Update sample codes not indented correctly.
This commit is contained in:
parent
bea372f51d
commit
4378dfece7
1 changed files with 131 additions and 131 deletions
262
docs/cookbook.md
262
docs/cookbook.md
|
|
@ -2748,26 +2748,26 @@ This Window doesn't close after button clicks. To achieve this the buttons are
|
|||
Very simple script that will launch a program as a subprocess. Great for making a desktop launcher toolbar.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
CHROME = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [ [sg.Text('Text area', key='_TEXT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='_URL_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Chrome'), sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == 'Chrome':
|
||||
sp = subprocess.Popen([CHROME, values['_URL_']], shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
CHROME = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [ [sg.Text('Text area', key='_TEXT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='_URL_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Chrome'), sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == 'Chrome':
|
||||
sp = subprocess.Popen([CHROME, values['_URL_']], shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
|
||||
window.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2919,31 +2919,31 @@ while True:
|
|||
break
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
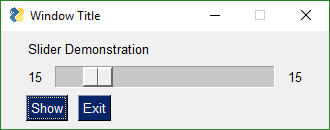
## One Element Updating Another - Compound Elements
|
||||
## One Element Updating Another - Compound Elements
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily build "compound elements" in a single like of code. This recipe shows you how to add a numeric value onto a slider.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Slider Demonstration'), sg.Text('', key='_OUTPUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.T('0',key='_LEFT_'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((1,100), key='_SLIDER_', orientation='h', enable_events=True, disable_number_display=True),
|
||||
sg.T('0', key='_RIGHT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Show'), sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
window['_LEFT_'].update(values['_SLIDER_'])
|
||||
window['_RIGHT_'].update(values['_SLIDER_'])
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Slider Demonstration'), sg.Text('', key='_OUTPUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.T('0',key='_LEFT_'),
|
||||
sg.Slider((1,100), key='_SLIDER_', orientation='h', enable_events=True, disable_number_display=True),
|
||||
sg.T('0', key='_RIGHT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Show'), sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
print(event, values)
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
break
|
||||
window['_LEFT_'].update(values['_SLIDER_'])
|
||||
window['_RIGHT_'].update(values['_SLIDER_'])
|
||||
|
||||
window.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2959,38 +2959,38 @@ This recipe is a design pattern for multiple windows where the first window is n
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
"""
|
||||
PySimpleGUI The Complete Course Lesson 7 - Multiple Windows"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Design pattern 1 - First window does not remain active
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('Window 1'),],
|
||||
[sg.Input()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', key='_OUTPUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Launch 2')]]
|
||||
|
||||
win1 = sg.Window('Window 1', layout)
|
||||
win2_active=False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ev1, vals1 = win1.Read(timeout=100)
|
||||
if ev1 == sg.WIN_CLOSED:
|
||||
break
|
||||
win1.['_OUTPUT_'].update(vals1[0])
|
||||
|
||||
if ev1 == 'Launch 2' and not win2_active:
|
||||
win2_active = True
|
||||
win1.Hide()
|
||||
layout2 = [[sg.Text('Window 2')], # note must create a layout from scratch every time. No reuse
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
win2 = sg.Window('Window 2', layout2)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ev2, vals2 = win2.Read()
|
||||
if ev2 == sg.WIN_CLOSED or ev2 == 'Exit':
|
||||
win2.Close()
|
||||
win2_active = False
|
||||
win1.UnHide()
|
||||
"""
|
||||
PySimpleGUI The Complete Course Lesson 7 - Multiple Windows"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
# Design pattern 1 - First window does not remain active
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[ sg.Text('Window 1'),],
|
||||
[sg.Input()],
|
||||
[sg.Text('', key='_OUTPUT_')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Launch 2')]]
|
||||
|
||||
win1 = sg.Window('Window 1', layout)
|
||||
win2_active=False
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ev1, vals1 = win1.Read(timeout=100)
|
||||
if ev1 == sg.WIN_CLOSED:
|
||||
break
|
||||
win1['_OUTPUT_'].update(vals1[0])
|
||||
|
||||
if ev1 == 'Launch 2' and not win2_active:
|
||||
win2_active = True
|
||||
win1.Hide()
|
||||
layout2 = [[sg.Text('Window 2')], # note must create a layout from scratch every time. No reuse
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
|
||||
win2 = sg.Window('Window 2', layout2)
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ev2, vals2 = win2.Read()
|
||||
if ev2 == sg.WIN_CLOSED or ev2 == 'Exit':
|
||||
win2.Close()
|
||||
win2_active = False
|
||||
win1.UnHide()
|
||||
break
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -3317,65 +3317,65 @@ Use the upper half to generate your hash code. Then paste it into the code in t
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
|
||||
'''
|
||||
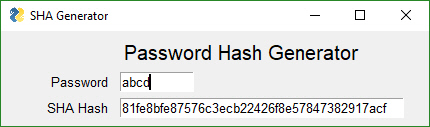
Create a secure login for your scripts without having to include your password in the program. Create an SHA1 hash code for your password using the GUI. Paste into variable in final program
|
||||
1. Choose a password
|
||||
2. Generate a hash code for your chosen password by running program and entering 'gui' as the password
|
||||
3. Type password into the GUI
|
||||
4. Copy and paste hash code Window GUI into variable named login_password_hash
|
||||
5. Run program again and test your login!
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
# Use this GUI to get your password's hash code
|
||||
def HashGeneratorGUI():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Password Hash Generator', size=(30,1), font='Any 15')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Password'), sg.In(key='password')],
|
||||
[sg.T('SHA Hash'), sg.In('', size=(40,1), key='hash')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('SHA Generator', layout, auto_size_text=False, default_element_size=(10,1),
|
||||
text_justification='r', return_keyboard_events=True, grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
password = values['password']
|
||||
try:
|
||||
password_utf = password.encode('utf-8')
|
||||
sha1hash = hashlib.sha1()
|
||||
sha1hash.update(password_utf)
|
||||
password_hash = sha1hash.hexdigest()
|
||||
window['hash'].update(password_hash)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------------------------- Paste this code into your program / script -----------------------------
|
||||
# determine if a password matches the secret password by comparing SHA1 hash codes
|
||||
def PasswordMatches(password, hash):
|
||||
password_utf = password.encode('utf-8')
|
||||
sha1hash = hashlib.sha1()
|
||||
sha1hash.update(password_utf)
|
||||
password_hash = sha1hash.hexdigest()
|
||||
if password_hash == hash:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
login_password_hash = '5baa61e4c9b93f3f0682250b6cf8331b7ee68fd8'
|
||||
password = sg.popup_get_text('Password', password_char='*')
|
||||
if password == 'gui': # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
HashGeneratorGUI() # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
exit(69) # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
if PasswordMatches(password, login_password_hash):
|
||||
print('Login SUCCESSFUL')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('Login FAILED!!')
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Create a secure login for your scripts without having to include your password in the program. Create an SHA1 hash code for your password using the GUI. Paste into variable in final program
|
||||
1. Choose a password
|
||||
2. Generate a hash code for your chosen password by running program and entering 'gui' as the password
|
||||
3. Type password into the GUI
|
||||
4. Copy and paste hash code Window GUI into variable named login_password_hash
|
||||
5. Run program again and test your login!
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
# Use this GUI to get your password's hash code
|
||||
def HashGeneratorGUI():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Password Hash Generator', size=(30,1), font='Any 15')],
|
||||
[sg.T('Password'), sg.In(key='password')],
|
||||
[sg.T('SHA Hash'), sg.In('', size=(40,1), key='hash')],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
window = sg.Window('SHA Generator', layout, auto_size_text=False, default_element_size=(10,1),
|
||||
text_justification='r', return_keyboard_events=True, grab_anywhere=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
event, values = window.read()
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED:
|
||||
exit(69)
|
||||
|
||||
password = values['password']
|
||||
try:
|
||||
password_utf = password.encode('utf-8')
|
||||
sha1hash = hashlib.sha1()
|
||||
sha1hash.update(password_utf)
|
||||
password_hash = sha1hash.hexdigest()
|
||||
window['hash'].update(password_hash)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------------------------- Paste this code into your program / script -----------------------------
|
||||
# determine if a password matches the secret password by comparing SHA1 hash codes
|
||||
def PasswordMatches(password, hash):
|
||||
password_utf = password.encode('utf-8')
|
||||
sha1hash = hashlib.sha1()
|
||||
sha1hash.update(password_utf)
|
||||
password_hash = sha1hash.hexdigest()
|
||||
if password_hash == hash:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
login_password_hash = '5baa61e4c9b93f3f0682250b6cf8331b7ee68fd8'
|
||||
password = sg.popup_get_text('Password', password_char='*')
|
||||
if password == 'gui': # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
HashGeneratorGUI() # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
exit(69) # Remove when pasting into your program
|
||||
if PasswordMatches(password, login_password_hash):
|
||||
print('Login SUCCESSFUL')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('Login FAILED!!')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Desktop Floating Toolbar
|
||||
|
|
@ -3755,4 +3755,4 @@ The PySimpleGUI Organization
|
|||
|
||||
This documentation as well as all PySimpleGUI code and documentation is Copyright 2018, 2019, 2020 by PySimpleGUI.org
|
||||
|
||||
Send correspondence to PySimpleGUI@PySimpleGUI.com prior to use of documentation
|
||||
Send correspondence to PySimpleGUI@PySimpleGUI.com prior to use of documentation
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue