Release 3.30. New PySimpleGUIdebugger release to PyPI
This commit is contained in:
parent
bf762e12b9
commit
7348cb67ba
8 changed files with 527 additions and 309 deletions
121
PySimpleGUIdebugger/readme.md
Normal file
121
PySimpleGUIdebugger/readme.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
|
||||
PySimpleGUI now has it's own built-in, sorta, debugger.
|
||||
|
||||
What you can do with this "debugger" is:
|
||||
* Set "watch points" that update in realtime
|
||||
* Write expressions that update in realtime
|
||||
* Use a REPL style prompt to type in "code" / modify variables
|
||||
|
||||
All of this is done using a window secondary and separate from your primary application window.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out this video as a guide. The user's window is the smaller one one top. The PySimpleGUIdebugger is the green window on the buttom. You can watch variables, evaluate expressions, even xecute code.
|
||||
|
||||
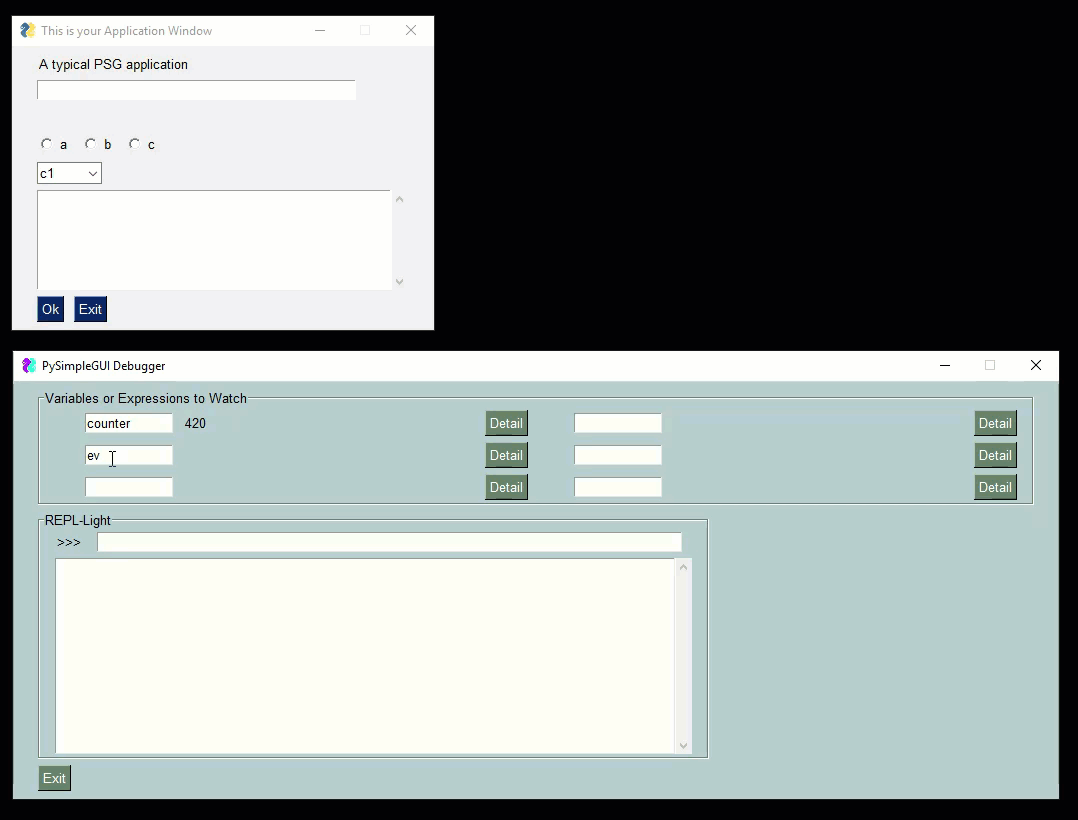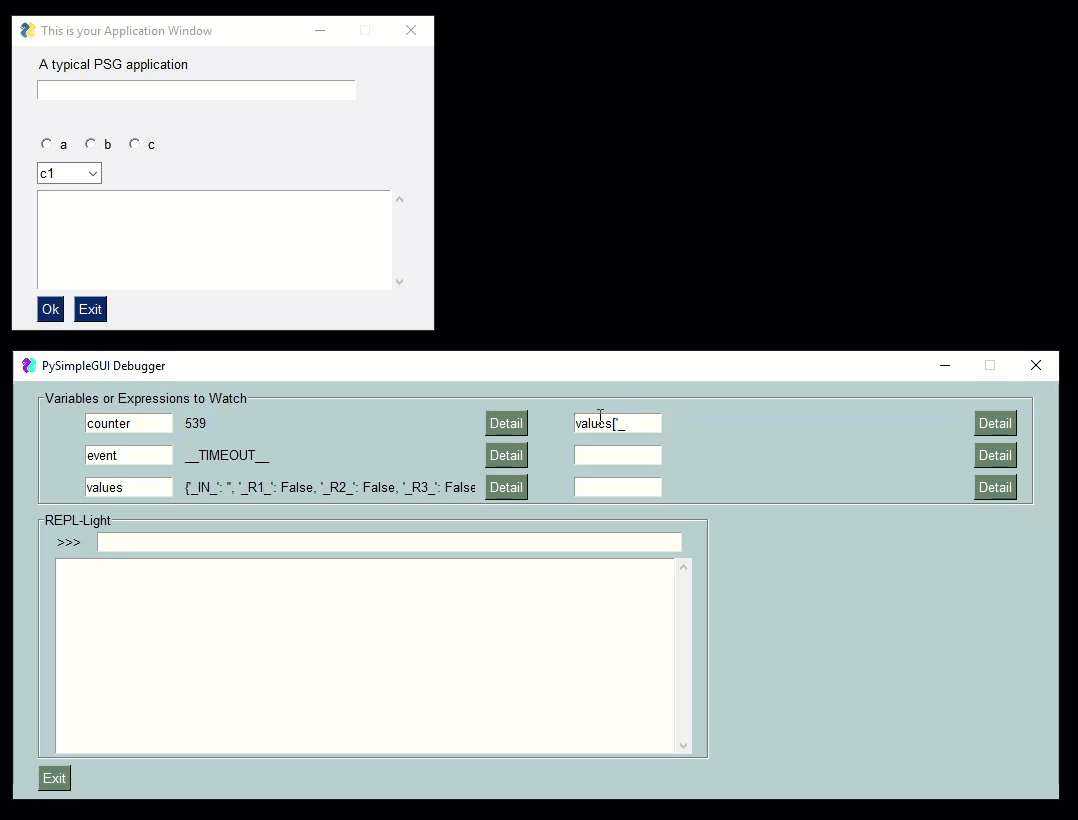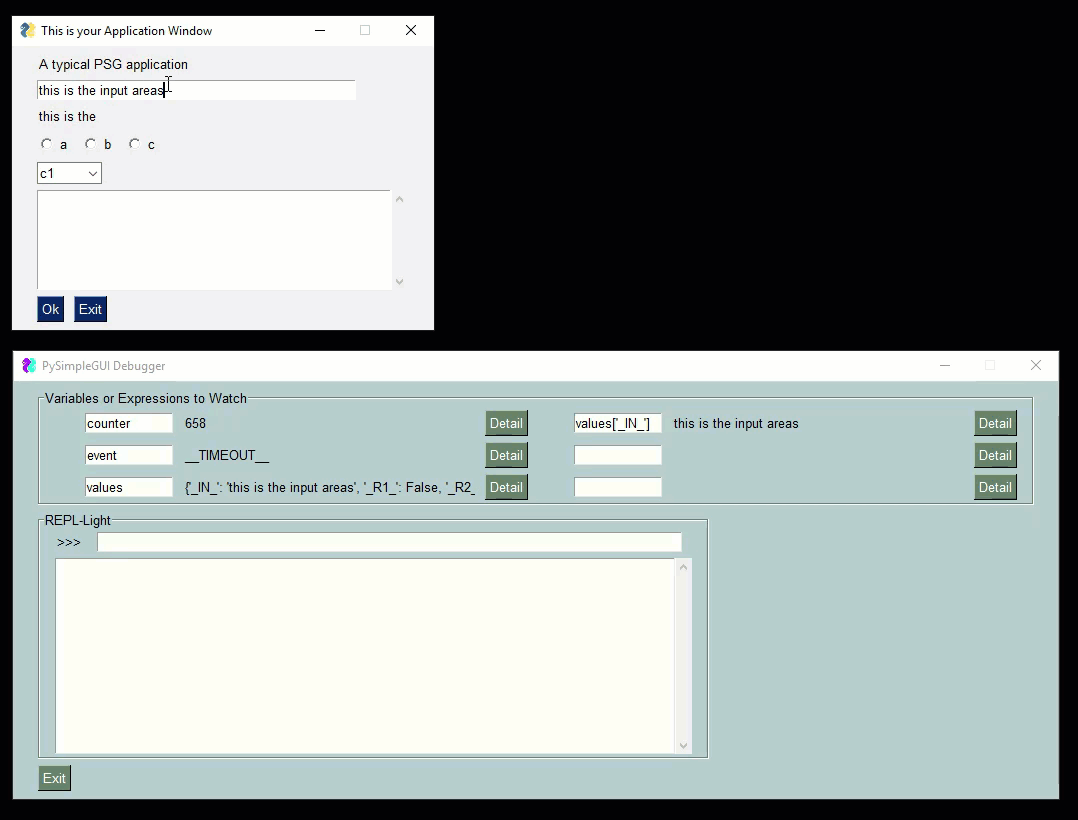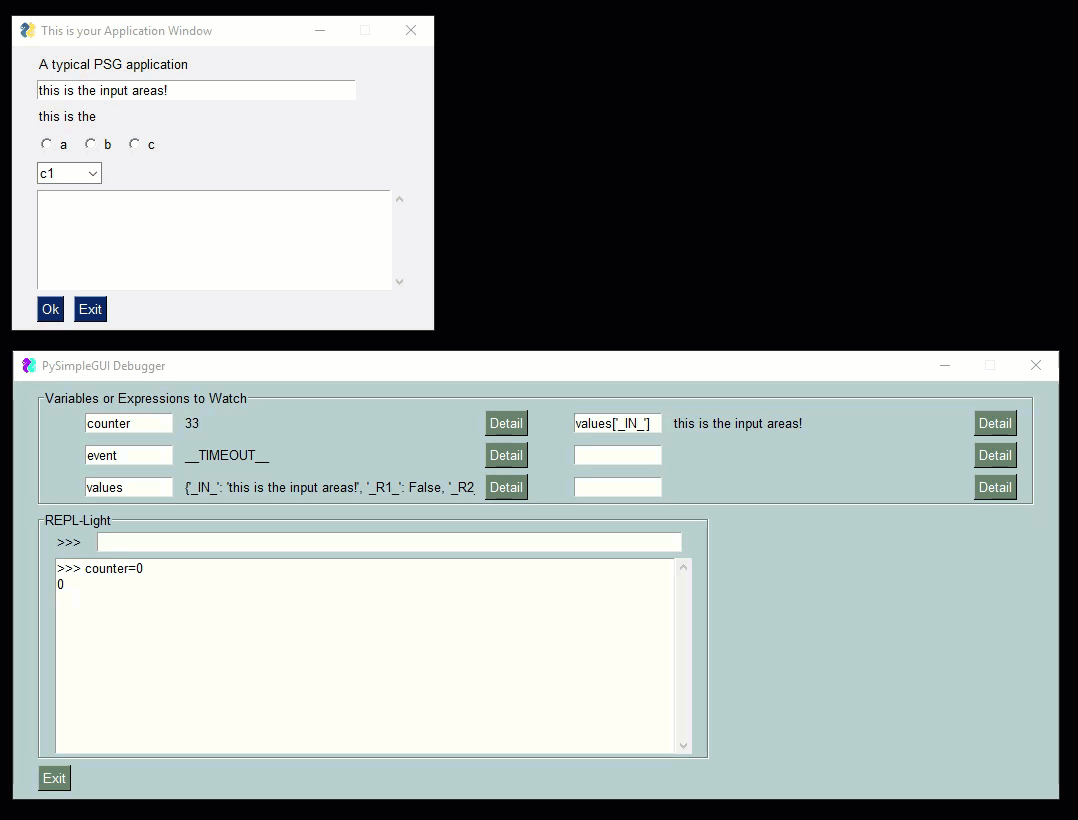
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Installation is via pip:
|
||||
|
||||
`pip install PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
or if you need to upgrade later:
|
||||
|
||||
`pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
Should this not work, you can copy and paste the file PySimpleGUIdebugger.py into your application folder.
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrating PySimpleGUIdebugger Into Your Application
|
||||
|
||||
There are 3 lines of code to add to a PySimpleGUI program in order to make it debugger ready - The import, an initialization, once each time through the even loop.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an entire program including this integration code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Demo program that shows you how to integrate the PySimpleGUI Debugger
|
||||
into your program.
|
||||
There are THREE steps, and they are copy and pastes.
|
||||
1. At the top of your app to debug add
|
||||
import PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
2. Initialize the debugger by calling:
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()
|
||||
2. At the top of your app's event loop add
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals())
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [
|
||||
[sg.T('A typical PSG application')],
|
||||
[sg.In(key='_IN_')],
|
||||
[sg.T(' ', key='_OUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Radio('a',1, key='_R1_'), sg.Radio('b',1, key='_R2_'), sg.Radio('c',1, key='_R3_')],
|
||||
[sg.Combo(['c1', 'c2', 'c3'], size=(6,3), key='_COMBO_')],
|
||||
[sg.Output(size=(50,6))],
|
||||
[sg.Ok(), sg.Exit()],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('This is your Application Window', layout)
|
||||
window.Element('_OUT_').Update(background_color='red')
|
||||
# Variables that we'll use to demonstrate the debugger's features
|
||||
counter = 0
|
||||
timeout = 100
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals()) # call the debugger to refresh the items being shown
|
||||
event, values = window.Read(timeout=timeout)
|
||||
if event in (None, 'Exit'):
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif event == 'Ok':
|
||||
print('You clicked Ok.... this is where print output goes')
|
||||
counter += 1
|
||||
window.Element('_OUT_').Update(values['_IN_'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using PySimpleGUIdebugger
|
||||
|
||||
To use the debugger in your code you will need to add TWO lines of code:
|
||||
The import at the top of your code:
|
||||
`import PySimpleGUIdebugger`
|
||||
|
||||
You need to "initialize" the PySimpleGUIdebugger package by calling near the top of your code. This is what creates the debugger window:
|
||||
`PySimpleGUIdebugger.initialize()`
|
||||
|
||||
This "refresh" call that must be added to your event loop. Your `window.Read` call should have a timeout value so that it does not block. If you do not have a timeout value, the debugger will not update in realtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Add this line to the top of your event loop.
|
||||
`PySimpleGUIdebugger.refresh(locals(), globals())`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need to have PySimpleGUI installed.
|
||||
|
||||
The debugger itself is written using PySimpleGUI, the tkinter version. It could be changed to use Qt for example.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## What's it good for, when should it be used??
|
||||
|
||||
Hell if I know. Maybe it's a terrible idea! Or, maybe it'll be really helpful, particularly in situations where you don't have many resources on the target system and perhaps you can't fit a debugger onto that system. PySimpleGUIdebugger provides another tool for your PySimpleGUI GUI Toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Design
|
||||
# Author
|
||||
Mike B.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL 3) +
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue