=True), sg.T('ms')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Inner Loop Count', size=(15,1), justification='r'), sg.In(default_text='100', size=(5,1), key='CountInner', do_not_clear=True) ,
|
||||
sg.T('Delay'), sg.In(default_text='10', key='TimeInner', size=(5,1), do_not_clear=True), sg.T('ms')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Show', pad=((0,0), 3), bind_return_key=True), sg.T('me the meters!')]
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Show', pad=((0,0), 3), bind_return_key=True), sg.T('me the meters!')]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('One-Line Progress Meter Demo').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'Show':
|
||||
if event == 'Show':
|
||||
max_outer = int(values['CountOuter'])
|
||||
max_inner = int(values['CountInner'])
|
||||
delay_inner = int(values['TimeInner'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,8 +77,8 @@ def CustomMeter():
|
|||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i+1)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -84,4 +84,4 @@ window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI', for
|
|||
fig_photo = draw_figure(window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas, fig)
|
||||
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -76,4 +76,4 @@ window = sg.Window('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI', for
|
|||
fig_photo = draw_figure(window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas, fig)
|
||||
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -55,18 +55,18 @@ def Launcher2():
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button in ('EXIT', None):
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in ('EXIT', None):
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
if button in ('Shortcut 1', 'Fav Program'):
|
||||
if event in ('Shortcut 1', 'Fav Program'):
|
||||
print('Quickly launch your favorite programs using these shortcuts')
|
||||
print('Or copy files to your github folder. Or anything else you type on the command line')
|
||||
# copyfile(source, dest)
|
||||
elif button is 'Run':
|
||||
for index, file in enumerate(value['demolist']):
|
||||
elif event is 'Run':
|
||||
for index, file in enumerate(values['demolist']):
|
||||
print('Launching %s'%file)
|
||||
window.Refresh() # make the print appear immediately
|
||||
if value['wait']:
|
||||
if values['wait']:
|
||||
execute_command_blocking(LOCATION_OF_YOUR_SCRIPTS + file)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
execute_command_nonblocking(LOCATION_OF_YOUR_SCRIPTS + file)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ stores the result in the variable fname, just like the command line parsing did.
|
|||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
button, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').LayoutAndRead([[sg.T('Document to open')],
|
||||
event, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').LayoutAndRead([[sg.T('Document to open')],
|
||||
[sg.In(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Open(), sg.Cancel()]])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,11 +27,11 @@ window = sg.Window('Spinner simulation').Layout(layout)
|
|||
# --- Event Loop --- #
|
||||
counter = 0
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'Ok' or button is None: # be nice to your user, always have an exit from your form
|
||||
if event == 'Ok' or event is None: # be nice to your user, always have an exit from your form
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# --- do spinner stuff --- #
|
||||
counter += 1 if button =='+' else -1 if button == '-' else 0
|
||||
counter += 1 if event == '+' else -1 if event == '-' else 0
|
||||
window.FindElement('spin').Update(counter)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,6 +18,6 @@ layout = [
|
|||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple Data Entry Window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,6 @@ else:
|
|||
import PySimpleGUI27 as sg
|
||||
import csv
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def table_example():
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('filename to open', no_window=True, file_types=(("CSV Files","*.csv"),))
|
||||
# --- populate table with file contents --- #
|
||||
|
|
@ -29,14 +28,19 @@ def table_example():
|
|||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data, headings=header_list, max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True, justification='right', size=(None, len(data)))]]
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data,
|
||||
headings=header_list,
|
||||
max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True,
|
||||
justification='right',
|
||||
alternating_row_color='lightblue',
|
||||
num_rows=len(data))]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13*10*len(header_list), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 char per column * num columns
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)],]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,8 @@
|
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
from Demo_Turtle import canvas
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,12 +24,16 @@ if filename is not None:
|
|||
|
||||
sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data[1:][:], headings=[data[0][x] for x in range(len(data[0]))], max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True, display_row_numbers=True, justification='right', size=(None, len(data)))]]
|
||||
headings = [data[0][x] for x in range(len(data[0]))]
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=(1200,600), scrollable=True)],]
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data[1:][:], headings=headings, max_col_width=25,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=True, display_row_numbers=True, justification='right', num_rows=len(data), alternating_row_color='lightblue')]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13 * 10 * len(headings), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 per column * num columns
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)],]
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,13 +31,13 @@ def table_example():
|
|||
# sg.SetOptions(element_padding=(0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
col_layout = [[sg.Table(values=data, headings=header_list, display_row_numbers=True,
|
||||
auto_size_columns=False, size=(None, len(data)))]]
|
||||
auto_size_columns=False, num_rows=len(data))]]
|
||||
|
||||
canvas_size = (13*10*len(header_list), 600) # estimate canvas size - 13 pixels per char * 10 per column * num columns
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Column(col_layout, size=canvas_size, scrollable=True)]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Table', grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
b, v = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
event, values = window.LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
sys.exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,13 +37,13 @@ def TableSimulation():
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Table', return_keyboard_events=True, grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
# --- Process buttons --- #
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button == 'About...':
|
||||
elif event == 'About...':
|
||||
sg.Popup('Demo of table capabilities')
|
||||
elif button == 'Open':
|
||||
elif event == 'Open':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('filename to open', no_window=True, file_types=(("CSV Files","*.csv"),))
|
||||
# --- populate table with file contents --- #
|
||||
if filename is not None:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -44,8 +44,8 @@ window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(la
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.PopupNonBlocking(b,v)
|
||||
print(b,v)
|
||||
if b is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.PopupNonBlocking(event, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(la
|
|||
print('Are there enough tabs for you?')
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button,values)
|
||||
if button is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,8 +19,7 @@ window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(la
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
b, v = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.PopupNonBlocking('button = %s'%b,'Values dictionary', v)
|
||||
print(b,v)
|
||||
if b is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
sg.PopupNonBlocking('button = %s' % event, 'Values dictionary', values)
|
||||
if event is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
|||
[ sg.Button('Next Window')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -------------------------------------#
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, value)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,8 +22,10 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('Tree Test') ],
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Tree Element Test').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
print(treedata)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, value)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,8 +18,9 @@ import turtle
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('My layout') ],
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(500,500), key='_canvas_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('F'), sg.RButton('B'), sg.RButton('L'), sg.RButton('R')]]
|
||||
[sg.Canvas(size=(800,800), key='_canvas_')],
|
||||
[ sg.RButton('F'), sg.RButton('B'), sg.RButton('L'), sg.RButton('R')],
|
||||
[sg.RButton('Spiral'), sg.RButton('Inside Out'), sg.RButton('Circles')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('My new window').Layout(layout).Finalize()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,20 +29,56 @@ canvas = window.FindElement('_canvas_').TKCanvas
|
|||
t = turtle.RawTurtle(canvas)
|
||||
t.pencolor("#ff0000") # Red
|
||||
|
||||
t.penup() # Regarding one of the comments
|
||||
t.pendown() # Regarding one of the comments
|
||||
t.penup()
|
||||
t.pendown()
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'F':
|
||||
if event == 'F':
|
||||
t.forward(100)
|
||||
elif button == 'B':
|
||||
elif event == 'B':
|
||||
t.back(100)
|
||||
elif button == 'L':
|
||||
elif event == 'L':
|
||||
t.left(90)
|
||||
elif button == 'R':
|
||||
elif event == 'R':
|
||||
t.right(90)
|
||||
|
||||
elif event == 'Spiral':
|
||||
canvas.config(bg='light green')
|
||||
t.color("blue")
|
||||
def sqrfunc(size):
|
||||
for i in range(4):
|
||||
t.fd(size)
|
||||
t.left(90)
|
||||
size = size - 5
|
||||
sqrfunc(146)
|
||||
sqrfunc(126)
|
||||
sqrfunc(106)
|
||||
sqrfunc(86)
|
||||
sqrfunc(66)
|
||||
sqrfunc(46)
|
||||
sqrfunc(26)
|
||||
elif event == 'Inside Out':
|
||||
canvas.config(bg = "light green")
|
||||
t.color("blue")
|
||||
def sqrfunc(size):
|
||||
for i in range(4):
|
||||
t.fd(size)
|
||||
t.left(90)
|
||||
size = size + 5
|
||||
sqrfunc(6)
|
||||
sqrfunc(26)
|
||||
sqrfunc(46)
|
||||
sqrfunc(66)
|
||||
sqrfunc(86)
|
||||
sqrfunc(106)
|
||||
sqrfunc(126)
|
||||
sqrfunc(146)
|
||||
elif event == 'Circles':
|
||||
t.speed(0)
|
||||
for i in range(400):
|
||||
t.circle(2 * i*.25)
|
||||
t.circle(-2 * i*.25)
|
||||
t.left(i)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,11 +11,11 @@ layout = [[ sg.Text('My Window') ],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('My window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'Disappear':
|
||||
window.Disapper()
|
||||
if event == 'Disappear':
|
||||
window.Disappear()
|
||||
sg.Popup('Click OK to make window reappear')
|
||||
window.Reappear()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,6 +6,6 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('What is your name?')],
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Title of Window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup('Hello {}'.format(values[0]))
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ def DownloadSubtitlesGUI():
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, gui) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button in ('EXIT', None):
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event in ('EXIT', None):
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
link = gui['link']
|
||||
if button is 'Get List':
|
||||
link = values['link']
|
||||
if event is 'Get List':
|
||||
print('Getting list of subtitles....')
|
||||
window.Refresh()
|
||||
command = [f'C:/Python/PycharmProjects/GooeyGUI/youtube-dl --list-subs {link}',]
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,8 +44,8 @@ def DownloadSubtitlesGUI():
|
|||
combobox.Update(values=lang_list)
|
||||
print('Done')
|
||||
|
||||
elif button is 'Download':
|
||||
lang = gui['lang']
|
||||
elif event is 'Download':
|
||||
lang = values['lang']
|
||||
if lang is '':
|
||||
lang = 'en'
|
||||
print(f'Downloading subtitle for {lang}...')
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -62,14 +62,14 @@ def main():
|
|||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if 'Mouse' in button or 'Control' in button or 'Shift' in button:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if 'Mouse' in event or 'Control' in event or 'Shift' in event:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if button == 'Sort by Name':
|
||||
if event == 'Sort by Name':
|
||||
psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
|
||||
procs = psutil.process_iter()
|
||||
all_procs = [[proc.cpu_percent(), proc.name(), proc.pid] for proc in procs]
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,13 +78,16 @@ def main():
|
|||
for process in sorted_by_cpu_procs:
|
||||
display_list.append('{:5d} {:5.2f} {}\n'.format(process[2], process[0]/10, process[1]))
|
||||
window.FindElement('_processes_').Update(display_list)
|
||||
elif button == 'Kill':
|
||||
elif event == 'Kill':
|
||||
processes_to_kill = values['_processes_']
|
||||
for proc in processes_to_kill:
|
||||
pid = int(proc[0:5])
|
||||
if sg.PopupYesNo('About to kill {} {}'.format(pid, proc[13:]), keep_on_top=True) == 'Yes':
|
||||
if sg.PopupYesNo('About to kill {} {}'.format(pid, proc[12:]), keep_on_top=True) == 'Yes':
|
||||
try:
|
||||
kill_proc_tree(pid=pid)
|
||||
elif button == 'Sort by % CPU':
|
||||
except:
|
||||
sg.PopupAutoClose('Error killing process', auto_close_duration=1)
|
||||
elif event == 'Sort by % CPU':
|
||||
psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
|
||||
procs = psutil.process_iter()
|
||||
all_procs = [[proc.cpu_percent(), proc.name(), proc.pid] for proc in procs]
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,3 +107,4 @@ def main():
|
|||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
5099
PySimpleGUI27Gen.py
5099
PySimpleGUI27Gen.py
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
187
docs/cookbook.md
187
docs/cookbook.md
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,9 +36,9 @@ Same GUI screen except the return values are in a list instead of a dictionary a
|
|||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values[0], values[1], values[2])
|
||||
print(event, values[0], values[1], values[2])
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple data entry - Return Values As Dictionary
|
||||
A simple GUI with default values. Results returned in a dictionary.
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,9 +59,9 @@ A simple GUI with default values. Results returned in a dictionary.
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry GUI').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
print(event, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,9 +79,9 @@ Browse for a filename that is populated into the input field.
|
|||
[sg.InputText(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
(button, (source_filename,)) = sg.Window('SHA-1 & 256 Hash').Layout(GUI_rows).Read()
|
||||
(event, (source_filename,)) = sg.Window('SHA-1 & 256 Hash').Layout(GUI_rows).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, source_filename)
|
||||
print(event, source_filename)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
## Add GUI to Front-End of Script
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,7 +94,7 @@ Quickly add a GUI allowing the user to browse for a filename if a filename is no
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
|
||||
button, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').Layout([[sg.Text('Document to open')],
|
||||
event, (fname,) = sg.Window('My Script').Layout([[sg.Text('Document to open')],
|
||||
[sg.In(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Open(), sg.Cancel()]]).Read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
@ -102,7 +103,7 @@ Quickly add a GUI allowing the user to browse for a filename if a filename is no
|
|||
if not fname:
|
||||
sg.Popup("Cancel", "No filename supplied")
|
||||
raise SystemExit("Cancelling: no filename supplied")
|
||||
print(button, fname)
|
||||
print(event, fname)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,9 +124,9 @@ Browse to get 2 file names that can be then compared.
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('File Compare').Layout(gui_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
## Nearly All Widgets with Green Color Theme
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,11 +181,11 @@ Example of nearly all of the widgets in a single window. Uses a customized colo
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup('Title',
|
||||
'The results of the window.',
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button),
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(event),
|
||||
'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -193,7 +194,7 @@ Example of nearly all of the widgets in a single window. Uses a customized colo
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-Blocking Window With Periodic Update
|
||||
An async Window that has a button read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. Note that `value` is checked for None which indicates the window was closed using X.
|
||||
An async Window that has a event read loop. A Text Element is updated periodically with a running timer. Note that `value` is checked for None which indicates the window was closed using X.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,11 +213,11 @@ An async Window that has a button read loop. A Text Element is updated periodic
|
|||
# Event Loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
i += 1 * (timer_running is True)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit': # if user closed the window using X or clicked Quit button
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif button == 'Start/Stop':
|
||||
elif event == 'Start/Stop':
|
||||
timer_running = not timer_running
|
||||
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format((i // 100) // 60, (i // 100) % 60, i % 100))
|
||||
|
|
@ -254,13 +255,13 @@ The architecture of some programs works better with button callbacks instead of
|
|||
# Event loop. Read buttons, make callbacks
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# Read the Window
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
event, value = window.Read()
|
||||
# Take appropriate action based on button
|
||||
if button == '1':
|
||||
if event == '1':
|
||||
button1()
|
||||
elif button == '2':
|
||||
elif event == '2':
|
||||
button2()
|
||||
elif button =='Quit' or button is None:
|
||||
elif event =='Quit' or event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# All done!
|
||||
|
|
@ -293,10 +294,10 @@ This recipe implements a remote control interface for a robot. There are 4 dire
|
|||
# your program's main loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
window.CloseNonBlocking() # Don't forget to close your window!
|
||||
|
|
@ -370,12 +371,12 @@ Buttons can have PNG of GIF images on them. This Media Player recipe requires 4
|
|||
# Our event loop
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# Read the window (this call will not block)
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# If a button was pressed, display it on the GUI by updating the text element
|
||||
if button:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(button)
|
||||
if event:
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
## Script Launcher - Persistent Window
|
||||
|
|
@ -412,14 +413,14 @@ This Window doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are
|
|||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to call scripts --- #
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'EXIT' or button is None:
|
||||
(event, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'EXIT' or event is None:
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
if button == 'script1':
|
||||
if event == 'script1':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('pip', 'list')
|
||||
elif button == 'script2':
|
||||
elif event == 'script2':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('python', '--version')
|
||||
elif button == 'Run':
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess(value[0])
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
|
|
@ -459,7 +460,7 @@ A standard non-blocking GUI with lots of inputs.
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Machine Learning Front End', font=("Helvetica", 12)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
## Custom Progress Meter / Progress Bar
|
||||
|
|
@ -480,8 +481,8 @@ Perhaps you don't want all the statistics that the EasyProgressMeter provides an
|
|||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
window.FindElement('progbar').UpdateBar(i + 1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -507,13 +508,13 @@ Instead of
|
|||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
you can write this line of code for the exact same result (OK, two lines with the import):
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(
|
||||
event, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(
|
||||
[[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()]]).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -549,9 +550,9 @@ To make it easier to see the Column in the window, the Column background has bee
|
|||
|
||||
# Display the Window and get values
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line Window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line Window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Persistent Window With Text Element Updates
|
||||
|
|
@ -574,9 +575,9 @@ This simple program keep a window open, taking input values until the user termi
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Math').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
if event is not None:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
numerator = float(values['numerator'])
|
||||
denominator = float(values['denominator'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -619,12 +620,12 @@ While it's fun to scribble on a Canvas Widget, try Graph Element makes it a down
|
|||
cir = canvas.TKCanvas.create_oval(50, 50, 100, 100)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'Blue':
|
||||
if event == 'Blue':
|
||||
canvas.TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill="Blue")
|
||||
elif button == 'Red':
|
||||
elif event == 'Red':
|
||||
canvas.TKCanvas.itemconfig(cir, fill="Red")
|
||||
|
||||
## Graph Element - drawing circle, rectangle, etc, objects
|
||||
|
|
@ -653,14 +654,14 @@ Just like you can draw on a tkinter widget, you can also draw on a Graph Element
|
|||
line = graph.DrawLine((0,0), (100,100))
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Blue':
|
||||
if event is 'Blue':
|
||||
graph.TKCanvas.itemconfig(circle, fill = "Blue")
|
||||
elif button is 'Red':
|
||||
elif event is 'Red':
|
||||
graph.TKCanvas.itemconfig(circle, fill = "Red")
|
||||
elif button is 'Move':
|
||||
elif event is 'Move':
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(point, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(circle, 10,10)
|
||||
graph.MoveFigure(oval, 10,10)
|
||||
|
|
@ -707,15 +708,15 @@ There are a number of features used in this Recipe including:
|
|||
# Loop forever reading the window's values, updating the Input field
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read() # read the window
|
||||
if button is None: # if the X button clicked, just exit
|
||||
event, values = window.Read() # read the window
|
||||
if event is None: # if the X button clicked, just exit
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button == 'Clear': # clear keys if clear button
|
||||
if event == 'Clear': # clear keys if clear button
|
||||
keys_entered = ''
|
||||
elif button in '1234567890':
|
||||
elif event in '1234567890':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input'] # get what's been entered so far
|
||||
keys_entered += button # add the new digit
|
||||
elif button == 'Submit':
|
||||
keys_entered += event # add the new digit
|
||||
elif event == 'Submit':
|
||||
keys_entered = values['input']
|
||||
window.FindElement('out').Update(keys_entered) # output the final string
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -762,8 +763,8 @@ Use the Canvas Element to create an animated graph. The code is a bit tricky to
|
|||
dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
# Our event loop
|
||||
for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
ax.cla()
|
||||
|
|
@ -823,30 +824,30 @@ In other GUI frameworks this program would be most likely "event driven" with ca
|
|||
window.FindElement('Submit').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
recording = have_data = False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
if button is 'Start':
|
||||
if event is 'Start':
|
||||
window.FindElement('Start').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Stop').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Reset').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Submit').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
recording = True
|
||||
elif button is 'Stop' and recording:
|
||||
elif event is 'Stop' and recording:
|
||||
window.FindElement('Stop').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Start').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Submit').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
have_data = True
|
||||
elif button is 'Reset':
|
||||
elif event is 'Reset':
|
||||
window.FindElement('Stop').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Start').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Submit').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Reset').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
recording = False
|
||||
have_data = False
|
||||
elif button is 'Submit' and have_data:
|
||||
elif event is 'Submit' and have_data:
|
||||
window.FindElement('Stop').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Start').Update(disabled=False)
|
||||
window.FindElement('Submit').Update(disabled=True)
|
||||
|
|
@ -887,8 +888,8 @@ Use the upper half to generate your hash code. Then paste it into the code in t
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
password = values['password']
|
||||
|
|
@ -981,21 +982,21 @@ You can easily change colors to match your background by changing a couple of pa
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Floating Toolbar', no_titlebar=True, keep_on_top=True).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input (buttons) --- #
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input (events) --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
(button, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'EXIT' or button is None:
|
||||
(event, value) = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'EXIT' or event is None:
|
||||
break # exit button clicked
|
||||
if button == 'Program 1':
|
||||
if event == 'Program 1':
|
||||
print('Run your program 1 here!')
|
||||
elif button == 'Program 2':
|
||||
elif event == 'Program 2':
|
||||
print('Run your program 2 here!')
|
||||
elif button == 'Run':
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
file = value['demofile']
|
||||
print('Launching %s'%file)
|
||||
ExecuteCommandSubprocess('python', os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, file))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
|
||||
def ExecuteCommandSubprocess(command, *args, wait=False):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
|
@ -1059,25 +1060,25 @@ Much of the code is handling the button states in a fancy way. It could be much
|
|||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
if not paused:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
current_time = int(round(time.time() * 100)) - start_time
|
||||
else:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'button':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'button':
|
||||
button = window.FindElement(button).GetText()
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is 'Reset':
|
||||
if event is 'Reset':
|
||||
start_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
current_time = 0
|
||||
paused_time = start_time
|
||||
elif button == 'Pause':
|
||||
elif event == 'Pause':
|
||||
paused = True
|
||||
paused_time = int(round(time.time() * 100))
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
element.Update(text='Run')
|
||||
elif button == 'Run':
|
||||
elif event == 'Run':
|
||||
paused = False
|
||||
start_time = start_time + int(round(time.time() * 100)) - paused_time
|
||||
element = window.FindElement('button')
|
||||
|
|
@ -1119,10 +1120,10 @@ The spinner changes the number of seconds between reads. Note that you will get
|
|||
# ---------------- main loop ----------------
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# --------- Read and update window --------
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
# --------- Do Button Operations --------
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
interval = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -1172,14 +1173,14 @@ If you double click the dashed line at the top of the list of choices, that menu
|
|||
|
||||
# ------ Loop & Process button menu choices ------ #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print('Button = ', button)
|
||||
print('Button = ', event)
|
||||
# ------ Process menu choices ------ #
|
||||
if button == 'About...':
|
||||
if event == 'About...':
|
||||
sg.Popup('About this program', 'Version 1.0', 'PySimpleGUI rocks...')
|
||||
elif button == 'Open':
|
||||
elif event == 'Open':
|
||||
filename = sg.PopupGetFile('file to open', no_window=True)
|
||||
print(filename)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1221,7 +1222,7 @@ for x in range(-100,100):
|
|||
y = math.sin(x/20)*50
|
||||
graph.DrawCircle((x,y), 1, line_color='red', fill_color='red')
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1251,9 +1252,9 @@ layout = [[sg.TabGroup([[sg.Tab('Tab 1', tab1_layout, tooltip='tip'), sg.Tab('Ta
|
|||
window = sg.Window('My window with tabs', default_element_size=(12,1)).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, v = window.Read()
|
||||
print(button,values)
|
||||
if button is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
print(event,values)
|
||||
if event is None: # always, always give a way out!
|
||||
break
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
182
docs/index.md
182
docs/index.md
|
|
@ -3,6 +3,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[](http://pepy.tech/project/pysimplegui)
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,7 +73,7 @@ Or how about a ***custom GUI*** in 1 line of code?
|
|||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example'). Layout([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]).Read()
|
||||
event, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example'). Layout([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]).Read()
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,7 +223,7 @@ An example of many widgets used on a single window. A little further down you'l
|
|||
sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel(), sg.Button('Customized', button_color=('white', 'green'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -791,9 +793,9 @@ Finally we can put it all together into a program that will display our window.
|
|||
[sg.Input()],
|
||||
[sg.OK()] ]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Enter a number example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Enter a number example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, number)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, number)
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 2 - Get a filename
|
||||
Let's say you've got a utility you've written that operates on some input file and you're ready to use a GUI to enter than filename rather than the command line. Follow the same steps as the previous example - draw your window on paper, break it up into rows, label the elements.
|
||||
|
|
@ -809,9 +811,9 @@ Writing the code for this one is just as straightforward. There is one tricky t
|
|||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, number)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, number)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Read on for detailed instructions on the calls that show the window and return your results.
|
||||
|
|
@ -838,7 +840,7 @@ window_rows = [[sg.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('SHA-1 & 256 Hash').Layout(window_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
source_filename = values[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -860,10 +862,10 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Persistent window')],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Window that stays open').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -884,7 +886,7 @@ The key to custom windows in PySimpleGUI is to view windows as ROWS of Elements
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Rename Files or Folders')
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -911,7 +913,7 @@ For return values the window is scanned from top to bottom, left to right. Each
|
|||
|
||||
In our example window, there are 2 fields, so the return values from this window will be a list with 2 values in it.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
folder_path, file_path = values
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -924,37 +926,78 @@ Isn't this what a Python programmer looking for a GUI wants? Something easy to w
|
|||
|
||||
As of version 2.8 there are 2 forms of return values, list and dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return values as a list
|
||||
### Two Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
All Window Read and ReadNonBlocking calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
All of the demo programs and the Cookbook recipes have this line of code for windows that are normal reads (not non-blocking). A similar line of code is used for non-blocking window reads:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't HAVE to write your reads in this way. You can name your variables however you want. But if you want to code them in a way that other programmers using PySimpleGUI are used to, then use these statements.
|
||||
|
||||
The first parameter `event` describes **why** the read completed. What was the 'event' that caused us to return from reading the window. Events are one of these:
|
||||
|
||||
For all Windows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Button click
|
||||
* Window closed using X
|
||||
|
||||
For Windows that have specifically enabled these. Please see the appropriate section in this document to learn about how to enable these and what the event return values are.
|
||||
|
||||
* Keyboard key press
|
||||
* Mouse wheel up/down
|
||||
* Menu item selected
|
||||
* An Element Changed (slider, spinner, etc)
|
||||
* A list item was clicked
|
||||
* Return key was pressed in input element
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
***Most*** of the time the event will be a button click or the window was closed.
|
||||
|
||||
Another convention to follow is the check for windows being closed with an X. This is an important event to catch. If you don't check for this and you attempt to use the window, your program will crash. Please check for closed window and exit your program gracefully.
|
||||
|
||||
To check for a closed window use this line of code:
|
||||
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### The 'values' Variable - Return values as a list
|
||||
|
||||
The second parameter from a Read call is either a list or a dictionary of the input fields on the Window.
|
||||
|
||||
By default return values are a list of values, one entry for each input field.
|
||||
|
||||
Return information from Window, PSG's primary window builder interface, is in this format:
|
||||
|
||||
button, (value1, value2, ...)
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the Elements that are Input Elements will have a value in the list of return values. You can unpack your GUI directly into the variables you want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename, folder1, folder2, should_overwrite) = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, (filename, folder1, folder2, should_overwrite) = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
Or, more commonly, you can unpack the return results separately.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
button, value_list = window.Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, value_list = window.Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
value1 = value_list[0]
|
||||
value2 = value_list[1]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
However, this method isn't good when you have a lot of input fields. If you insert a new element into your window then you will have to shuffle your unpacks down, modifying each of the statements to reference `value_list[x] `.
|
||||
|
||||
The more common / advanced method is to request your values be returned as a dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return values as a dictionary
|
||||
|
||||
For those of you that have not encountered a Python dictionary, don't freak out! Just copy and paste this code and modify it. Follow this design pattern and you'll be fine. And you might learn something along the way.
|
||||
|
||||
For windows longer than 3 or 4 fields you will want to use a dictionary to help you organize your return values. In almost all (if not all) of the demo programs you'll find the return values being passed as a dictionary. It is not a difficult concept to grasp, the syntax is easy to understand, and it makes for very readable code.
|
||||
|
||||
The most common window read statement you'll encounter looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("My title").Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
All of your return values will be stored in the variable `values`. When using the dictionary return values, the `values` variable is a dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
To use a dictionary, you will need to:
|
||||
* Mark each input element you wish to be in the dictionary with the keyword `key`.
|
||||
|
|
@ -967,28 +1010,37 @@ Let's take a look at your first dictionary-based window.
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry window')
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='name')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('2', key='address')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('3', key='phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='_name_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('2', key='_address_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('3', key='_phone_')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, values['_name_'], values['_address_'], values['_phone_'])
|
||||
|
||||
To get the value of an input field, you use whatever value used as the `key` value as the index value. Thus to get the value of the name field, it is written as
|
||||
|
||||
values['name']
|
||||
|
||||
Think of the variable values in the same way as you would a list, however, instead of using 0,1,2, to reference each item in the list, use the values of the key. The Name field in the window above is referenced by `values['_name_']`.
|
||||
|
||||
You will find the key field used quite heavily in most PySimpleGUI windows unless the window is very simple.
|
||||
|
||||
### Button Return Values
|
||||
Another convention you'll see in some of the demo programs is keys being named with an underscore at the beginning and the end. You don't HAVE to do this... your key value may look like this:
|
||||
`key = 'name'`
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for this naming convention is that when you are scanning the code, these key values jump out at you. You instantly know it's a key. Try scanning the code above and see if those keys pop out.
|
||||
`key = '_name_'`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Button Event Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
The button value from a Read call will be one of 3 values:
|
||||
1. The Button's text
|
||||
2. The Button's key
|
||||
3. None
|
||||
|
||||
If a button has a key set for it when it's created, then that key will be returned. If no key is set, then the button text is returned. If no button was clicked, but the window returned anyway, the button value is None.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -997,8 +1049,8 @@ None is returned when the user clicks the X to close a window.
|
|||
If your window has an event loop where it is read over and over, remember to give your user an "out". You should always check for a None value and it's a good practice to provide an Exit button of some kind. Thus design patterns often resemble this Event Loop:
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
## The Event Loop / Callback Functions
|
||||
|
|
@ -1027,10 +1079,10 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Click read to read the input value')],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Persistent GUI Window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the Event Loop we are reading the window and then doing a series of button compares to determine what to do based on the button that was clicks (value of `button` variable)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1048,7 +1100,7 @@ Whether or not this is a "proper" design for GUI programs can be debated. It's
|
|||
## All Widgets / Elements
|
||||
|
||||
This code utilizes many of the common Elements. It does not include Tabs/Tab Groups.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
|
@ -1093,13 +1145,13 @@ This code utilizes many of the common Elements. It does not include Tabs/Tab Gr
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup('Title',
|
||||
'The results of the window.',
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button),
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(event),
|
||||
'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
This is a somewhat complex window with quite a bit of custom sizing to make things line up well. This is code you only have to write once. When looking at the code, remember that what you're seeing is a list of lists. Each row contains a list of Graphical Elements that are used to create the window.
|
||||
|
||||
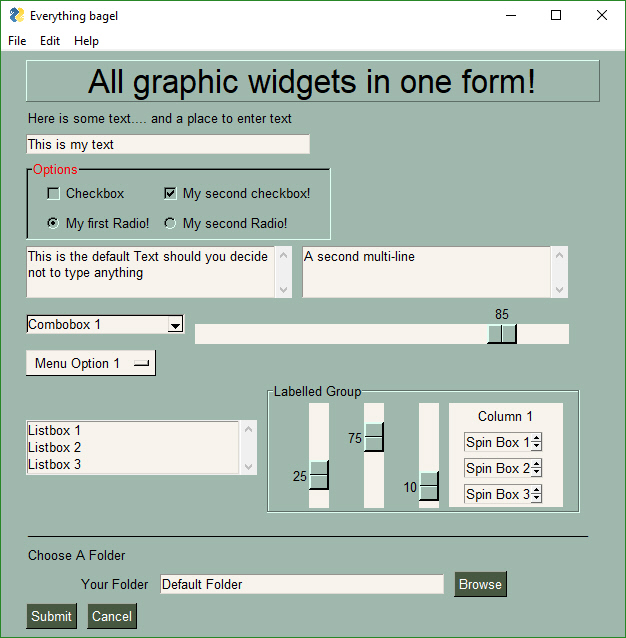
|
||||
|
|
@ -1255,7 +1307,7 @@ Call to force a window to go through the final stages of initialization. This w
|
|||
#### Read()
|
||||
|
||||
Read the Window's input values and button clicks in a blocking-fashion
|
||||
Returns button, values
|
||||
Returns event, values
|
||||
|
||||
#### ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1401,7 +1453,7 @@ If you are going to do anything beyond the basic stuff with your GUI, then you n
|
|||
Keys are a way for you to "tag" an Element with a value that will be used to identify that element. After you put a key in an element's definition, the values returned from Read will use that key to tell you the value. For example, if you have an input field:
|
||||
Input(key='mykey')
|
||||
And your read looks like this:
|
||||
button, values = Read()
|
||||
event, values = Read()
|
||||
Then to get the input value from the read it would be:
|
||||
values['mykey']
|
||||
You also use the same key if you want to call Update on an element. Please see the section below on Updates to understand that usage.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2185,10 +2237,10 @@ Somewhere later in your code will be your main event loop. This is where you do
|
|||
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
sg.Print(button)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
sg.Print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2254,8 +2306,8 @@ Another way of using a Progress Meter with PySimpleGUI is to build a custom wind
|
|||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i + 1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -2284,8 +2336,8 @@ Here's a complete solution for a chat-window using an Async window with an Outpu
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'SEND':
|
||||
event, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'SEND':
|
||||
print(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
@ -2346,9 +2398,9 @@ This code produced the above window.
|
|||
# Display the window and get values
|
||||
# If you're willing to not use the "context manager" design pattern, then it's possible
|
||||
# to collapse the window display and read down to a single line of code.
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
The Column Element has 1 required parameter and 1 optional (the layout and the background color). Setting the background color has the same effect as setting the window's background color, except it only affects the column rectangle.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2431,7 +2483,7 @@ The order of operations to obtain a tkinter Canvas Widget is:
|
|||
fig_photo = draw_figure(window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas, fig)
|
||||
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
To get a tkinter Canvas Widget from PySimpleGUI, follow these steps:
|
||||
* Add Canvas Element to your window
|
||||
|
|
@ -2842,8 +2894,8 @@ Typically when reading a window you check `if Button is None` to determine if a
|
|||
The proper code to check if the user has exited the window will be a polling-loop that looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2895,8 +2947,8 @@ See the sample code on the GitHub named Demo Media Player for another example of
|
|||
|
||||
for i in range(1, 1000):
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i / 100), 60), i % 100))
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
@ -2946,8 +2998,8 @@ In some programs these updates happen in response to another Element. This prog
|
|||
window = sg.Window("Font size selector", grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
# Event Loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
sz_spin = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
sz_slider = int(values['slider'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -3019,13 +3071,13 @@ Key Sym is a string such as 'Control_L'. The Key Code is a numeric representati
|
|||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == "OK" or (button is None and value is None):
|
||||
print(button, "exiting")
|
||||
if event == "OK" or (event is None and value is None):
|
||||
print(event, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(button)
|
||||
if eventis not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
You want to turn off the default focus so that there no buttons that will be selected should you press the spacebar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -3041,13 +3093,13 @@ Use realtime keyboard capture by calling
|
|||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == "OK":
|
||||
print(button, value, "exiting")
|
||||
if event == "OK":
|
||||
print(event, value, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if eventis not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
elif value is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
182
readme.md
182
readme.md
|
|
@ -3,6 +3,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[](http://pepy.tech/project/pysimplegui)
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,7 +73,7 @@ Or how about a ***custom GUI*** in 1 line of code?
|
|||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example'). Layout([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]).Read()
|
||||
event, (filename,) = sg.Window('Get filename example'). Layout([[sg.Text('Filename')], [sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()], [sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]).Read()
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,7 +223,7 @@ An example of many widgets used on a single window. A little further down you'l
|
|||
sg.FolderBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel(), sg.Button('Customized', button_color=('white', 'green'))]]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Everything bagel', auto_size_text=True, default_element_size=(40, 1)).Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -791,9 +793,9 @@ Finally we can put it all together into a program that will display our window.
|
|||
[sg.Input()],
|
||||
[sg.OK()] ]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Enter a number example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Enter a number example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, number)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, number)
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 2 - Get a filename
|
||||
Let's say you've got a utility you've written that operates on some input file and you're ready to use a GUI to enter than filename rather than the command line. Follow the same steps as the previous example - draw your window on paper, break it up into rows, label the elements.
|
||||
|
|
@ -809,9 +811,9 @@ Writing the code for this one is just as straightforward. There is one tricky t
|
|||
[sg.Input(), sg.FileBrowse()],
|
||||
[sg.OK(), sg.Cancel()] ]
|
||||
|
||||
button, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, (number,) = sg.Window('Get filename example').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, number)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, number)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Read on for detailed instructions on the calls that show the window and return your results.
|
||||
|
|
@ -838,7 +840,7 @@ window_rows = [[sg.Text('SHA-1 and SHA-256 Hashes for the file')],
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('SHA-1 & 256 Hash').Layout(window_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
source_filename = values[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -860,10 +862,10 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Persistent window')],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Window that stays open').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -884,7 +886,7 @@ The key to custom windows in PySimpleGUI is to view windows as ROWS of Elements
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Rename Files or Folders')
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -911,7 +913,7 @@ For return values the window is scanned from top to bottom, left to right. Each
|
|||
|
||||
In our example window, there are 2 fields, so the return values from this window will be a list with 2 values in it.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
folder_path, file_path = values
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -924,37 +926,78 @@ Isn't this what a Python programmer looking for a GUI wants? Something easy to w
|
|||
|
||||
As of version 2.8 there are 2 forms of return values, list and dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return values as a list
|
||||
### Two Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
All Window Read and ReadNonBlocking calls return 2 values. By convention a read statement is written:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
All of the demo programs and the Cookbook recipes have this line of code for windows that are normal reads (not non-blocking). A similar line of code is used for non-blocking window reads:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't HAVE to write your reads in this way. You can name your variables however you want. But if you want to code them in a way that other programmers using PySimpleGUI are used to, then use these statements.
|
||||
|
||||
The first parameter `event` describes **why** the read completed. What was the 'event' that caused us to return from reading the window. Events are one of these:
|
||||
|
||||
For all Windows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Button click
|
||||
* Window closed using X
|
||||
|
||||
For Windows that have specifically enabled these. Please see the appropriate section in this document to learn about how to enable these and what the event return values are.
|
||||
|
||||
* Keyboard key press
|
||||
* Mouse wheel up/down
|
||||
* Menu item selected
|
||||
* An Element Changed (slider, spinner, etc)
|
||||
* A list item was clicked
|
||||
* Return key was pressed in input element
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
***Most*** of the time the event will be a button click or the window was closed.
|
||||
|
||||
Another convention to follow is the check for windows being closed with an X. This is an important event to catch. If you don't check for this and you attempt to use the window, your program will crash. Please check for closed window and exit your program gracefully.
|
||||
|
||||
To check for a closed window use this line of code:
|
||||
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### The 'values' Variable - Return values as a list
|
||||
|
||||
The second parameter from a Read call is either a list or a dictionary of the input fields on the Window.
|
||||
|
||||
By default return values are a list of values, one entry for each input field.
|
||||
|
||||
Return information from Window, PSG's primary window builder interface, is in this format:
|
||||
|
||||
button, (value1, value2, ...)
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the Elements that are Input Elements will have a value in the list of return values. You can unpack your GUI directly into the variables you want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
button, (filename, folder1, folder2, should_overwrite) = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, (filename, folder1, folder2, should_overwrite) = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
Or, more commonly, you can unpack the return results separately.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
button, value_list = window.Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('My title').Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
event, value_list = window.Layout(window_rows).Read()
|
||||
value1 = value_list[0]
|
||||
value2 = value_list[1]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
However, this method isn't good when you have a lot of input fields. If you insert a new element into your window then you will have to shuffle your unpacks down, modifying each of the statements to reference `value_list[x] `.
|
||||
|
||||
The more common / advanced method is to request your values be returned as a dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return values as a dictionary
|
||||
|
||||
For those of you that have not encountered a Python dictionary, don't freak out! Just copy and paste this code and modify it. Follow this design pattern and you'll be fine. And you might learn something along the way.
|
||||
|
||||
For windows longer than 3 or 4 fields you will want to use a dictionary to help you organize your return values. In almost all (if not all) of the demo programs you'll find the return values being passed as a dictionary. It is not a difficult concept to grasp, the syntax is easy to understand, and it makes for very readable code.
|
||||
|
||||
The most common window read statement you'll encounter looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window("My title").Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
All of your return values will be stored in the variable `values`. When using the dictionary return values, the `values` variable is a dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
To use a dictionary, you will need to:
|
||||
* Mark each input element you wish to be in the dictionary with the keyword `key`.
|
||||
|
|
@ -967,28 +1010,37 @@ Let's take a look at your first dictionary-based window.
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Simple data entry window')
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.Text('Please enter your Name, Address, Phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='name')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('2', key='address')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('3', key='phone')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Name', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('1', key='_name_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Address', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('2', key='_address_')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Phone', size=(15, 1)), sg.InputText('3', key='_phone_')],
|
||||
[sg.Submit(), sg.Cancel()]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, values['name'], values['address'], values['phone'])
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, values['_name_'], values['_address_'], values['_phone_'])
|
||||
|
||||
To get the value of an input field, you use whatever value used as the `key` value as the index value. Thus to get the value of the name field, it is written as
|
||||
|
||||
values['name']
|
||||
|
||||
Think of the variable values in the same way as you would a list, however, instead of using 0,1,2, to reference each item in the list, use the values of the key. The Name field in the window above is referenced by `values['_name_']`.
|
||||
|
||||
You will find the key field used quite heavily in most PySimpleGUI windows unless the window is very simple.
|
||||
|
||||
### Button Return Values
|
||||
Another convention you'll see in some of the demo programs is keys being named with an underscore at the beginning and the end. You don't HAVE to do this... your key value may look like this:
|
||||
`key = 'name'`
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for this naming convention is that when you are scanning the code, these key values jump out at you. You instantly know it's a key. Try scanning the code above and see if those keys pop out.
|
||||
`key = '_name_'`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Button Event Return Values
|
||||
|
||||
The button value from a Read call will be one of 3 values:
|
||||
1. The Button's text
|
||||
2. The Button's key
|
||||
3. None
|
||||
|
||||
If a button has a key set for it when it's created, then that key will be returned. If no key is set, then the button text is returned. If no button was clicked, but the window returned anyway, the button value is None.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -997,8 +1049,8 @@ None is returned when the user clicks the X to close a window.
|
|||
If your window has an event loop where it is read over and over, remember to give your user an "out". You should always check for a None value and it's a good practice to provide an Exit button of some kind. Thus design patterns often resemble this Event Loop:
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
## The Event Loop / Callback Functions
|
||||
|
|
@ -1027,10 +1079,10 @@ layout = [[sg.Text('Click read to read the input value')],
|
|||
window = sg.Window('Persistent GUI Window').Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None or button == 'Exit':
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
print(button, values)
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the Event Loop we are reading the window and then doing a series of button compares to determine what to do based on the button that was clicks (value of `button` variable)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1048,7 +1100,7 @@ Whether or not this is a "proper" design for GUI programs can be debated. It's
|
|||
## All Widgets / Elements
|
||||
|
||||
This code utilizes many of the common Elements. It does not include Tabs/Tab Groups.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
sg.ChangeLookAndFeel('GreenTan')
|
||||
|
|
@ -1093,13 +1145,13 @@ This code utilizes many of the common Elements. It does not include Tabs/Tab Gr
|
|||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Everything bagel', default_element_size=(40, 1), grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup('Title',
|
||||
'The results of the window.',
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(button),
|
||||
'The button clicked was "{}"'.format(event),
|
||||
'The values are', values)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
This is a somewhat complex window with quite a bit of custom sizing to make things line up well. This is code you only have to write once. When looking at the code, remember that what you're seeing is a list of lists. Each row contains a list of Graphical Elements that are used to create the window.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
@ -1255,7 +1307,7 @@ Call to force a window to go through the final stages of initialization. This w
|
|||
#### Read()
|
||||
|
||||
Read the Window's input values and button clicks in a blocking-fashion
|
||||
Returns button, values
|
||||
Returns event, values
|
||||
|
||||
#### ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1401,7 +1453,7 @@ If you are going to do anything beyond the basic stuff with your GUI, then you n
|
|||
Keys are a way for you to "tag" an Element with a value that will be used to identify that element. After you put a key in an element's definition, the values returned from Read will use that key to tell you the value. For example, if you have an input field:
|
||||
Input(key='mykey')
|
||||
And your read looks like this:
|
||||
button, values = Read()
|
||||
event, values = Read()
|
||||
Then to get the input value from the read it would be:
|
||||
values['mykey']
|
||||
You also use the same key if you want to call Update on an element. Please see the section below on Updates to understand that usage.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2185,10 +2237,10 @@ Somewhere later in your code will be your main event loop. This is where you do
|
|||
|
||||
while (True):
|
||||
# This is the code that reads and updates your window
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
sg.Print(button)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
sg.Print(event)
|
||||
if event == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2254,8 +2306,8 @@ Another way of using a Progress Meter with PySimpleGUI is to build a custom wind
|
|||
# loop that would normally do something useful
|
||||
for i in range(10000):
|
||||
# check to see if the cancel button was clicked and exit loop if clicked
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if event == 'Cancel' or values == None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# update bar with loop value +1 so that bar eventually reaches the maximum
|
||||
progress_bar.UpdateBar(i + 1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -2284,8 +2336,8 @@ Here's a complete solution for a chat-window using an Async window with an Outpu
|
|||
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input and using it to query HowDoI web oracle --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if button == 'SEND':
|
||||
event, value = window.Read()
|
||||
if event == 'SEND':
|
||||
print(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
|
@ -2346,9 +2398,9 @@ This code produced the above window.
|
|||
# Display the window and get values
|
||||
# If you're willing to not use the "context manager" design pattern, then it's possible
|
||||
# to collapse the window display and read down to a single line of code.
|
||||
button, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
event, values = sg.Window('Compact 1-line window with column').Layout(layout).Read()
|
||||
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
sg.Popup(event, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
The Column Element has 1 required parameter and 1 optional (the layout and the background color). Setting the background color has the same effect as setting the window's background color, except it only affects the column rectangle.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2431,7 +2483,7 @@ The order of operations to obtain a tkinter Canvas Widget is:
|
|||
fig_photo = draw_figure(window.FindElement('canvas').TKCanvas, fig)
|
||||
|
||||
# show it all again and get buttons
|
||||
button, values = window.Read()
|
||||
event, values = window.Read()
|
||||
|
||||
To get a tkinter Canvas Widget from PySimpleGUI, follow these steps:
|
||||
* Add Canvas Element to your window
|
||||
|
|
@ -2842,8 +2894,8 @@ Typically when reading a window you check `if Button is None` to determine if a
|
|||
The proper code to check if the user has exited the window will be a polling-loop that looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2895,8 +2947,8 @@ See the sample code on the GitHub named Demo Media Player for another example of
|
|||
|
||||
for i in range(1, 1000):
|
||||
window.FindElement('output').Update('{:02d}:{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(*divmod(int(i / 100), 60), i % 100))
|
||||
button, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or button == 'Quit':
|
||||
event, values = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if values is None or event == 'Quit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
time.sleep(.01)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
|
@ -2946,8 +2998,8 @@ In some programs these updates happen in response to another Element. This prog
|
|||
window = sg.Window("Font size selector", grab_anywhere=False).Layout(layout)
|
||||
# Event Loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if button is None:
|
||||
event, values= window.Read()
|
||||
if event is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
sz_spin = int(values['spin'])
|
||||
sz_slider = int(values['slider'])
|
||||
|
|
@ -3019,13 +3071,13 @@ Key Sym is a string such as 'Control_L'. The Key Code is a numeric representati
|
|||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# ---===--- Loop taking in user input --- #
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == "OK" or (button is None and value is None):
|
||||
print(button, "exiting")
|
||||
if event == "OK" or (event is None and value is None):
|
||||
print(event, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(button)
|
||||
if eventis not None:
|
||||
text_elem.Update(event)
|
||||
|
||||
You want to turn off the default focus so that there no buttons that will be selected should you press the spacebar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -3041,13 +3093,13 @@ Use realtime keyboard capture by calling
|
|||
window.Layout(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
button, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
event, value = window.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
|
||||
if button == "OK":
|
||||
print(button, value, "exiting")
|
||||
if event == "OK":
|
||||
print(event, value, "exiting")
|
||||
break
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if eventis not None:
|
||||
print(event)
|
||||
elif value is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue