Rename of PySimpleGUIdebugger to imwatchingyou
This commit is contained in:
parent
9f61064fc1
commit
a083a42c1b
3 changed files with 109 additions and 80 deletions
|
|
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
|
||||
A "debugger" that's based on PySimpleGUI. It was developed to help debug PySimpleGUI based programs, but it can be used to debug any program. The only requirement is that a `refresh()` function be called on a "periodic basis".
|
||||
|
||||
What you can do with this "debugger" is:
|
||||
* Set "watch points" that update in realtime
|
||||
* Write expressions / code that update in realtime
|
||||
* Use a REPL style prompt to type in "code" / modify variables
|
||||
|
||||
All of this is done using a window secondary and separate from your primary application window.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out this video as a guide. The user's window is the smaller one one top. The PySimpleGUIdebugger is the green window on the buttom. You can watch variables, evaluate expressions, even execute code.
|
||||
|
||||
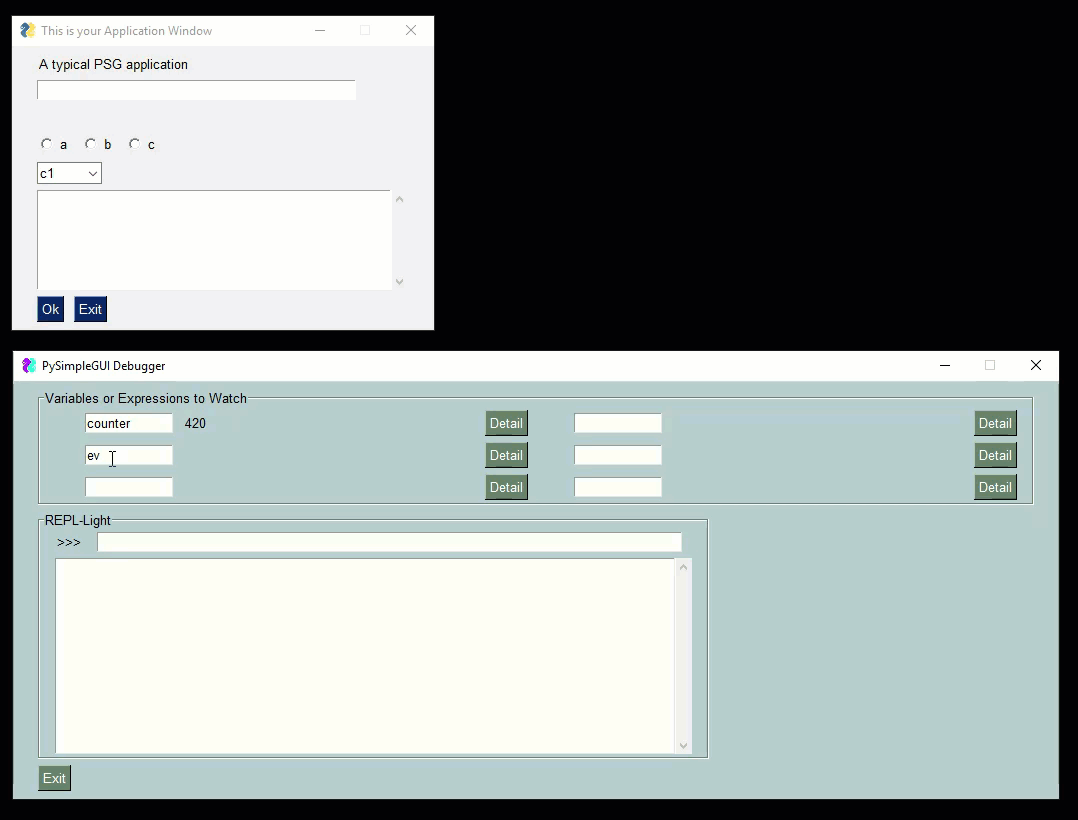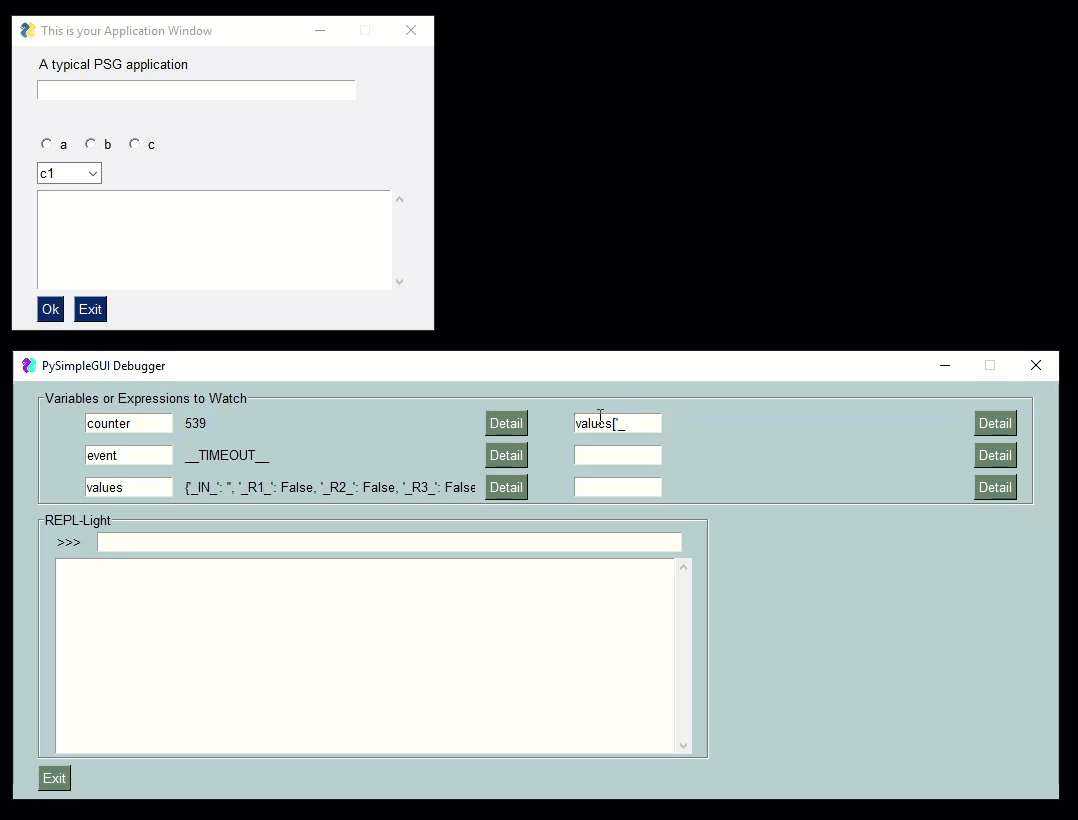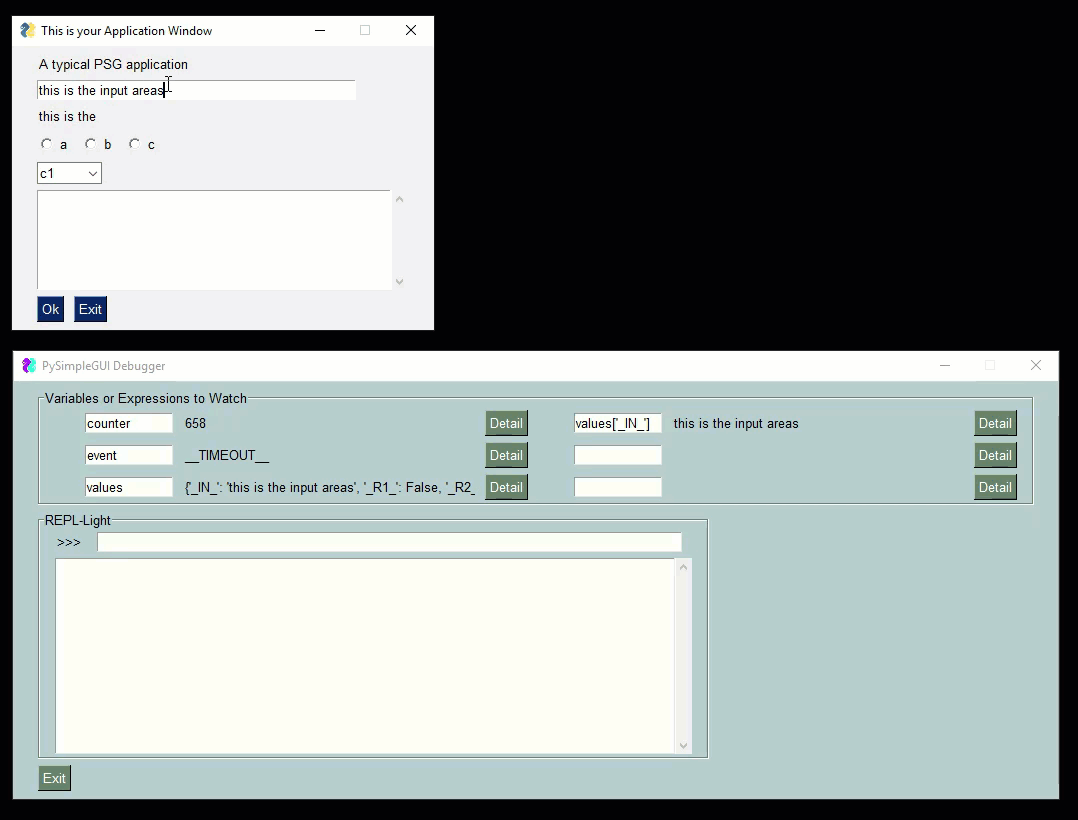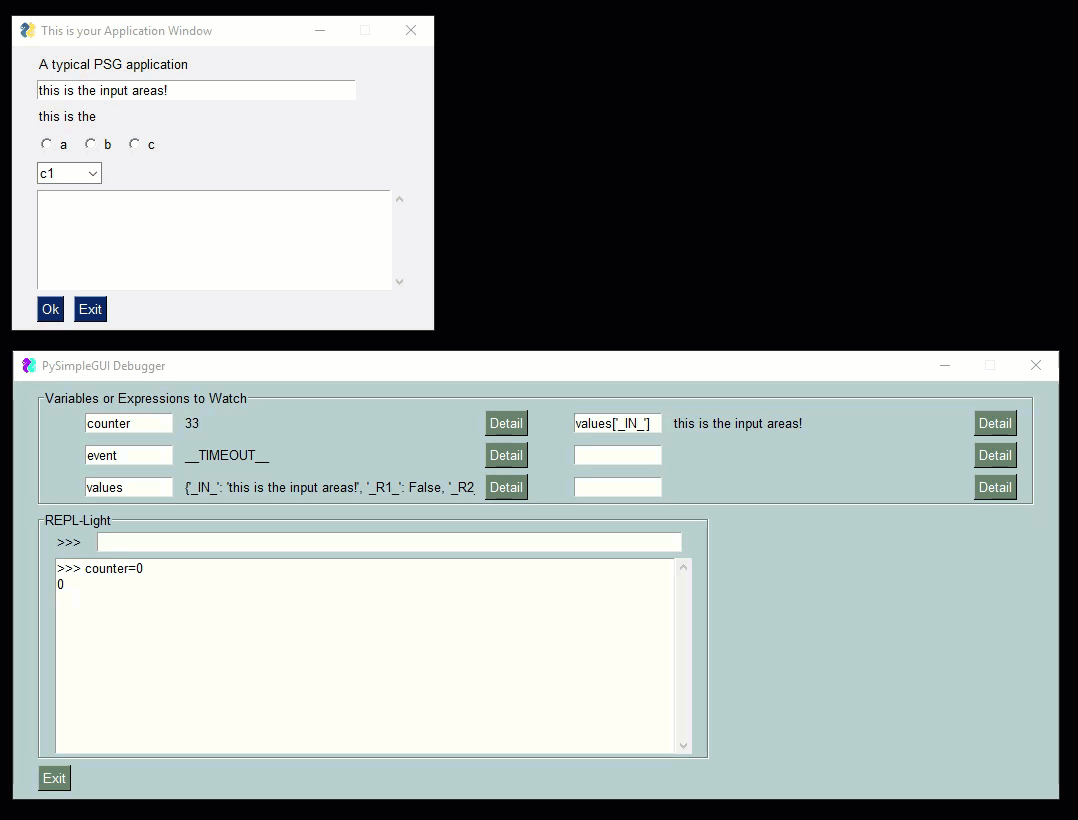
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Installation is via pip:
|
||||
|
||||
`pip install PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
or if you need to upgrade later:
|
||||
|
||||
`pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you need to install the debugger using pip rather than downloading. There are some detailed technical reasons for this.
|
||||
|
||||
So, don't forget: __You must pip install PySimpleGUIdebugger in order to use it.__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrating PySimpleGUIdebugger Into Your Application
|
||||
|
||||
There are 3 lines of code to add to a PySimpleGUI program in order to make it debugger ready - The import, an initialization, once each time through the even loop.
|
||||
|
||||
Copy and paste these lines of code into your code just as you see them written. Don't get clever and rename anything. Don't do an "import as". Just copy the lines of code.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an entire program including this integration code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Demo program that shows you how to integrate the PySimpleGUI Debugger
|
||||
into your program.
|
||||
There are THREE steps, and they are copy and pastes.
|
||||
1. At the top of your app to debug add
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
2. Initialize the debugger by calling:
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()
|
||||
2. At the top of your app's event loop add
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals())
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.T('A typical PSG application')],
|
||||
[sg.In(key='_IN_')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ', key='_OUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('a',1, key='_R1_'), sg.Radio('b',1, key='_R2_'), sg.Radio('c',1, key='_R3_')],
|
||||
[sg.Combo(['c1', 'c2', 'c3'], size=(6,3), key='_COMBO_')],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(50,6))],
|
||||
[sg.Ok(), sg.Exit()],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('This is your Application Window', layout)
|
||||
window.Element('_OUT_').Update(background_color='red')
|
||||
# Variables that we'll use to demonstrate the debugger's features
|
||||
counter = 0
|
||||
timeout = 100
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals()) # call the debugger to refresh the items being shown
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=timeout)
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Ok':
|
||||
print('You clicked Ok.... this is where print output goes')
|
||||
counter += 1
|
||||
window.Element('_OUT_').Update(values['_IN_'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
|
||||
To use the debugger in your code you will need to add TWO lines of code:
|
||||
The import at the top of your code:
|
||||
`import PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
You need to "initialize" the PySimpleGUIdebugger package by calling near the top of your code. This is what creates the debugger window:
|
||||
`PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()`
|
||||
|
||||
This "refresh" call that must be added to your event loop. Your `window.Read` call should have a timeout value so that it does not block. If you do not have a timeout value, the debugger will not update in realtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Add this line to the top of your event loop.
|
||||
`PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals())`
|
||||
|
||||
### Using in "when needed" mode
|
||||
|
||||
The Demo Program was recently updated so that instead of launching with the Debugger window immediately shown, the program launches with the Debugger not started. With this new code, you can open and close the Debugger as many times as you wish.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the code, based on the code shown previously in this readme, that has a "Debug" button
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger # STEP 1
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Demo program that shows you how to integrate the PySimpleGUI Debugger
|
||||
into your program.
|
||||
In this example, the debugger is not started initiallly. You click the "Debug" button to launch it
|
||||
There are THREE steps, and they are copy and pastes.
|
||||
1. At the top of your app to debug add
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
2. Initialize the debugger at the start of your program by calling:
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()
|
||||
3. At the top of your app's Event Loop add:
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals())
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.T('A typical PSG application')],
|
||||
[sg.In(key='_IN_')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ', key='_OUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('a',1, key='_R1_'), sg.Radio('b',1, key='_R2_'), sg.Radio('c',1, key='_R3_')],
|
||||
[sg.Combo(['c1', 'c2', 'c3'], size=(6,3), key='_COMBO_')],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(50,6))],
|
||||
[sg.Ok(), sg.Exit(), sg.B('Debug')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('This is your Application Window', layout)
|
||||
|
||||
counter = 0
|
||||
timeout = 100
|
||||
debug_started = False
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Your Event Loop
|
||||
if debug_started:
|
||||
debug_started = PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals()) # STEP 3 - refresh debugger
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=timeout)
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Ok':
|
||||
print('You clicked Ok.... this is where print output goes')
|
||||
elif event == 'Debug' and not debug_started:
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize() # STEP 2
|
||||
debug_started = True
|
||||
counter += 1
|
||||
window.Element('_OUT_').Update(values['_IN_'])
|
||||
window.Close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This puts the launching of the debugger firmly into the control of the program being debugged. Want debugger help? Then press the debug button.
|
||||
|
||||
In the future I want to add a "hotkey" or some other trivial way of launching a debugger from any program that has is running PySimpleGUI. The only one with real trouble wit this will be the PySimpleGUIWeb one as multiple web windows gets a bit cluttered.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
** You'll need to have PySimpleGUI installed. It will automatically be installed if it is not already installed. **
|
||||
|
||||
The debugger itself is written using PySimpleGUI, the tkinter version. It could be changed to use Qt for example by modifying the pip installed version.
|
||||
|
||||
You MUST run the debugger from the pip installed version. You cannot download the debugger from the GitHub at this point and use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## What's it good for, when should it be used??
|
||||
|
||||
Hell if I know. Maybe it's a terrible idea! Or, maybe it'll be really helpful, particularly in situations where you don't have many resources on the target system and perhaps you can't fit a debugger onto that system. PySimpleGUIdebugger provides another tool for your PySimpleGUI GUI Toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Future
|
||||
|
||||
LOTS of plans for this debugger in the future. One of the immediate things I want to do is to integrate this into the PySimpleGUI.py file itself. To include the debugger with the SDK so that it doesn't have to be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
This will enable the use of a "hotkey" or other mechanism to "magically launch" your very own PySimpleGUI Debugger.
|
||||
|
||||
I'll be adding a "Launch debugger" button for sure so that it's trivial for you to add this capability to your code.
|
||||
|
||||
Watch this space in the future! COOL SHIT COMING SOON!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Design
|
||||
# Author
|
||||
Mike B.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL 3) +
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue