Table display Recipe added to Cookbook
This commit is contained in:
parent
4e518e9667
commit
38dd2732e4
2 changed files with 39 additions and 65 deletions
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
# import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,7 +76,7 @@ def GUIAddOn():
|
|||
fname = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if not fname:
|
||||
sg.MsgBox("Cancel", "No filename supplied")
|
||||
sg.Popup("Cancel", "No filename supplied")
|
||||
# raise SystemExit("Cancelling: no filename supplied")
|
||||
|
||||
def Compare2Files():
|
||||
|
|
@ -276,7 +277,7 @@ def CallbackSimulation():
|
|||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# All done!
|
||||
sg.MsgBoxOK('Done')
|
||||
sg.PopupOk('Done')
|
||||
|
||||
def RealtimeButtons():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
|
@ -309,7 +310,7 @@ def RealtimeButtons():
|
|||
button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
if button is not None:
|
||||
print(button)
|
||||
if button == 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
if button is 'Quit' or values is None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
form.CloseNonBlockingForm()
|
||||
|
|
@ -345,7 +346,7 @@ def TabbedForm():
|
|||
results = sg.ShowTabbedForm('Tabbed form example', (form, layout_tab_1, 'First Tab'),
|
||||
(form2, layout_tab_2,'Second Tab'))
|
||||
|
||||
sg.MsgBox(results)
|
||||
sg.Popup(results)
|
||||
|
||||
def MediaPlayer():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
|
@ -586,7 +587,7 @@ def MultipleColumns():
|
|||
# to collapse the form display and read down to a single line of code.
|
||||
button, values = sg.FlexForm('Compact 1-line form with column').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
sg.MsgBox(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
sg.Popup(button, values, line_width=200)
|
||||
|
||||
def PersistentForm():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
|
@ -703,64 +704,21 @@ def InputElementUpdate():
|
|||
|
||||
in_elem.Update(keys_entered) # change the form to reflect current key string
|
||||
|
||||
# def EverythingInOne():
|
||||
# """
|
||||
# Animated Matplotlib Graph
|
||||
# Use the Canvas Element to create an animated graph. The code is a bit tricky to follow, but if you know Matplotlib then this recipe shouldn't be too difficult to copy and modify.
|
||||
# """
|
||||
# from tkinter import *
|
||||
# from random import randint
|
||||
# import PySimpleGUI as g
|
||||
# from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg, FigureCanvasAgg
|
||||
# from matplotlib.figure import Figure
|
||||
# import matplotlib.backends.tkagg as tkagg
|
||||
# import tkinter as Tk
|
||||
#
|
||||
#
|
||||
# def main():
|
||||
# fig = Figure()
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
|
||||
# ax.set_xlabel("X axis")
|
||||
# ax.set_ylabel("Y axis")
|
||||
# ax.grid()
|
||||
#
|
||||
# canvas_elem = g.Canvas(size=(640, 480)) # get the canvas we'll be drawing on
|
||||
#
|
||||
# layout = [[g.Text('Animated Matplotlib', size=(40, 1), justification='center', font='Helvetica 20')],
|
||||
# [canvas_elem],
|
||||
# [g.ReadFormButton('Exit', size=(10, 2), pad=((280, 0), 3), font='Helvetica 14')]]
|
||||
#
|
||||
# # create the form and show it without the plot
|
||||
# form = g.FlexForm('Demo Application - Embedding Matplotlib In PySimpleGUI')
|
||||
# form.Layout(layout)
|
||||
# form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
#
|
||||
# graph = FigureCanvasTkAgg(fig, master=canvas_elem.TKCanvas)
|
||||
# canvas = canvas_elem.TKCanvas
|
||||
#
|
||||
# dpts = [randint(0, 10) for x in range(10000)]
|
||||
# for i in range(len(dpts)):
|
||||
# button, values = form.ReadNonBlocking()
|
||||
# if button is 'Exit' or values is None:
|
||||
# exit(69)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ax.cla()
|
||||
# ax.grid()
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ax.plot(range(20), dpts[i:i + 20], color='purple')
|
||||
# graph.draw()
|
||||
# figure_x, figure_y, figure_w, figure_h = fig.bbox.bounds
|
||||
# figure_w, figure_h = int(figure_w), int(figure_h)
|
||||
# photo = Tk.PhotoImage(master=canvas, width=figure_w, height=figure_h)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# canvas.create_image(640 / 2, 480 / 2, image=photo)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# figure_canvas_agg = FigureCanvasAgg(fig)
|
||||
# figure_canvas_agg.draw()
|
||||
#
|
||||
# tkagg.blit(photo, figure_canvas_agg.get_renderer()._renderer, colormode=2)
|
||||
# # time.sleep(.1)
|
||||
|
||||
def TableSimulation():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display data in a table format
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Table Test')]]
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(20):
|
||||
row = [sg.T(f'Row {i} ', size=(10, 1))]
|
||||
layout.append([sg.T(f'{i}{j}', size=(4, 1), background_color='white', pad=(1, 1)) for j in range(10)])
|
||||
|
||||
sg.FlexForm('Table').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -------------------------------- GUI Starts Here -------------------------------#
|
||||
|
|
@ -768,7 +726,6 @@ def InputElementUpdate():
|
|||
# information to display. #
|
||||
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
|
||||
|
||||
# print(inspect.getsource(PyplotSimple))
|
||||
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -777,7 +734,8 @@ fig_dict = {'Simple Data Entry':SimpleDataEntry, 'Simple Entry Return Data as Di
|
|||
'Non-Blocking With Updates':NonBlockingWithUpdates, 'Non-Bocking With Context Manager':NonBlockingWithContext, 'Callback Simulation':CallbackSimulation,
|
||||
'Realtime Buttons':RealtimeButtons, 'Easy Progress Meter':EasyProgressMeter, 'Tabbed Form':TabbedForm, 'Media Player':MediaPlayer, 'Script Launcher':ScriptLauncher,
|
||||
'Machine Learning':MachineLearning, 'Custom Progress Meter':CustromProgressMeter, 'One Line GUI':OneLineGUI, 'Multiple Columns':MultipleColumns,
|
||||
'Persistent Form':PersistentForm, 'Canvas Widget':CanvasWidget, 'Input Element Update':InputElementUpdate}
|
||||
'Persistent Form':PersistentForm, 'Canvas Widget':CanvasWidget, 'Input Element Update':InputElementUpdate,
|
||||
'Table Simulation':TableSimulation}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# multiline_elem = sg.Multiline(size=(70,35),pad=(5,(3,90)))
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -827,3 +827,19 @@ Use the Canvas Element to create an animated graph. The code is a bit tricky to
|
|||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Tables
|
||||
|
||||
While there is no official support for "Tables" (e.g. there is no Table Element), it is possible to display information in a tabular way. This only works for smaller tables because there is no way to scroll a window or a column element. Until scrollable columns are implemented there is little use in creating a Table Element.
|
||||
|
||||
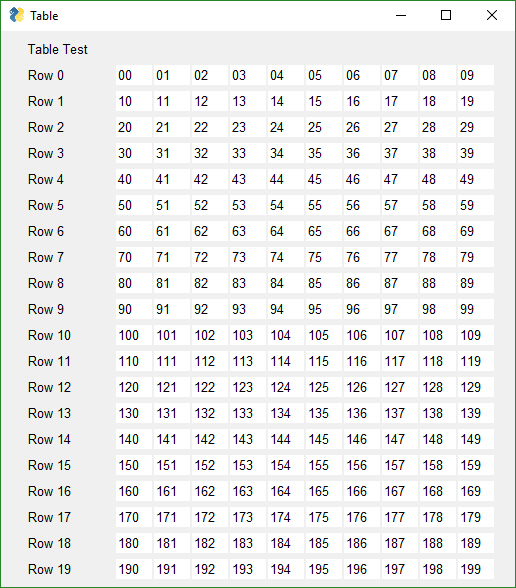
|
||||
|
||||
layout = [[sg.T('Table Test')]]
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(20):
|
||||
row = [sg.T(f'Row {i} ', size=(10,1))]
|
||||
layout.append([sg.T(f'{i}{j}', size=(4,1), background_color='white', pad=(1,1)) for j in range(10)])
|
||||
|
||||
sg.FlexForm('Table').LayoutAndRead(layout)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue