commit
0a3c9f9876
1 changed files with 76 additions and 74 deletions
150
docs/cookbook.md
150
docs/cookbook.md
|
|
@ -2293,6 +2293,82 @@ window.close()
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# Recipe Multiple Windows - `read_all_windows`
|
||||
|
||||
Beginning in version 4.28.0 you'll find that working with multiple windows in the tkinter port of PySimpleGUI to be much much easier.
|
||||
|
||||
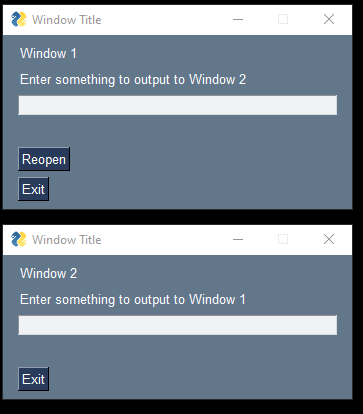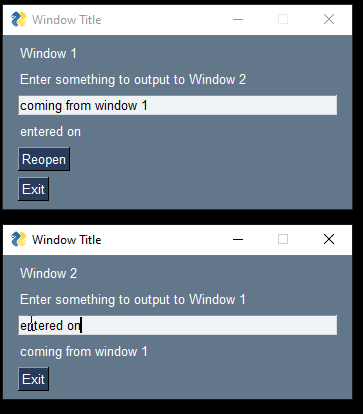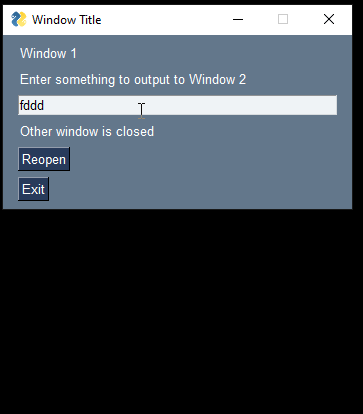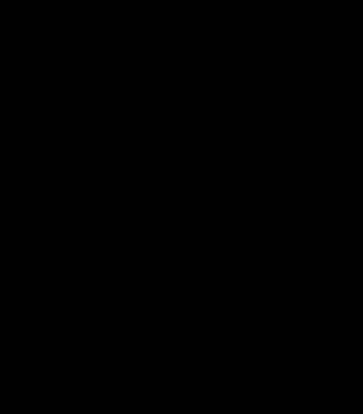
This Recipe shows 2 windows. Both of them are active and can be interacted with. When you enter something in window 1 it is updated in window 2. Notice that the keys are named the same in both windows. This makes it really easy to write generic code that will update fields in either window, the only difference will be which Window is updated.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll find that you'll have less chances for problems like "reusing layouts" if you put your layout and window creation into a function. This will guarantee a "fresh" window every time you call the function. If you close window 2 and then click the "Reopen" button in window 1, then all that is needed is to call the `make_win2` function again and move the new window to the location below the first window.
|
||||
|
||||
The program remains active until both windows have been closed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Demo - 2 simultaneous windows using read_all_window
|
||||
|
||||
Both windows are immediately visible. Each window updates the other.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2020 PySimpleGUI.org
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def make_win1():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Window 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Enter something to output to Window 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='-IN-', enable_events=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(size=(25,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Reopen')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
return sg.Window('Window Title', layout, finalize=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_win2():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Window 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Enter something to output to Window 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='-IN-', enable_events=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(size=(25,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
return sg.Window('Window Title', layout, finalize=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
window1, window2 = make_win1(), make_win2()
|
||||
|
||||
window2.move(window1.current_location()[0], window1.current_location()[1]+220)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
window, event, values = sg.read_all_windows()
|
||||
|
||||
if window == sg.WIN_CLOSED: # if all windows were closed
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
window.close()
|
||||
if window == window2: # if closing win 2, mark as closed
|
||||
window2 = None
|
||||
elif window == window1: # if closing win 1, mark as closed
|
||||
window1 = None
|
||||
elif event == 'Reopen':
|
||||
if not window2:
|
||||
window2 = make_win2()
|
||||
window2.move(window1.current_location()[0], window1.current_location()[1] + 220)
|
||||
elif event == '-IN-':
|
||||
output_window = window2 if window == window1 else window1
|
||||
if output_window: # if a valid window, then output to it
|
||||
output_window['-OUTPUT-'].update(values['-IN-'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
window['-OUTPUT-'].update('Other window is closed')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -2871,80 +2947,6 @@ while True: # Event Loop
|
|||
window.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# Recipe Multiple Windows - `read_all_windows`
|
||||
|
||||
Beginning in version 4.28.0 you'll find that working with multiple windows in the tkinter port of PySimpleGUI to be much much easier.
|
||||
|
||||
This Recipe shows 2 windows. Both of them are active and can be interacted with. When you enter something in window 1 it is updated in window 2. Notice that the keys are named the same in both windows. This makes it really easy to write generic code that will update fields in either window, the only difference will be which Window is updated.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll find that you'll have less chances for problems like "reusing layouts" if you put your layout and window creation into a function. This will guarantee a "fresh" window every time you call the function. If you close window 2 and then click the "Reopen" button in window 1, then all that is needed is to call the `make_win2` function again and move the new window to the location below the first window.
|
||||
|
||||
The program remains active until both windows have been closed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PySimpleGUI as sg
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Demo - 2 simultaneous windows using read_all_window
|
||||
|
||||
Both windows are immediately visible. Each window updates the other.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2020 PySimpleGUI.org
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def make_win1():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Window 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Enter something to output to Window 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='-IN-', enable_events=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(size=(25,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Reopen')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
return sg.Window('Window Title', layout, finalize=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_win2():
|
||||
layout = [[sg.Text('Window 2')],
|
||||
[sg.Text('Enter something to output to Window 1')],
|
||||
[sg.Input(key='-IN-', enable_events=True)],
|
||||
[sg.Text(size=(25,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],
|
||||
[sg.Button('Exit')]]
|
||||
return sg.Window('Window Title', layout, finalize=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
window1, window2 = make_win1(), make_win2()
|
||||
|
||||
window2.move(window1.current_location()[0], window1.current_location()[1]+220)
|
||||
|
||||
while True: # Event Loop
|
||||
window, event, values = sg.read_all_windows()
|
||||
|
||||
if window == sg.WIN_CLOSED: # if all windows were closed
|
||||
break
|
||||
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
|
||||
window.close()
|
||||
if window == window2: # if closing win 2, mark as closed
|
||||
window2 = None
|
||||
elif window == window1: # if closing win 1, mark as closed
|
||||
window1 = None
|
||||
elif event == 'Reopen':
|
||||
if not window2:
|
||||
window2 = make_win2()
|
||||
window2.move(window1.current_location()[0], window1.current_location()[1] + 220)
|
||||
elif event == '-IN-':
|
||||
output_window = window2 if window == window1 else window1
|
||||
if output_window: # if a valid window, then output to it
|
||||
output_window['-OUTPUT-'].update(values['-IN-'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
window['-OUTPUT-'].update('Other window is closed')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue